Science > Chemistry > Molecule and Molecular Mass > Molecular Mass by Regnault’s Method
In the last article, we have studied the molar volume method to determine molecular mass. In this article, we shall study the concept of molecular mass (molar mass) and Regnault’s method to determine it.
Molecule:
When two or more atoms are firmly held together by a chemical bond, a molecule is formed. The molecule of an element may consist of one or more atoms of the same kind, while that of the chemical compound consists of different kinds of atoms.
The smallest particle of an element or compound which can exist in a free state and does not take part in a chemical reaction is called molecule.
Molecules are denoted by formula indicating the number of constituent elements in the compound. For example molecular formula for oxygen is O2. Thus one molecule oxygen consists of two atoms of oxygen
Molecular Mass or Molar Mass:
The molecular mass or molar mass of a substance is defined as the ratio of the mass of one molecule of a substance to 1/12 th of the mass of 6C12 isotope taken as 12000 units.
Gram Molecular Mass or Molar Mass:
The molecular mass expressed in grams is called gram molecular mass (GMM)
Method – II (Regnault’s Method):
Principle:
In this method vapour densities of gases are determined by direct weighing. The vapour density of a gas is the ratio of the mass of a certain volume of a gas to the mass of the same volume of hydrogen at the same temperature & pressure.
Procedure:
In this method, two hollow glass globes of the same capacity, same mass and same size are taken. They are evacuated and suspended by two sides of a physical balance.
Now one of the glass globes is filled with a gas whose vapour density is to be found. then the mass of the globe is measured. the difference in the filled globe and empty globe gives the mass of the gas in the globe,
Now the globe is evacuated again and filled with hydrogen gas at same temperature and pressure. The mass of globe filled with hydrogen is measured again. The difference in the empty globe and hydrogen filled globe gives the mass of hydrogen.
Vapour density is found by using the formula.
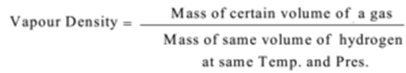
Now, Molecular Mass = 2 x Vapour density
Numerical Problems:
Example – 01:
1 dm3 of hydrogen at S.T.P. has a mass of 0.09 g. If 2 dm3 of gas at S.T.P. has a mass of 2.880 g. Calculate the vapour density and molecular mass of the gas.
Solution:
1 dm3 of hydrogen has a mass of 0.09 g.
2 dm3 of gas has a mass of 2.880 g.
Hence, 1 dm3 of gas has a mass of 1.440 g.

Now, Molecular Mass = 2 x Vapour density = = 2 x 16 = 32
Ans: The molecular mass of the gas is 32.
Example – 02:
The capacity of a glass bulb is 30.5 ml, 0.146 g of gas is filled in a bulb at 22 °C and 755 mm of Hg pressure. 1 dm3 of hydrogen at S.T.P. have a mass of 0.09 g. Calculate the vapour density and molecular mass of the gas.
Given: V = 30.5 ml, t = 22°C, T = 22 + 273 = 295 K, P = 755 mm of Hg , W = 0.146 g, Po = 760 mm of Hg, To = 273 K
Solution:
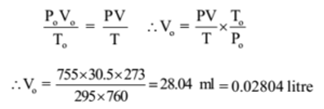
Po = 0.02804 litre = 0.02804 dm3

Now, Molecular Mass = 2 x Vapour density = 2 x 57.85 = 115.7
Ans: The molecular mass of the gas is 115.7.
Example – 03:
The capacity of a glass bulb is 127 ml, 0.4524 g of gas is filled in a bulb at 409 K and 758 mm of Hg pressure. 1 ml of hydrogen at S.T.P. has a mass of 0.00009 g. Calculate the vapour density and molecular mass of the gas.
Given: V = 127 ml, T = 409 K, P = 758 mm of Hg , W = 0.4524 g, Po = 760 mm of Hg, To = 273 K
Solution:


Now, Molecular Mass = 2 x Vapour density = 2 x 59.45 = 118.90
Ans: The molecular mass of the gas is 118.90
Example – 04:
In Regnault’s method, 27.32 ml of gas were found to have a mass of 0.1008 g. The experiment was performed at 16.5 °C and 694 mm of mercury. Calculate the molecular mass of the gas.
Given: V = 27.32 ml, t = 16.5 °C, T = 16.5 + 273 = 289.5 K, P = 694 mm of Hg , W = 0.1008 g, Po = 760 mm of Hg, To = 273 K
Solution:


Now, Molecular Mass = 2 x Vapour density = 2 x 47.6 = 95.2
Ans: The molecular mass of the gas is 95.2
Example – 05:
When a glass bulb with a stop cock is evacuated, weighed, and then filled with oxygen, the weight increases by 0.25 g. When the same bulb is evacuated and filled with another unknown gas under the same conditions of temperature and pressure, the mass increases by 0.5525 g. If the molecular mass of oxygen is 32, calculate the molecular mass of the unknown gas. Calculate the volume of the glass bulb assuming that it does not change appreciably with the change in pressure and temperature.
Solution:
The molecular mass of oxygen = 32
Vapour density of oxygen = 32 / 2 = 16
Mass of oxygen = 0.25 g

Now, the vapour density of the gas

Now, Molecular Mass = 2 x Vapour density = 2 x 35.36 = 70.72
Hence, the molecular mass of the gas is 70.72

Ans: The volume of the bulb is 0.1736 dm3.