Science > Chemistry > Concept of Atomic Mass and Equivalent Mass > Concept of Atomic Mass
The smallest particle of an element which can take part in a chemical reaction is called an atom. According to Dalton’s atomic theory atom is the smallest particle of an element which is indivisible. In modern research, it is proved that the atom is divisible into its constituent particles like electrons, protons, and neutrons. In this article, we shall understand the concept of atomic mass and gram atomic mass (GAM).
Atomic Mass:
Water contains 11.19 % of hydrogen and 88.89% of oxygen. Thus hydrogen and oxygen combine with each other in a ratio 1 : 8 by mass. Besides in water, there are 2 atoms of hydrogen and 1 atom of oxygen. From these two observations, it follows that the mass of oxygen atom is 16 times that of the hydrogen atom. In this hydrogen based system mass of hydrogen is taken as unity and masses of other element were determined relative to the mass of an atom of hydrogen.
A later atom of oxygen was chosen as reference atom because by taking its mass as 16 units, the relative atomic masses of other elements were very close to whole numbers. Oxygen has 3 isotopes. Hence the standard of oxygen was considered as inappropriate. Hence instead of taking the average atomic mass of the mixture of oxygen, stable isotope of carbon (C-12) was taken as standard. Hence in 1961 International Union of Chemists selected the most stable isotope of carbon (C – 12) as a standard atom to compare masses of various elements.
The relative atomic mass of an element is a mass of one atom of the element compared with the mass of an atom of 6C12 isotope taken as 12000 units.

Average Atomic Mass:
Isotopes are the atoms of the same element having the same atomic number containing the same number of protons and electrons but different numbers of neutrons hence they possess different mass numbers.
The observed atomic mass of the atom of the element is the average atomic mass of the element taking into consideration the natural abundance of the element. For example, atomic masses of chlorine’s two isotopes are 36 u and 37 u. u stands for unified mass. They are found in the ratio 3: 4 in nature. Hence average atomic mass of chlorine is
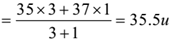
The gram atomic mass of an element is atomic mass expressed in grams (GAM). e.g. The gram atomic mass of chlorine is 35.5 g
Thus one gram hydrogen atom means 1.008 g of hydrogen. one gram atom of carbon means 12 g of carbon. 2 gram atom of chlorine means 2 × 35.5 = 71 g of chlorine.
Number of Atoms in Gram Atom:
By Avogadro’s law, one gram atom of an element contains 6.023 × 1023 atoms. Thus 1 gram atom (i.e. 1.008 g) of hydrogen contains 6.023 × 1023 atoms. Thus the mass of each atom of hydrogen is

Mass in gram = number of gram atom × gram atomic mass
Definition of Valency:
The valency of an element is the number of electrons an atom of the element can accept or donate in the formation of molecule of a compound. OR the number of a hydrogen atom, which can combine with or displaced by one atom of an element is called the valency of the element.
Relation Between Atomic Mass, equivalent Mass, and Valency:
Let A, E, and v be the atomic mass, equivalent mass, and valency of element X. Then the formula of its compound with hydrogen is XHv.
Thus v parts by mass of hydrogen will combine with A parts by mass of X.
i.e. 1 part by mass of hydrogen will combine with A/v parts by mass of X.
By definition A/v is equivalent mass of the element.
Thus E = A/v
At. Mass (A) = Equ. Mass (E) x Valency (v)
Calculation of Average Atomic Mass by Relative Abundance Method:
Example – 01:
Naturally, occurring lead is found to contain four isotopes 1.40 % 82Pb204 isotope with isotopic mass 203.973, 24.10 % 82Pb206 isotope with isotopic mass 205.974, 22.10 % 82Pb207 isotope with isotopic mass 206.976 and 52.40 % 82Pb208 isotope with isotopic mass 207.977. Calculate the average atomic mass of lead.
Solution:

Hence average atomic mass of lead is 207.2 u.
Example – 02:
Naturally, occurring neon is found to contain three isotopes 90.92 % 10Ne20 isotope with isotopic mass 9.9924, 8.82 % 10Ne22 isotope with isotopic mass 21.9914, 0.26 % 10Ne21 isotope with isotopic mass 20.9940 Calculate the average atomic mass of neon.
Solution:

Hence average atomic mass of neon is 20.17 u.
Example – 03:
Naturally, occurring lithium is found to contain two isotopes 8.24 % 3Li6 isotope with isotopic mass 6.0151 and 91.76 % 3Li7 isotope with isotopic mass 7.0160 Calculate the average atomic mass of lithium.
Solution:

Hence average atomic mass of lithium is 6.934 u.
Example – 04:
Naturally, occurring silicon is found to contain three isotopes 92.23 % 14Si28 , 4.67 % 14Si29, 3.10 % 14Si30 Calculate the average atomic mass of silicon.
Solution:

Hence average atomic mass of silicon is 28.1 u
Example – 05:
In naturally occurring neon the fractional abundance of various isotopes is as follows 0.9051 of 10Ne20, 0.0027 of 10Ne21, 0.0922 of 10Ne22. Calculate the average atomic mass of neon.
Solution:
Average atomic mass =0.9051 × 20 + 0.0027 × 21 + 0.0922 × 22
= 18.102 + 0.057 + 2.028 = 20.187 u
Hence average atomic mass of neon is 20.187 u.
Example – 06:
Nitrogen occurs in nature in the form of two isotopes with atomic mass 14 and 15 respectively. If the average atomic mass of nitrogen is 14.0067. What is the percentage abundance of the two isotopes?
Solution:
Let % abundance of the isotope with atomic mass 14 be ‘x’. Hence that of the isotope with atomic mass 15 will be (100 -x).

% abundance of isotope of nitrogen with atomic mass 14 is 99.33 and with atomic mass 15 is 0.67
Example – 07:
Boron occurs in nature in the form of two isotopes with atomic mass 10 and 11 respectively. If the average atomic mass of boron is 10.80 u. What is the percentage abundance of the two isotopes?
Solution:
Let % abundance of the isotope with atomic mass 10 be ‘x’. Hence that of isotope with atomic mass 11 will be (100 -x).

% abundance of isotope of boron with atomic mass 10 is 20 and
% abundance of the isotope of boron with atomic mass 11 is 80.
Example – 08:
Chlorine has two stable isotopes Cl – 35 and Cl -37, with atomic masses 34.968 u and 36.956 u respectively. If the average atomic mass is 35.452 u, calculate the % abundance of isotopes.
Solution:
Let % abundance of the isotope with atomic mass 35 be ‘x’. Hence that of the isotope with atomic mass 37 will be (100 -x).

% abundance of isotope of chlorine with atomic mass 35 is 75.65 and
% abundance of isotope of chlorine with atomic mass 37 is 24.35
In the next article, we shall study Cannizzaro’s method to determine atomic mass.
Previous Chapter: Laws of Chemical Combinations
Next Topic: Atomic Mass by Cannizzaro’s Method
