In the last article, we have studied the general term of an arithmetic progression. In this article, we shall study to find the sum of arithmetic progression.
General Term or nth term of an Arithmetic Progression:
If ‘a’ is the first term and ‘d’ is the common difference of an A.P. then the nth term is given by
tn = a + (n – 1)d
Sum up to nth term of an Arithmetic Progression
If ‘a’ is the first term and ‘d’ is the common difference of an A.P. then the sum of the first n terms is given by
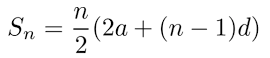
Sn = n/2(First term + Last term)
To Find Sum of Arithmetic Progression (A.P.):
Example – 01:
Find the sum of 3 + 8 + 13 + 18 + …. + n terms
Solution:
Given A.P. 3, 8, 13, 18 + …. + n terms
First term = a = 3, common difference = d = 8 – 3 = 5
The sum of n terms of an A.P. is given by Sn = n/2(2a + (n – 1)d)
∴ Sn = n/2(2 x 3 + (n – 1)5)
∴ Sn = n/2(6 + 5n – 5)
∴ Sn = n/2( 5n + 1)
∴ Sn = n(5n+1)/2
Ans: The sum of n terms of the A.P. is n(5n+1)/2
Example – 02:
Find the sum of 1 + 4 + 7 + 10 + …. + 22 terms
Solution:
Given A.P. 1, 4, 7, 10,….. n terms
First term = a = 1, common difference = d = 4 – 1 = 3
The sum sum of arithmetic progression of n terms is given by Sn = n/2(2a + (n – 1)d)
∴ Sn = n/2(2 x 1 + (n – 1)3)
∴ Sn = n/2(2 + 3n – 3)
∴ Sn = n/2( 3n – 1)
∴ Sn = n(3n – 1)/2
∴ S22 = 22(3 x 22 – 1)/2 = 11(66 – 1) = 11 x 65 = 715
Ans: The sum of 22 terms of the A.P. is 715.
Example – 03:
For an A.P. a = 3, d =4. Find S20.
Solution:
Given first term = a = 3, common difference = d =4
The sum of arithmetic progression of n term of an A.P. is given by Sn = n/2(2a + (n – 1)d)
∴ Sn = n/2(2 x 3 + (n – 1)4)
∴ Sn = n/2(6 + 4n – 4)
∴ Sn = n/2( 4n + 2)
∴ Sn = n(2n + 1)
∴ S20 = 20 x (2 x 20 + 1) = 20 x 41 = 820
Ans: S20 = 820
Example – 04:
For an A.P. S16 = 784, a = 4. Find d.
Solution:
Given first term = a = 4, S16 = 784
The sum of arithmetic progression n terms of an A.P. is given by
Sn = n/2(2a + (n – 1)d)
∴ S16 = 16/2(2 x 4 + (16 – 1)d)
∴ 784 = 8(8 + 15d)
∴ 784 = 64 + 120d
∴ 120 d = 784 – 64 = 720
∴ d = 6
Ans: d = 6
Example – 05:
For an A.P. S12 = – 78, d = – 3. Find a.
Solution:
Given S12 = 3, common difference = d = – 3
The sum of n terms of an A.P. is given by
Sn = n/2(2a + (n – 1)d)
∴ S12 = 12/2(2 a + (12 – 1) x (-3))
∴ – 78 = 6(2a – 33)
∴ – 13 = 2a – 33
∴ 2a = -13 + 33 = 20
∴ a = 10
Ans: a = 10
Example – 06:
For an A.P. t3 = 17 and t7 = 37. Find S16.
Solution:
Given for an A.P. t3 = 17 and t7 = 37
The nth term of an A.P. is given by
tn = a + (n – 1)d
∴ t3 = a + (3 – 1)d = 17
∴ a + 2d = 17 ………… (1)
∴ t7 = a + (7 – 1)d = 37
∴ a + 6d = 37 ………… (2)
Subtracting equation (1) from (2) we get
4 d = 30
∴ d = 5
Substituting in equation (1) we get
a + 2 x 5 = 17
∴ a + 10 = 17
∴ a = 7
The sum of n terms of an A.P. is given by
Sn = n/2(2a + (n – 1)d)
∴ S16 = 16/2(2 x 7 + (16 – 1)5)
∴ S16 = 8(14 + 75) = 8(89) = 712
Ans: S16 = 712
Example – 07:
For an A.P. t7 = 13 and S14 = 203. Find S8.
Solution:
Given for an A.P. t7 = 13
The nth term of an A.P. is given by
tn = a + (n – 1)d
∴ t7 = a + (7 – 1)d = 13
∴ a + 6d = 13 ………… (1)
Given for an A.P. S14 = 203
The sum of n terms of an A.P. is given by
Sn = n/2(2a + (n – 1)d)
∴ S14 = 14/2(2a + (14 – 1)d)
∴ 203 = 7(2a +13d)
∴ 2a +13d = 29 ………… (2)
Multiplying equation (1) by 2 and subtracting from equation (2)
d = 3
Substituting in equation (1) we get
a + 6 x 3 = 13
∴ a + 18 = 13
∴ a = – 5
The sum of n terms of an A.P. is given by Sn = n/2(2a + (n – 1)d)
∴ S8 = 8/2(2 x (-5) + (8 – 1)3)
∴ S8 = 4(- 10 + 21) = 4(11) = 44
Ans: S8 = 44
Example – 08:
Find n if 1 + 4 + 7 + 10 + …… +n terms = 590
Solution:
Given A.P. 1, 4, 7, 10,….. n terms
First term = a = 1, common difference = d = 4 – 1 = 3
The sum of n term of an A.P. is given by
Sn = n/2(2a + (n – 1)d)
∴ Sn = n/2(2 x 1 + (n – 1)3)
∴ Sn = n/2(2 + 3n – 3)
∴ Sn = n/2( 3n – 1)
∴ Sn = n(3n – 1)/2
∴ 590 = n(3n – 1)/2
∴ 1180 = 3n2 – n
∴ 3n2 – n – 1180 = 0
∴ 3n2 – 60n + 59 n – 1180 = 0
∴ 3n(n – 20) + 59(n – 20) = 0
∴ (n – 20) (3n + 59) = 0
∴ (n – 20) = 0 or (3n + 59) = 0
∴ n = 20 or n = -59/3
Now n ∈ N, hence n = -59/3 is not possible
Ans: n = 20
Example – 09:
Find n if 50 + 46 + 42 + 38 + …… +n terms = 336
Solution:
Given A.P. 50, 46, 42, 38,….. n terms
First term = a = 50, common difference = d = 46 – 50 = – 4
The sum of n term of an A.P. is given by
Sn = n/2(2a + (n – 1)d)
∴ Sn = n/2(2 x 50 + (n – 1)(-4))
∴ Sn = n/2(100 – 4n + 4)
∴ Sn = n/2( 104 – 4n)
∴ Sn = n(52 – 2n)
∴ 336 = n(52 – 2n)
∴ 336 = 52n – 2n2
∴ 2n2 – 52n + 336 = 0
∴ 2n2 – 28n – 24n + 336 = 0
∴ 2n(n – 14) – 24(n – 14) = 0
∴ (n – 14)(2n – 24) = 0
∴ (n – 14) = 0 or (2n – 24) = 0
∴ n = 14 or n =12
Ans: n = 14 or n = 12
Example – 10:
Find n if 25 + 22+ 19+ 16 + …… +n terms = 116
Solution:
Given A.P. 25, 22, 19, 16,….. n terms
First term = a = 25, common difference = d = 22 – 25 = -3
The sum of n term of an A.P. is given by
Sn = n/2(2a + (n – 1)d)
∴ Sn = n/2(2 x 25 + (n – 1)(-3))
∴ Sn = n/2(50 – 3n + 3)
∴ Sn = n/2( 53 – 3n)
∴ Sn = n(53 – 3n)/2
∴ 116 = n(53 – 3n)/2
∴ 232 = n(53 – 3n)
∴ 232 = 53n – 3n2
∴ 3n2 – 53n + 232 = 0
∴ 3n2 – 24n – 29 n – 232 = 0
∴ 3n(n – 8) – 29(n – 8) = 0
∴ (n – 8)(3n – 29) = 0
∴ (n – 8) = 0 or (3n – 29) = 0
∴ n = 8 or n = 29/3
Now n ∈ N, hence n = 59/3 is not possible
Ans: n = 8
Example – 11:
Find the sum of all natural numbers from 1 t0 200 which is divisible by 5.
Solution:
Given numbers are 1, 2, 3, ……., 198, 199, 200
In forwward pass through given set of numbers, the first number divisible by 5 is 5
In backward pass through given set of numbers, the first number divisible by 5 is 200
Thus the required sequence is 5, 10, 15, 20, ……, 200
First term = a = 5, common difference = 10 – 5 = 5, tn = 200
The nth term of an A.P. is given by
tn = a + (n – 1)d
∴ 200 = 5 + (n – 1)5
∴ 200 = 5 + 5n – 5
∴ 200 = 5n
∴ n = 40
The sum of n term of an A.P. is given by
Sn = n/2(2a + (n – 1)d)
∴ Required sum = Sn = 40/2(2 x 5 + (40 – 1)(5))
∴ Sn = 20(10 + 195) = 20 x 205 = 4100
Ans: The sum of all natural numbers from 1 to 200 which is divisible by 5 is 4100.
Example – 12:
Find the sum of all natural numbers from 1 t0 200 which is divisible by 3.
Solution:
Given numbers are 1, 2, 3, ……., 198, 199, 200
In forwward pass through given set of numbers, the first number divisible by 3 is 3
In backward pass through given set of numbers, the first number divisible by 3 is 198
Thus the required sequence is 3, 6, 9,12, …., 198
First term = a = 3, common difference = 6 – 3 = 3, tn = 198
The nth term of an A.P. is given by
tn = a + (n – 1)d
∴ 198 = 3 + (n – 1)3
∴ 198 = 3 + 3n – 3
∴ 198 = 3n
∴ n = 66
The sum of n terms of an A.P. is given by
Sn = n/2(2a + (n – 1)d)
∴ Required sum = Sn = 66/2(2 x 3 + (66 – 1)(3))
∴ Sn = 33(6 + 195) = 33 x 201 = 6633
Ans: The sum of all natural numbers from 1 t0 200 which is divisible by 3 is 6633.