Science > Biology > Applied Biology > Human Health and Diseases > Transmission and Types of Communicable Diseases
Transmission of Communicable Diseases
Infectious diseases can be transmitted either directly or indirectly
Direct transmission of Diseases:
In this case, the pathogens are transmitted from an infected person to a healthy person directly without any intermediate agent. e.g. skin infections and eye infections.
Direct Contact With Infected Person:
Certain diseases produce sores and lesions on the skin. If a healthy person comes in contact with the material discharged by these sores or lesions get infected. Contagious diseases like chickenpox ( चेचक, कांजिण्या), smallpox (देवी), athlete’s foot, Measles (गोवर), Leprosy (कुष्ठरोग), ringworm (नायटा), gonorrhoea (गरमी), syphilis, etc spread through physical contact between the infected person and a healthy person. Entamoeba gingivalis causing periodontal diseases (Periodontal diseases are infections of the structures around the teeth.) is directly transmitted from the mouth during mouth kissing.
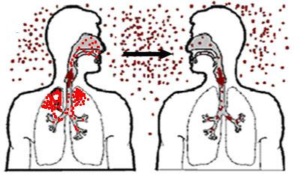
Droplet Infection:
Some diseases are caught by merely being at the same place especially in confined space like a room, theatres, bus, trains, etc. Contagious diseases like diphtheria, Influenza, whooping cough, common cold, pneumonia, mumps, and tuberculosis spread through contact or close proximity during spitting, speaking, coughing or sneezing by infected persons. It is called droplet infection because germs are spread in tiny droplets of mucus from infected persons nasal; membrane, throat, and lungs. Since droplets fall to the ground within a few feet, this type of transmission requires close proximity.
Animal Bites:
The bite of rabies-infected animals like dogs, monkeys, cats, etc. can inject rabies virus in a human being. Which leads to rabies or hydrophobia in a human being.
Contact With Soil:
Tetanus is an infection caused by a bacterium called Clostridium tetani. Spores of tetanus bacteria are everywhere in the environment, including soil, dust, and manure. The spores develop into bacteria when they enter the body. The bacterium causing tetanus enters through cuts and wounds. Hence skin injuries should not be neglected.
Transplacental Transmission:
Pregnant women can also transmit infectious diseases to their unborn children via the placenta. Viruses of German measles, Some STDs (Sexually Transmitted Diseases), syphilis, including gonorrhoea can be passed from mother to baby during childbirth. The pathogens pass from maternal blood to foetal blood.
Through Contaminated Needles, Syringes, Razors:
These diseases spread through contaminated needles and syringes, e.g. hepatitis B, AIDS, etc.
Blood Transfusion:
If the blood transfused to a healthy person is infected, the healthy person gets infected. e.g. hepatitis B, AIDS, etc.
Indirect Transmissions:
In this case, the pathogens are transmitted from the reservoir of infection to a healthy person through some intermediate agents.
Vectors:
Animals that transmit diseases are called vectors. Housefly carries pathogens of cholera, typhoid, dysentery, and tuberculosis on their legs and mouthparts from faeces and sputum on food. When such contaminated food is consumed it causes infection. Cockroaches, ants, crickets are other vectors for transmission of these diseases. Houseflies also caries microbes responsible for ophthalmia and conjunctivitis from eye to eye.
When a mosquito carrying diseases causing organisms in their body bites an infected human, it transfers the diseases causing organisms, to a healthy person. By this, it can spread the germs that cause malaria, the virus that causes dengue fever and yellow fever, or the filarial worms that cause filariasis or elephantiasis.
Certain blood-sucking insects like the female of Anopheles mosquito (spreads malaria), Culex mosquito (spreads filariasis), body-louse (spreads typhus), sand flies (spreads kala-azar and oriental sores), Tse-tse fly (spreads African sleeping sickness), Rat flea (spreads Bubonic Plague), Aedes ( spreads yellow fever), ticks (spreads rocky mountain fever) are the vectors of many diseases.
Dogs, monkeys, and other mammals carry the rabies virus. When infected animals bite humans, they transfer the virus through their saliva.
Vehicle Borne:
In this case, food and water are responsible for the transmission of diseases. Many lakes and streams near heavily-populated areas having poor sanitation get contaminated through sewage. Water from such source contain germs that cause typhoid, dysentery, diarrhea, and jaundice. If this water accidentally gets mixed with the drinking water supply system, it may spread several diseases. Mosquitoes breed in still water.
Pathogens of cholera, dysentery, typhoid and hepatitis B, polio, etc. are spread through food and water. Many diseases producing helminths get into the body through the food and water. Some diseases are transmitted through blood. e.g. AIDS.
Air-borne:
The pathogen may reach humans with air and dust, The epidemic typhus spreads by inhalation of dried faeces of infected lice.
Fomite Borne:
Many pathogens .make colonies on articles, particularly moist. These diseases spread through fomites like soiled clothes, towels, utensils, crockery, toys, soap, surgical instruments, injections, etc. Diphtheria, Influenza, cholera, skin infections, and eye infections spread by this method.
Unclean Hands:
Eating with unclean hands may lead to amoebic dysentery, amoebiasis, ascariasis, enterobiasis.
Types of Communicable Diseases:
On the basis of the causative agents, the diseases are classified as
Virus Based:
The causative agent is a virus. Examples: Common cold (Rhinitis), Influenza, Chickenpox, Smallpox, Measles, Mumps, Rabies (Hydrophobia), Polio, AIDS, Viral hepatitis, Dengue Fever (Break-bone fever), Chikungunya, Yellow fever, Rubella (German measles), Swine flue, Genital herpes, Genital warts.
Rickettsia Based:
The causative agent is Rickettsia (the obligate intracellular parasites). Previously they were considered viruses. Examples: Rickettsialpox, Trench fever, Q-fever, Typhus fever, Rocky Mountain spotted fever.
Bacteria Based:
The causative agent is bacteria. Examples: Cholers, typhoid, Plague, Leprosy, Pneumonia, Tuberculosis, Diarrhoea, Tetanus, Diptheria, Whooping cough, gonorrhoea, syphilis and anthrax in animals.
Protozoan Based:
The causative agent is Protozoans. Example: Amoebiasis, Malaria, Trypanosomiasis (African sleeping sickness), Leishmaniasis (Kala-azar), Oriental Sore, Giardiasis (Diarrhoea)
Helminthic Based:
The causative agent is Flatworms and roundworms. Example: Taeniasis, Schistosomiasis, Fasciolopsiasis, Hydatid Disease, Liver rot, Ascariasis, Cysticercosis, Filariasis.
Fungi Based:
The causative agent is fungi. Examples: Ringworm (Tinea), Athlete’s foot.
Previous Topic: Communicable or Infectious Diseases