Science > Biology > General Biology > Introduction to Biology > Characteristics of life
Biology is a branch of science which studies living beings that all plants and animals including humans. Biology examines the structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, and distribution of living things. It classifies and describes organisms, their functions, how species come into existence, and the interactions they have with each other and with the natural environment. Four principles form the foundation of modern biology are cell theory, evolution, genetics, and homeostasis. In this article, we shall study the characteristics of life.
Growth and Change:
All living organisms have the ability to grow and change. An increase in mass and an increase in the number of individuals are two characteristics of the growth. Multicellular organisms grow by cell division. A seed under the right conditions will sprout and form a seedling that will grow into a larger plant.

Even the smallest bacteria grow by binary fission. The growth is also required for the persistence of the species. The growth of plants takes place throughout life and at a specific portion of the body but the growth in the animal is time-bound and overall. After some period, the growth in animals occurs by cell division of certain tissues to replace the lost cells. In unicellular organisms, the growth is by the increase in the mass.
Nonliving objects like mountains, boulders and sand dunes also grow but this growth is due to the accumulation of substance on their surface. Thus both the living and non-living grow. Hence growth cannot be considered as characteristic of life.
Reproduction:
All living organisms (multicellular and unicellular) have the ability to reproduce. Living things make more organisms like themselves. If a species does not reproduce the next generation, the species will go extinct. Reproduction is the process of producing the next generation. Reproduction may be a sexual or asexual process. Sexual reproduction involves two parents and the fusion of gametes, haploid sex cells from each parent. Sexual reproduction produces offspring that are genetically unique and increases genetic variation within a species. Asexual reproduction involves only one parent. It occurs without a fusion of gametes and produces offspring that are all genetically identical to the parent. Genetic variation is not possible in asexual reproduction.
Many organisms like mules, sterile worker bee, warblers, infertile human couples, etc. do not reproduce. Thus reproduction cannot be considered as a characteristic feature of living organisms.
Cellular Organization:
All living organisms, whether made up of one cell or many cells, have some degree of organization. A cell is the smallest unit that can perform all life’s processes. Some organisms, like bacteria, are made up of one cell and are called unicellular organisms. Other organisms, such as humans or higher-level plants, are made up of multiple cells and are called multicellular organisms.
Complex multicellular organisms at the highest level, the organism is made up of organ systems, or groups of specialized parts that carry out a certain function in the organism. For example, the digestive system of humans. Organ systems are made up of organs. For example, the digestive system is made of organs like mouth, esophagus, stomach, liver, gall bladder, small intestine, large intestine, etc. Organs are structures that carry out specialized jobs within an organ system. Thus in the digestive system, the stomach performs the function of churning the food and add acid to it. All organs are made up of tissues. Tissues are groups of cells that have similar abilities and that allow the organ to function. Tissues are made up of cells. A cell is covered by a membrane, contains all genetic information necessary for replication, and be able to carry out all cell functions. Within each cell are organelles. Organelles are tiny structures that carry out functions necessary for the cell to stay alive. Organelles are made up of biological molecules, the chemical compounds that provide physical structure and that bring about movement, energy use, and other cellular functions. All biological molecules are made up of atoms. Atoms are the simplest particle of an element that retains all the properties of a certain element.
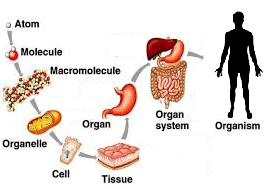
Beyond the organism level, organisms form populations which make up parts of an ecosystem. Different ecosystems collectively form the biosphere. Thus the cellular organization is a defining feature of living organisms.
Metabolism:
Metabolism is essentially a collection of chemical reactions occurring within the body (or cell). In body two activities are continuously taking place anabolic activities (making up) and catabolic activities (breaking up). All living organisms are made up of chemical substances. These chemical substances belong to different classes like carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, etc. Collectively they are called biomolecules. During anabolic activities, the food material is digested, absorbed and assimilated in the body. In catabolic activities, the stored substances are broken down by hydrolysis or oxidation to produce energy in the form of ATP which is required for doing regular activities by the body. Metabolism includes processes such as protein synthesis, chemical digestion, cell division, or energy transformation.
Metabolism is observed in all living organisms. Hence metabolism is a defining feature of all living beings.
Maintain Homeostasis:
All living things, from single cells to entire organisms, have mechanisms that allow them to maintain stable internal conditions despite changes in their external environment. This process is called homeostasis and is an important characteristic of all living organisms. By this process, the body temperature, sugar level in the body is maintained at a constant level. Multicellular organisms usually have more than one way of maintaining important aspects of their internal environment.
Without these mechanisms, organisms can die. For example, a cell’s water content is closely controlled by the taking in or releasing water. A cell that takes in too much water will rupture and die. A cell that doesn’t get enough water will also shrivel and die. It is a vital characteristic of life. If it is disturbed, it will result in diseases and if not controlled can threaten the life of the organism.
Responding to the Environment:
All living organisms respond to their environment. Living things know what is going on around them (consciousness) and respond to the changes in the environment. The response may be physical, chemical or biological. Human beings are only animals with self-consciousness. When touch me not plant is touched its leaves close. The Venus flytrap traps insects.

The stem of the plant moves in the direction of light and above the ground. (positively phototropic and negatively geotropic. The Root grows towards the soil and away from light (positively geotropic and negatively phototropic).

Heredity:
Heredity means that our genetic information can be passed from one generation to another. This way characteristics are transferred from one generation to the other.
Adaptation:
An adaptation refers to the process of becoming adjusted to an environment. Adaptations may include structural, physiological, or behavioral traits that improve an organism’s likelihood of survival.
Conclusion: Characteristics of Life of Living Organisms?
Thus the main characteristics of life (living organisms) are the self-replicating, evolving and self-regulating interactive systems that can respond to external stimuli.
