Law > Medical Jurisprudence > Law and Medicine > Pattern Injuries to Pedestrians in Road Accident
A traffic or road accident is defined as an accident involving at least one vehicle on a road open to public traffic in which at least one person is injured or killed. The main cause of accidents and crashes are due to human errors. Most of the road users are quite well aware of the general rules and safety measures while using roads but it is only the laxity on part of road users, which cause accidents and crashes. In this article, we shall study medico-legal aspect of road accident. In this article we shall discuss impact injuries and secondary injuries caused to pedestrian due to road accident.
The main causes for road accidents are:
- Over-speeding and lane cutting
- Distraction during driving
- Drunken driving
- Jumping red signal
- Tailgating
- Wrong lane driving
- Potholes and damaged roads
- Poor maintenance of vehicles
- Large numbers and unruly pedestrians and animals
- Poor lightings on roads
The road traffic injuries may be sustained to:
- Pedestrians
- Cyclists/ Motor cyclists
- Occupants of a vehicle
Pattern Injuries to Pedestrians:
In case of pedestrians following injuries are often seen:
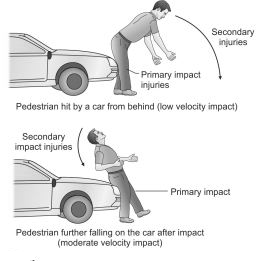
Primary Impact Injuries:
These are the injuries caused by vehicle when it first struck and hit the person whether crossing the road from one side to the other side or walking with or against the traffic. The importance of primary impact injury is that the body of victim may bear design / pattern of the part of vehicle in form of imprint abrasion pattern bruised. Bumper, wing, headlights, mirrors, grill, headlights, radiator, door handles may cause primary impact injuries.
Projections of vehicle may cause specific injuries like fracture of tibia & fibula of one or both the legs. In case of children the fracture will be in femur. Height of the victim determines site of injury. The impact depends on the speed and weight of the vehicle.
The body part which bears the injury depends upon the position of the person such as:
- Was the pedestrian struck by the front of Vehicle?
- Was the pedestrian struck by the side of Vehicle?
- Was the pedestrian standing on road?
- Was the pedestrian walking on road?
- Was the pedestrian lying on road?
The findings of primary impact injury are important to find out the relative position of pedestrian and vehicle and kind of vehicle involved in the Incident.

Impact Against Bumper (Bumper Injuries):
Injuries at the site of bumper impact, in the form of abrasion, contusion, laceration, internal hemorrhage in the calves etc. Most characteristic fracture due to bumper fractures are fracture of the tibia. The fracture fragments are wedge shaped and is displaced forwards. The base of the wedge indicates the site of the impact, the apex points in the direction in which the vehicle was travelling. Rarely, fibula also may get fractured. In children, bumper fracture is seen in femur. When brakes are applied, the height of the bumper dips down, thus the height of the bumper fracture is less than the height of the bumper. When accelerator is pressed, the phenomenon is reversed.
The level of bumper injury (i.e, the height of injury from ground level) varies with height of bumper of different vehicle. The vehicle can be identified from the height of the bumper fracture from the ground and matching the same with the offending vehicle’s height of bumper from the ground. Frequently Bumper injuries are at different level of the two legs or absent on one leg, which suggest that the victim was walking or running when struck. If bumper injuries are at the same level on both legs, then it means the person is standing.
Impact against mud guard or head lamp:
At impact against the headlamp or mudguard may result in fracture of the pelvis or fracture dislocation of the sacroiliac joint. Injuries usually depend how the victim was positioned. Frontal impacts may cause head injury, chest injury, fracture of ribs. Side impact causes injuries of arms. Rear impact causes injuries to buttocks and sacroiliac joints. The fractured portion of the vertebral column may move forward and may cause transection of the spinal cord and thoracic aorta.
Impact when struck from front:
Injuries are virtually the same, except that the injuries are more on the frontal aspect. Intra-abdominal injuries are seen, like linear superficial tears of the abdomen and inguinal regions, due to over stretching of the skin. They appear dry, yellow and bloodless. Liver and splenic injuries are common. There may be injuries to chest wall and thoracic contents. Direct impact to thorax may cause rupture of the aorta below the arch at the level of ligamentum arteriosum due to sudden increase in the intravascular pressure. The heart may show bruising, laceration and rupture.
Impact when struck on one side:
The injuries are seen predominantly on one side. The opposite side receives injuries while falling on the road.
Impact when the pedestrian walks into the side of the moving vehicle:
There may be injuries on the side of the front of face, chest and arms in the form of glancing abrasions, patterned abrasions, crush lacerations, tear lacerations, fracture ribs with or without lung involvement, abdominal injuries etc.
Secondary Impact Injuries:
They are caused by the second impact with the vehicle (eg: the body of thrown onto the vehicle). They are caused when after sustaining primary impact of injury, the person may be lifted off the ground and thrown of the vehicle. Here the person strikes to windshield or bonnet or placed on the top of car/ vehicle. Usually, such injuries are on the opposite side of primary impact.

Injuries are variable, depending on the area of the body involved. If the feet slide forward, the whole body falls backwards, with a secondary impact of the head against the windshield. If the victim falls on the hood, tangential force is directed by hood to the buttock and thigh, causing separation of the skin and sub cutaneous tissues from the muscle. This produces a pocket in the upper thigh and buttock, leading to collection of large amounts of blood, which is often not visible, externally. If the feet are not firmly fixed on the ground, the victim may be scooped up and thrown in the air and may land over the roof of the vehicle, head hitting first, or may even land on the road behind the vehicle, where he may be run over by other vehicles. Atlanto-occipital dislocation and partial disruption of intervertebral discs are quite common in this situation.
Secondary and tertiary injuries:
They are caused when the body strikes the ground after the collision or striking another stationary object or another vehicle. When the victim is thrown high up in air and strikes the ground injuries are more severe. All kinds of injuries, including abrasions, contusions, lacerations, fractures etc may be seen.

Sometimes the victim may be run over by the same vehicle and another vehicle. Brain damage is frequent without any associated skull fractures. Fracture of the skull and ribs due direct contact with a surface, and fracture of spine due to hyperflexion or extension may be seen. In pedestrian accidents, the common cause of death is head injuries and fracture dislocation of cervical spine.
Run-Over Injuries:
They are caused when the vehicle runs over some part of the body of the victim. In this case the severity of injury depends on the part oof the body run over and the weight of the vehicle.
Abrasions in the form of grazes, impact or imprint abrasions of the tire marks may be seen. They are spread out a little due to yielding and flattening of body from pressure. Skull may be crushed from side to side or forced open with extrusion of the brain matter. The ribs may be fractured at multiple places. The abdomen may be ruptured with extrusion of the contents. The whole body maybe crushed or hemisected.