In this article, we shall study to find the value of trigonometric expressions involving standard angles. Trigonometric functions values of some standard angles are given below:

Evaluate the following:
Example 01:
sin20c + sin2(π/6)c + sin2(π/3)c + sin2(π/2)c
= (0)2 + (1/2)2 + (√3/2)2 + (1)2
= 0 + 1/4 + 3/4 + 1 = 1+ 1 = 2
Ans: sin20c + sin2(π/6)c + sin2(π/3)c + sin2(π/2)c = 2
Example 02:
cos20 + cos2(π/6)c + cos2(π/3)c + cos2(π/2)c
= (1)2 + (√3/2)2 + (1/2)2 + (0)2
= 1 + 3/4 + 1/4 + 0 = 1+ 1 = 2
Ans: cos20 + cos2(π/6)c + cos2(π/3)c + cos2(π/2)c = 2
Example 03:
sin (π)c + 2 cos (π)c + 3 sin (3π/2)c + 4 cos (3π/2)c – 5 sec (π)c + 6 cosec (π/2)c
= (0) + 2(-1) + 3(-1) + 4 (0) – 5 (-1) + 6 (1)
= 0 – 2 – 3 + 5 + 6 = 6
Ans: sin (π)c + 2 cos (π)c + 3 sin (3π/2)c + 4 cos (3π/2)c – 5 sec (π)c + 6 cosec (π/2)c = 6
Example 04:
sin (0)c + 2 cos (0)c + 3 sin (π/2)c + 4 cos (π/2)c + 5 sec (0)c + 6 cosec (π/2)c
= 0 + 2 (1) + 3 (1) + 4 (0) + 5 (1) + 6 (1)
= 2 + 3 + 0 + 5 + 6 = 16
Ans: sin (0)c + 2 cos (0)c + 3 sin (π/2)c + 4 cos (π/2)c + 5 sec (0)c + 6 cosec (π/2)c = 16
Example 05:
4 cot 45° – sec2 60° + sin2 30°
= 4 (1) – (2)2 + (1/2)2
= 4 – 4 + 1/4 = 1/4
Ans: 4 cot 45° – sec2 60° + sin2 30° = 1/4
Verify the Following:
Example 06:
- cot2 60° + sin2 45° + sin2 30° + cos2 90° = 13/12
- Solution:
L.H.S. = cot2 60° + sin2 45° + sin2 30° + cos2 90°
∴ L.H.S. = (1/√3)2 + (1/√2)2 + (1/2)2 + (0)2
∴ L.H.S. = 1/3 + 1/2 + 1/4 = 5/6 + 1/4
∴ L.H.S. = 26/24 = 13/12 = R.H.S.
∴ cot2 60° + sin2 45° + sin2 30° + cos2 90° = 13/12 (Proved)
Example 07:
- sin2 30° + cos2 60° + tan2 45° + sec2 60° – cosec2 30° = 3/2
- Solution:
L.H.S. = sin2 30° + cos2 60° + tan2 45° + sec2 60° – cosec2 30°
∴ L.H.S. = (1/2)2 + (1/2)2 + (1)2 + (2)2 – (2)2
∴ L.H.S. = 1/4 + 1/4 + 1 + 4 – 4 = 2/4 +1
∴ L.H.S. = 1/2 + 1 = 3/2 = R.H.S.
∴ sin2 30° + cos2 60° + tan2 45° + sec2 60° – cosec2 30° = 3/2 (Proved)
Example 08:
- 4 cot2 30° + 9 sin2 60° – 6 cosec2 60° -(9/4) tan2 60° = 4
- Solution:
L.H.S. = 4 cot2 30° + 9 sin2 60° – 6 cosec2 60° – (9/4) tan2 60°
∴ L.H.S. = 4 (√3)2 + 9 (√3/2)2 – 6 (2/√3)2 – (9/4)(√3) 2
∴ L.H.S. = 4 x 3 + 9 (3/4) – 6 (4/3) – (9/4)(3)
∴ L.H.S. = 12 + 27/4 – 8 – 27/4 = 4 = R.H.S,
∴ 4 cot2 30° + 9 sin2 60° – 6 cosec2 60° -(9/4) tan2 60° = 4 (Proved)
Example 09:
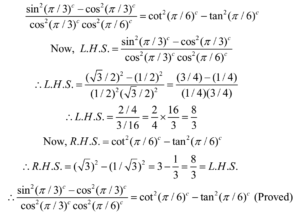
Example 10:
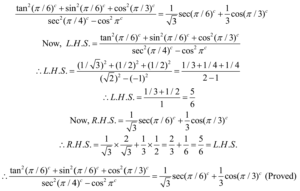
Example 11:
- If 2 cos2θ + 3cosθ = 2, then find cosθ.
- Solution:
Given 2 cos2θ + 3cosθ = 2 i.e 2 cos2θ + 3cosθ – 2 = 0
let cosθ = x
∴ 2 x2 + 3x – 2 = 0
∴ 2 x2 + 4x – x – 2 = 0
∴ 2 x(x + 2) – 1(x + 2) = 0
∴ (x + 2)(2x – 1) = 0
∴ (x + 2) = 0 or (2x – 1) = 0
∴ x = – 2 or x = 1/2
∴ cosθ = – 2 or cosθ = 1/2
Now – 1 ≤ cos θ ≤ 1, thus cosθ = – 2 is not possible.
∴ cosθ = 1/2\
Example 12:
- If 6sin2θ – 11sinθ + 4 = 0, find cosθ.
- Solution:
Given 6sin2θ – 11sinθ + 4 = 0
let sinθ = x
∴ 6x2 – 11x + 4 = 0
∴ 6x2 – 8x – 3x + 4 = 0
∴ 2x(3x – 4) – 1(3x – 4) = 0
∴ (3x – 4)(2x – 1) = 0
∴ 3x – 4 = 0 or 2x – 1 = 0
∴ x = 4/3 or x = 1/2
Now – 1 ≤ sin θ ≤ 1, thus sinθ = 4/3 is not possible.
∴ sinθ = 1/2
Example 13:
- If 3tan2θ – 4√3 tanθ + 3 = 0, then find tanθ.
- Solution:
Given 3tan2θ – 4√3 tanθ + 3 = 0
let tanθ = x
∴ 3x2 – 4√3 x + 3 = 0
∴ 3x2 – 3√3 x –√3 x + 3 = 0
∴ √3 x √3 x2 – 3√3 x –√3 x + 3= 0
∴ √3 x ( √3x – 3 ) – 1(√3 x – 3) = 0
∴ (√3x – 3 )( √3 x – 1) = 0
∴ √3x – 3 = 0 or √3 x – 1 = 0
∴ x = 3/√3 or x = 1/√3
∴ x = √3 or x = 1/√3
∴ tanθ = √3 or tanθ = 1/√3
Example 14:
- If 4sin2θ – 2(√3 + 1)sinθ + √3 = 0, then find sinθ. Hence find the angle θ.
- Solution:
Given 4sin2θ – 2(√3 + 1)sinθ + √3 = 0
let sinθ = x
∴ 4x2 – 2(√3 + 1)x + √3 = 0
∴ 4x2 – 2√3x – 2x + √3 = 0
∴ 2x(2x – √3) – 1(2x – √3 ) = 0
∴ (2x – √3)(2x – 1) = 0
∴ 2x – √3 = 0 or 2x – 1 = 0
∴ x = √3/2 or x = 1/2
∴ sinθ = √3/2 or sinθ = 1/2
∴ θ = sin-1(√3/2) or θ = sin-1(1/2)
∴ θ = (π/3)c i.e. 60° or θ = (π/6)c i.e. 30°
Example 15:
- Find the acute angles A and B satisfying cot (A + B) = 1 and cosec (A- B) = 2
- Solution:
Given cot (A + B) = 1 and cosec (A- B) = 2
we know that cot 45° = 1 and cosec 30° = 2
∴ A + B = 45° and A- B = 30°
Adding the two equations we get
2A = 75° i.e. A = 37.5°
Subtracting the two equations we get
2B = 15° i.e. B = 7.5°
∴ A = 37.5° and B = 7.5°
Example 16:
- Find the acute angles secA.cotB – secA – 2 cotB + 2 = 0
- Solution:
Given secA.cotB – secA – 2 cotB + 2 = 0
secA.(cotB – 1) – 2 (cotB – 1) = 0
(cotB – 1)(secA – 2) = 0
∴ cotB – 1 = 0 and/or secA – 2 = 0
∴ cotB = 1 and/or secA = 2
∴B = cot-11 and/or A = sec-12
∴B = (π/4)c i.e. 45° and/or A = (π/3)c i.e. 60°
∴ A = (π/3)c i.e. 60° and B = (π/4)c i.e. 45°