Management > Managerial Statistics > Index Number By Simple Average of Relative Method
Simple Average of Relative Method Using Arithmetic Mean:
In this method, average of price relative of commodity is calculated.
Steps involved
- Find price relative for each commodity for the current year using the formula R = (P1 / P0) × 100.
- Add all price relatives of all the commodities.
- Divide sum obtained in step 2 by the number of commodities (N).
- Overall formula for the method is.
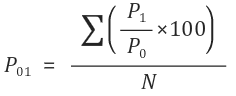
Example – 01:
Prices of commodities for the year 2000 and 2004 are as given in the table. Find the price index by a simple average of relative method and using the arithmetic mean from the data given in the table.
|
Commodity |
Unit |
Price in Rs. Per unit |
|
|
2000 |
2004 |
||
|
Wheat |
1 kg |
10 |
15 |
|
Rice |
1 kg |
40 |
30 |
|
Pulses |
1 kg |
10 |
12 |
|
Onions |
1 kg |
5 |
13 |
|
Oil |
1 litre |
40 |
50 |
Solution:
|
Commodity |
Unit |
Price in Rs. Per unit |
R = (P1 / P0) × 100 |
|
|
2000 |
2004 |
|||
|
Wheat |
1 kg |
10 |
15 |
(15/10) x 100 = 150.0 |
|
Rice |
1 kg |
40 |
30 |
(30/40) x 100 = 75.0 |
|
Pulses |
1 kg |
10 |
12 |
(12/10) x 100 = 120.0 |
|
Onions |
1 kg |
5 |
13 |
(13/5) x 100 = 260.0 |
|
Oil |
1 litre |
40 |
50 |
(50/40) x 100 = 125.0 |
|
Total |
∑ R = 730 |
|||
The price index number by simple average of relative method using arithmetic mean for 2004 taking 2000 as base year is given by
P01 = (1/N)(∑ R)
P01 = (1/5)(730)
P01 = 146.0
Simple Average Relative Method Using Geometric Mean:
Steps involved
- Find price relative for each commodity for the current year using the formula R = (P1 / P0) × 100.
- Find log R in each case.
- Add all logs of price relatives of all the commodities.
- Divide sum obtained in step 3 by the number of commodities (N).
- Find antilog of the number obtained in step 4
- Overall formula for the method is.
P01 =Antilog ((1/N) (∑ Log R)) = Antilog [(1/N)(∑ log ((P1 / P0) × 100)))]
Example – 02:
Prices of commodities for the year 2000 and 2004 are as given in table. Find the price index by simple average of relative method and using geometric mean from the data given in the table.
|
Commodity |
Unit |
Price in Rs. Per unit |
|
|
2000 |
2004 |
||
|
Wheat |
1 kg |
10 |
15 |
|
Rice |
1 kg |
40 |
30 |
|
Pulses |
1 kg |
10 |
12 |
|
Onions |
1 kg |
5 |
13 |
|
Oil |
1 litre |
40 |
50 |
Solution:
|
Commodity |
Unit |
Price in Rs. Per unit |
R = (P1 / P0) × 100 |
Log R |
|
|
2000 |
2004 |
||||
|
Wheat |
1 kg |
10 |
15 |
(15/10) x 100 = 150.0 |
Log 150 = 2.1761 |
|
Rice |
1 kg |
40 |
30 |
(30/40) x 100 = 75.0 |
Log 75 = 1.8751 |
|
Pulses |
1 kg |
10 |
12 |
(12/10) x 100 = 120.0 |
Log 120 = 2.0792 |
|
Onions |
1 kg |
5 |
13 |
(13/5) x 100 = 260.0 |
Log 260 = 2.4250 |
|
Oil |
1 litre |
40 |
50 |
(50/40) x 100 = 125.0 |
Log 125 = 2.0970 |
|
Total |
∑ Log R = 10.6704 |
||||
The price index number by simple average of relative method
using geometric mean for 2004 taking 2000 as base year is given by
P01 = Antilog [(1/N)(∑ log R)]
P01 = Antilog [(1/5)(10.6704)]
P01 = Antilog 2.1341
P01 = 136.2
Example – 03:
Prices of commodities for the year 2002 and 2003 are as given in table. Find the price index by a simple average of relative method and using a) arithmetic mean and b) geometric mean.
|
Prices |
||
|
Commodity |
2002 |
2003 |
|
Corn |
800 |
880 |
|
Wheat |
500 |
480 |
|
Cocoa |
900 |
940 |
Solution:
|
Prices |
R = (P1 / P0) × 100 |
Log R |
||
|
Commodity |
2002 |
2003 |
||
|
Corn |
800 |
880 |
(880/800) x 100 = 110 |
Log 110 = 2.0414 |
|
Wheat |
500 |
480 |
(480/500) x 100 = 96 |
Log 96 = 1.9823 |
|
Cocoa |
900 |
940 |
(940/900) x 100 = 104.44 |
Log 104.4 = 2.0187 |
|
Total |
∑ R = 310.44 |
∑ log R = 6.0424 |
||
Solution:
Simple average of relative method and using arithmetic mean:
The price index number by simple average of relative method
using arithmetic mean for 2003 taking 2002 as base year is given by
P01 = (1/N)(∑ R)
P01 = (1/3)(310.44)
P01 = 103.48
Simple average of relative method and using geometric mean:
The price index number by simple average of relative method
using geometric mean for 2003 taking 2002 as base year is given by
P01 = Antilog [(1/N)(∑ log R)]
P01 = Antilog [(1/3)( 6.0424)]
P01 = Antilog 2.0141
P01 = 103.30
Merits of Simple Average of Relative Method:
- It is not affected by units in which prices are quoted.
- As prices are converted into price relatives, it is not affected by absolute values of prices.
- It gives equal importance to all items and hence extreme values of certain items do not unduly affect the index number.
- The index number calculated by this method satisfies the unit test.
Demerits of Simple Average of Relative Method:
- As it is unweighted average, the importance of all the items is assumed to be the same.
- The index number constructed by this method does not satisfy the criteria laid down for index number.
- The index number is unduly influenced by high or low prices when the arithmetic mean is used.
- The index number constructed using geometric mean is tedious and time-consuming.
Previous Topic: Index Number by Simple Aggregative Method
Next Topic: Index Number by Laspeyre’s Method
One reply on “Simple Average of Relative Method”
i found this very helpful. thanks