Science > Biology > Zoology > Criteria for Animal Classification
In this article, we shall study the criteria for animal classification. Animals are classified as follows:
On the Basis of Number of Germ Layers:
Animals in which the cells are arranged in two embryonic layers, an external ectoderm, and an internal endoderm, are called diploblastic animals. e.g. coelenterates. An undifferentiated layer, mesoglea, is present in between the ectoderm and the endoderm

Those animals in which the developing embryo has a third germinal layer, mesoderm, in between the ectoderm and endoderm, are called triploblastic animals e.g. Platyhelminthes to Chordates
On the Basis of Animal Body Plan:
There are three body plans among animals.
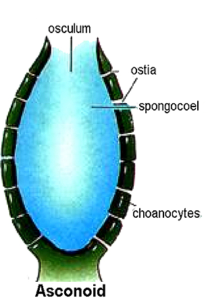
Cell aggregate plan:
These animals show aggregation of cells with the least division of labour. The cells do not form tissues or organs. There is no nervous coordination between them. Examples: Members of phylum Porifera. Sponges. Sponge Asconoid
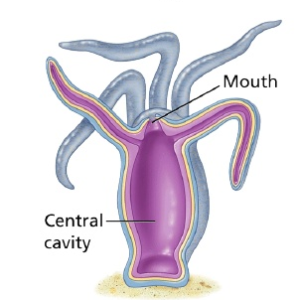
Blind sac body plan:
In these animals, there is a digestive cavity and a single opening which acts as a mouth and anus. The digestive system is incomplete. Examples: Members of phylum Cnidaria.

Tube within tube plan:
This body plan is present in all advanced and highly evolved animals. The digestive system is complete and has two openings one at each end. Examples: Members of phylum Annelida onwards.

On the Basis of Body Symmetry:
Symmetry means similarity in shape, size and number of parts on the opposite sides of the meridian line.There are three body symmetry plans among animals.
Asymmetrical Animals:
In such animals, there is no plane that passes through the centre and divides them into equal halves. Examples: Certain sponges, snails.

Radially symmetrical animals:
When any plane passing through the central axis of the body divides the organism into two identical halves, then the symmetry is called radial symmetry. Examples: Coelenterates, ctenophores and echinoderms, hydra, starfish.

Bilaterally symmetrical animals:
When a single plane passing through the central axis of the body divides the organism into two identical halves, then the symmetry is called bilateral symmetry. Examples: Fish, Frog, human being.

On the basis of Body Cavity or Coelom:
It is the space between the body wall and the alimentary canal, which is produced by splitting of mesoderm, during embryonic development.On the basis of nature of the coelom, animals are classified into three types.
Acoelomates:
In certain animals, there is no body cavity or coelom. Hence they are called acoelomates. The space between the body wall and the alimentary canal is filled with parenchymatous tissue. Examples: Members of phylum Platyhelminthes.

Pseudocoelomates:
In certain animals, there is a false body cavity or coelom. Hence they are called pseudocoelomates. The space between the body wall and the alimentary canal is lined by patches of mesodermal cells. Examples: Members of phylum Aschelminthes.

Coelomates:
In triploblastic animals, the mesoderm splits into two layers enclosing a cavity called coelom. The outer layer lines the body wall while the inner layer covers the alimentary canal. The cavity is filled with coelomic fluid. Examples: all mammals.

On the Basis of Body Segmentation or Metamerism:
In some animals, the body is externally and internally divided into segments with a serial repetition of at least some organs. The external segmentation matches with internal segmentation. For example, in the earthworm, the body shows this pattern called metameric segmentation and the phenomenon is known as metamerism.

On the Basis of Body Support:
The internal or external framework that provides support to the body is called a skeleton. It has two types exoskeleton and endoskeleton. Lower animals like cockroaches have exoskeleton for their protection. While higher animals like fishes, cobra parrots possess both the exoskeleton and endoskeleton.
On the Basis of Presence of Notochord:
The notochord is a mesodermally derived rod-like structure formed on the dorsal side during embryonic development in some animals. Animals with notochord are called chordates e.g. Human beings, reptiles, birds. The animals which do not form notochord structure are called non-chordates, e.g., Porifera to echinoderms.