Science > Chemistry > Molecule and Molecular Mass > Calculation of Number of Moles and Molecules
In this article, we shall solve problems to calculate number of moles and number of molecules and atoms present in given quantity of a substance.
Example 01:
3.49 g of ammonia at STP occupies 4.48 dm3. Calculate molar mass of ammonia.
Given: Mass of gas = m = 3.49 g = 3.49 x 10-3 kg, Volume of gas = V = 4.48 dm3 = 4.48 x 10-3 m3, P = 1.01325 x 105 Pa, T = 273.15 K, Universal gas constant = R = 8.314 J K-1 mol-1.
To Find: Molar mass of gas = M =?
Solution:
PV = nRT
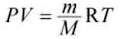
∴ M = mRT/ PV
∴ M = (3.49 x 10-3 x 8.314 x 273.15) / (1.01325 x 105 x 4.48 x 10-3 )
∴ M = 17.46 x 10-3 kg mol-1 = 17.46 g mol-1
Ans: Molecular mass of the gas is 17.46 g mol-1.
Example 02:
2.8 x 10-4 kg of a gas at STP occupies 0.224 dm3. Calculate molar mass of the gas.
Given: Mass of gas = m = 2.8 x 10-3 kg, Volume of gas = V = 0.224 dm3 = 0.224 x 10-3 m3, P = 1.01325 x 105 Pa, T = 273.15 K, Universal gas constant = R = 8.314 J K-1 mol-1.
To Find: Molar mass of gas = M =?
Solution:
PV = nRT
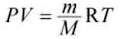
∴ M = mRT/ PV
∴ M = (2.8 x 10-3 x 8.314 x 273.15) / (1.01325 x 105 x 0.224 x 10-3 )
∴ M = 28.015 x 10-3 kg mol-1 = 28.02 g mol-1
Ans: Molecular mass of the gas is 28.02 g mol-1.
Example 03:
Calculate the mass of
a) 2.5 gram-atom of calcium. Ans:100 g.
Given: Given mass = 2.5 gram-atom
Solution:
Atomic mass of calcium = 40 g
1 gram atom of calcium corresponds to 40 g of calcium
2.5 gram atom of calcium corresponds to 40 x 2.5 = 100 g of calcium
Ans: Mass of calcium = 100 g
b) 1.5 gram-molecule of water.
Given: Given mass = 1.5 gram molecule
Solution:
Molecular mass of water (H2O) = 1 x 2 + 16 x 1
Molecular mass of water (H2O) = 2 + 16 = 18 g
1 gram molecule of water corresponds to 18 g of water
1.5 gram molecule of water corresponds to 18 x 1.5 = 27 g of water
Ans: Mass of water = 27 g
c) 2 gram-molecule of sulphuric acid.
Given: Given mass = 2 gram molecule
Solution:
Molecular mass of sulphuric acid (H2SO4) = 1 x 2 + 32 x 1 + 16 x 4
Molecular mass of sulphuric acid (H2SO4) = 2 + 32 + 64 = 98 g
1 gram molecule of sulphuric acid corresponds to 98 g of sulphuric acid
2 gram molecule of sulphuric acid corresponds to 98 x 2 = 196 g of sulphuric acid
Ans: Mass of sulphuric acid = 196 g
d) 0.5 gram-molecule of iodine.
Given: Given mass = 0.5 gram molecule
Solution:
Molecular mass of iodine (I2) = 127 x 2 = 254 g
1 gram molecule of iodine corresponds to 127 g of iodine
0.5 gram molecule of iodine corresponds to 254 x 0.5 = 127 g of iodine
Ans: Mass of iodine = 127 g
e) 1.5 gram-molecule of sucrose. Ans: 513 g.
Given: Given mass = 1.5 gram sucrose
Solution:
Molecular mass of sucrose (C12H22O11) = 12 x 12 + 1 x 22 + 16 x11
Molecular mass of sucrose = 342 g
1 gram molecule of sucrose corresponds to 342 g of sucrose
1.5 gram molecule of sucrose corresponds to 342 x 1.5 = 513 g of sucrose
Ans: Mass of sucrose = 513 g
Example 04:
Calculate the number of gram-atoms and gram-molecules of 25.4 mg of iodine.
Given: Given mass = 25.4 mg of iodine = 25.4 x 10-3 g of iodine
Solution:
Molecular mass of iodine (I2) = 127 x 2 = 254 g
254 g of iodine corresponds to 1 gram molecule of iodine.
25.4 x 10-3 g of iodine corresponds to (1 x 25.4 x 10-3)/ 254 gram molecule of iodine.
25.4 x 10-3 g of iodine corresponds to 1 x 10-4 gram molecule of iodine.
Iodine is diatomic molecule
25.4 x 10-3 g of iodine corresponds to 1 x 10-4 x 2 gram atom of iodine
25.4 x 10-3 g of iodine corresponds to 2 x 10-4 gram atom of iodine
Ans:2 x 10-4 gram-atom and 1 x 10-4 gram-molecule of molecule.
Example 05:
What is the molar mass of a gas if 1.00 dm3 of the gas weighs 1.50 g at 273 K and 1 atmospheric pressure?
Given: Mass of gas = m = 1.50 g = 1.50 x 10-3 kg, Volume of gas = V = 1 dm3 = 1 x 10-3 m3, P = 1 atm = 1.01325 x 105 Pa, T = 273 K, Universal gas constant = R = 8.314 J K-1 mol-1.
To Find: Molar mass of gas = M =?
Solution:
PV = nRT
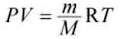
∴ M = mRT/ PV
∴ M = (1.50 x 10-3 x 8.314 x 273) / (1.01325 x 105 x 1 x 10-3 )
∴ M = 33.59 x 10-3 kg mol-1 = 33.59 g mol-1
Ans: Molecular mass of the gas is 33.59 g mol-1.
Example 06:
What is the mass of one mole electrons.
Given: Mass of each electron = 9.1 x 10-31 kg, Avogadro’s number = N = 6.022 x 1023.
1mole of electrons contain 6.022 x 1023 electrons
Mass of 1 mole of electrons = 6.022 x 1023 x 9.1 x 10-31
Mass of 1 mole of electrons = 5.48 x 10-7 kg
Ans: Mass of 1 mole of electrons = 5.48 x 10-7 kg
Example 07:
What is the molar volume of water at 273 K. Given density of water as 1.00 g cm-3.
Solution:
Molecular mass of water (H2O) = 1 x 2 + 16 x 1
Molecular mass of water (H2O) = 2 + 16 = 18 g
Molar volume = Molar mass/ Density = 18 g /1 g cm-3 = 18 cm3
Ans: molar volume of water at 273 K is 18 cm3
Example 08:
Calculate the molar mass of glucose and find number of atoms of each kind in 0.18 g of glucose.
Solution:
Molecular mass of glucose (C6H12O6) = 12 x 6 + 1 x 12 + 16 x 6
Molecular mass of sucrose = 72 + 12 + 96 = 180 g mol-1 or 180 u
Number of moles = Given mass/Molecular mass
Number of moles = 0.18/180 = 10-3
1 mole of glucose contain 6.022 x 1023 molecules of glucose.
10-3 mole of glucose contain 6.022 x 1023 x 10-3 molecules of glucose.
10-3 mole of glucose contain 6.022 x 1020 molecules of glucose.
There are 6 carbon atoms, 12 hydrogen atoms and 6 oxygen atoms in one molecule of glucose.
Number of carbon atoms = 6.022 x 1020 x 6 = 36.13 x 1020
Number of hydrogen atoms = 6.022 x 1020 x 12 = 72.16 x 1020
Number of oxygen atoms = 6.022 x 1020 x 6 = 36.13 x 1020
Example 09:
Calculate the number of atoms of each kind present in 3.42 g of sucrose.
Solution:
Molecular mass of sucrose (C12H22O11) = 12 x 12 + 1 x 22 + 16 x11
Molecular mass of sucrose = 144 + 22 + 176 = 342 g
Number of moles = Given mass/Molecular mass
Number of moles = 3.42/342 = 10-2
1 mole of sucrose contain 6.022 x 1023 molecules of sucrose.
10-2 mole of sucrose contain 6.022 x 1023 x 10-2 molecules of sucrose.
10-2 mole of sucrose contain 6.022 x 1021 molecules of sucrose.
There are 12 carbon atoms, 22 hydrogen atoms and 11 oxygen atoms in one molecule of sucrose.
Number of carbon atoms = 6.022 x 1021 x 12 = 72.26 x 1021
Number of hydrogen atoms = 6.022 x 1021 x 22 = 132.5 x 1021
Number of oxygen atoms = 6.022 x 1021 x 11 = 66.24 x 1021
Example 10:
Calculate the number of atoms of each kind present in 5.6 g of urea (CO(NH2)2). Molecular mass of urea = 60 g mol-1.
Solution:
Molecular mass of urea (CO(NH2)2) = 60 g
Number of moles = Given mass/Molecular mass
Number of moles = 5.6/60 = 0.0933 mole of urea
1 mole of urea contain 6.022 x 1023 molecules of urea.
0.0933 mole of urea contain 6.022 x 1023 x 0.0933 molecules of urea.
0.0933 mole of urea contain 5.618 x 1022 molecules of urea.
There are 1 carbon atom, 4 hydrogen atoms, 1 oxygen atom and 2 nitrogen atoms in one molecule of urea.
Number of carbon atoms = 5.618 x 1022 x 1 = 5.618 x 1022
Number of hydrogen atoms = 5.618 x 1022 x 4 = 22.47 x 1022
Number of oxygen atoms = 5.618 x 1022 x 1 = 5.618 x 1022
Number of nitrogen atoms = 5.618 x 1022 x 2 = 11.24 x 1022
Example 11:
Calculate the number of atoms of each kind present in 72.5 g of isopropanal (C3H7OH). Molecular mass of isopropanol = 60 g mol-1.
Solution:
Molecular mass of isopropanal (C3H7OH) = 60 g mol-1
Number of moles = Given mass/Molecular mass
Number of moles = 72.5/60 = 1.208
1 mole of isopropanal contain 6.022 x 1023 molecules of isopropanal.
1.208 mole of isopropanal contain 6.022 x 1023 x 1.208 molecules of isopropanal.
1.208 mole of isopropanal contain 7.275 x 1023 molecules of isopropanal.
There are 3 carbon atoms, 8 hydrogen atoms and 1 oxygen atom in one molecule of isopropanal.
Number of carbon atoms = 7.275 x 1023 x 3 = 21.83 x 1023
Number of hydrogen atoms = 7.275 x 1023 x 8 = 58.2 x 1023
Number of oxygen atoms = 7.275 x 1023 x 1 = 7.275 x 1023
Example 12:
Calculate the number of water molecules in a drop of water weighing 0.05 g. If this drop evaporates in one hour. Calculate the number of molecules evaporating per second.
Solution:
Molecular mass of water (H2O) = 1 x 2 + 16 x 1
Molecular mass of water (H2O) = 2 + 16 = 18 g
Number of moles = Given mass/Molecular mass
Number of moles = 0.05/18 = 0.0028
1 mole of water contains 6.022 x 1023 molecules of water.
0.0028 mole of water contains 6.022 x 1023 x 0.0028 molecules of water.
0.0028 mole of water contains 1.686 x 1021 molecules of water.
Rate of evaporation = 1.686 x 1021 / (1 x 60 x 60)
= 4.68 x 1017 molecules s-1.
Ans: Rate of evaporation is 4.68 x 1017 molecules s-1.
Example 13:
How many oxygen are present in 300 g of calcium carbonate?
Solution:
Molecular mass of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) = 40 x 1 + 12 x 1 + 16 x 3
Molecular mass of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) = 100 g
Number of moles = Given mass/ Molecular mass
Number of moles = 300/100 = 3
1 mole of calcium carbonate contains 6.022 x 1023 molecules of calcium carbonate.
3 moles of calcium carbonate contain 6.022 x 1023 x 3 molecules of calcium carbonate.
3 moles of calcium carbonate contain 18.066 x 1023 molecules of calcium carbonate.
Each molecule of calcium carbonate contains 3 atoms of oxygen
Number of oxygen atom in 3 moles of calcium carbonate
= 18.066 x 1023 x 3 = 5.42 x 1024
Ans: Number of oxygen atom in 300 g of calcium carbonate is 5.42 x 1024
Example 14:
How many molecules of water of hydration are present in 252 mg of oxalic acid. (H2C2O4.2H2O)
Solution:
Molecular mass of oxalic acid. (H2C2O4.2H2O)
= 1 x 2 + 12 x 2 + 16 x 4 + 2(1 x 2 + 16 x 1)
Molecular mass of oxalic acid. (H2C2O4.2H2O) = 126 g
Number of moles = Given mass/Molecular mass
Number of moles = 252 x 10-3/126 = 2 x 10-3
1 mole of oxalic acid contains 6.022 x 1023 molecules of oxalic acid.
2 x 10-3 mole of oxalic acid contains 6.022 x 1023 x 2 x 10-3 molecules of oxalic acid.
2 x 10-3 mole of oxalic acid contains 12.044 x 1020 molecules of oxalic acid.
For each molecule of oxalic acid, there are 2 molecules of water.
Number of molecules of water of hydration = 12.044 x 1020 x 2
= 24.088 x 1020
Ans: Number of molecules of water of hydration are 2.408 x 1021.