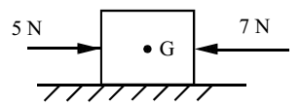
Science > Physics > Force > Newton’s First Law of Motion Newton’s laws of motion are three physical laws that, together, laid the foundation for classical mechanics. In this article, we shall discuss Newton’s first law of motion and the concept of inertia of a body. Statement of Newton’s First Law of Motion: Every material body […]
Newton’s First Law of Motion