Science > Physics > Motion in a Straight Line > Concept of Distance and Displacement
Motion is an important part of our life. Our daily activities involve motion of different kinds. When a body moves along a straight-line path, its motion is called the one-dimensional motion or motion in a straight line or rectilinear motion. Example: the motion of a car along a straight road. When we study motion, we come across to important concepts namely distance travelled and displacement. In this article, we shall study the meaning of the two terms, there characteristics and distinguishing between them.
Notes
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Short Answer Type Questions
Essay Type Answer Questions
Concept Application
Distance:
The length of the path travelled by a body is called the distance travelled by it. The path of a body may not be straight. Distance is also referred as path length.
It is denoted by ‘s’ or ‘x’. Its S.I. unit is metre (m) and the c.g.s. unit is centimetre (cm). Its dimensions are [L1M0T0]
Mathematically,
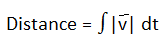
Characteristics of Distance:
- It is the length of the path followed by the object in a certain time. The path followed may or may not be along a straight line.
- It is a scalar quantity.
- It depends on the path followed by the object.
- It is always positive.
- It can be more than or equal to displacement.
- It may not be zero even if the displacement is zero.
- Distance between a given set of initial and final position can have infinite value.
- distance does not dectrease with time and never be zero for moving body.
Displacement:
The shortest distance from the initial position to the final position of the body is called the magnitude of the displacement.
It is a vector quantity whose direction is from initial position to final position. Its S.I. unit is metre (m) and the c.g.s. unit is centimetre (cm). Its dimensions are [L1M0T0]
Mathematically

Characteristics of Displacement:
- It is the shortest distance between the initial position to the final position of the body. It is always along a straight line.
- It is a vector quantity whose direction is from the initial position to final position.
- It is independent of the path followed by the object.
- It may be positive, negative or zero.
- It may be equal but cannot be more than the distance travelled.
- It is zero when the distance travelled is zero.
- Displacement is not dependent on the choice of origin.
- The displacement of an object between two pints is the unique path that takes the body from its initial to final position.
- Displacement does not give any idea about the shape of path followed by the body to move between the two positions.
- The displacement between a given set of initial and final position have unique value.
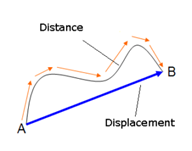
Displacement Vector:
Position Vector of a Point:

Let us consider point P be in a space, whose coordinates are (x1, y1, z1). Then its position vector w.r.t. origin O(0, 0, 0) is given as

Displacement Vector:
Let particle moves from point P with coordinates (x1, y1, z1) to point Q with coordinates (x2, y2, z2).

Then the displacement vector is given by

Concepts:
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1. Define distance.
The length of the path travelled by a body is called the distance travelled by it.
Q2.Define displacement.
The shortest distance from the initial position to the final position of the body is called the magnitude of the displacement.
Q3. Give c.g.s., m.k.s. and S.I. units of distance, displacement
Distance:
| c.g.s. unit | centimetre (cm) |
| m.k.s. unit | metre (m) |
| S.I. unit | metre (m) |
Displacement;
| c.g.s. unit | centimetre (cm) |
| m.k.s. unit | metre (m) |
| S.I. unit | metre (m) |
Q4. What are the dimensions of distance and displacement.
Dimensions of distance and displacement are the same [L1M0T0]
Q5. When is the magnitude of displacement equal to its distance?
When an object moves in a straight line in the fixed direction without coming back, it’s displacement and distance magnitude will always be equal.
Short Answer Type Questions:
Q1. What are the characteristics of distance?
The characteristics of distance are as follows:
- It is the length of the path followed by the object in a certain time. The path followed may or may not be along a straight line.
- It is a scalar quantity.
- It depends on the path followed by the object.
- It is always positive.
- It can be more than or equal to displacement.
- It may not be zero even if the displacement is zero.
Q2. What are the characteristics of displacement?
The characteristics of displacement are as follows:
- It is the shortest distance between the initial position to the final position of the body. It is always along a straight line.
- It is a vector quantity whose direction is from the initial position to final position.
- It is independent of the path followed by the object.
- It may be positive, negative or zero.
- It may be equal but cannot be more than the distance travelled.
- It is zero when the distance travelled is zero.
Q3. Distinguish between distance and displacement.
| Distance | Displacement |
| The length of the path travelled by a body is called the | The shortest distance from the initial position to the final position of the body is called the magnitude of the displacement. |
| The distance travelled by the body can be more than or equal to displacement. | Displacement can never be greater than the distance travelled by the body. |
| It is always positive | it may be positive or negative or zero. |
| Distance depends upon the path followed and hence can have multiple values. | The displacement depends on the initial and the final position of the body and hence is single-valued. |
| Distance is a scalar quantity. it has only magnitude. | The displacement is a vector quantity. It has both the magnitude and the direction. |
| Distance between a given set of initial and final position can have infinite value. | The displacement between a given set of initial and final position have unique value. |
| It may not be zero even if displacement is zero. | It is zero when distance travelled is zero. |
Q4. Why is displacement referred to as a vector quantity and distance as scalar quantity?
Displacement is a vector quantity because it can be only described by using both magnitude as well as direction. while distanceis a scalar quantity, because it can be expressed completely by giving the length of the path (magnitude) taken by the body.
Q5. Explain “the displacement can be zero even if the distance is not zero”.
The length of the path travelled by a body is called the distance travelled by it, while The shortest distance from the initial position to the final position of the body is called the magnitude of the displacement. If a body, after travelling, comes back to its starting point, the displacement is zero but distance travelled is not zero.
Essay Type Answer Questions
Q1. Explain “displacement May be Positive or Negative or Zero”.
Case – 1: When Distance travelled and displacement are equal.
If an object moves along the positive direction of the x-axis through 4m and further moves by 3 m in the same direction. In this case, the distance travelled by the object is 7m and displacement is also 7 m.

Case – 2: When Distance travelled and displacement are not equal and displacement is positive
If an object moves along the positive direction of the x-axis through 4m and further moves by 3 m in the opposite direction. In this case, the distance travelled by the object is 7m and displacement is also + 1 m (along the positive direction of the x-axis).

Case – 3: When Distance travelled and displacement are not equal and displacement is negative
If an object moves along the positive direction of the x-axis through 3m and further moves by 4 m in the opposite direction. In this case, the distance travelled by the object is 7m and displacement is also – 1 m (along the negative direction of the x-axis).

Case – 4: When Distance travelled and displacement are not equal and displacement is zero
If an object moves along the positive direction of the x-axis through 4m and further moves by 4 m in the opposite direction. In this case, the distance travelled by the object is 8 m and the displacement is also 0 m.

Concept Application:
Q1. A body is first displaced by 5 m and then by 12 m in different directions. The minimum displacement it can have is …….. m.
The minimum displacement, the body can have = 12 m – 5 m = 7 m
Q2. A body is first displaced by 5 m and then by 12 m in different directions. The maximum displacement it can have is …….. m.
The maximum displacement, the body can have = 12 m + 5 m = 17 m
Q3. A cop gets information that a thief is 10 km away from the police station. Is it possible for cop to trace the thief with the given information?

This information is not sufficient as the direction in which the cop has to trace is not mentioned. The cop has to move along a circumference of a circle of radius 10 km through each and every point. At point T he can nab the thief. Thus, only specifying that a thief is 10 km away from the police station is not sufficient and it makes the task almost impossible. To trace the thief effectively with the distance direction also should be specified.
Thus for displacement both the magnitude and the direction is required. It is a vector quantity.
Q4. A horse is tied to a rope of length ‘r’ and the other end of the rope is tied to a pole. Find the displacement and the distance travelled by the horse in the following cases:
- When the horse makes half revolution along a circular path.
- When it makes one full revolution.
- When it makes 3/4 th of the revolution.
When the horse makes half revolution along a circular path.

The starting point of journey is P and the end point is at Q
Distance travelled = Circumference/2 = 2πr/2 = πr units
Displacement = PQ = r + r = 2r units
When it makes one full revolution.

The starting point of journey is P and the end point is at Q
Distance travelled = Circumference = 2πr units
Displacement = PQ = 0 units
When it makes 3/4 th of the revolution.

The starting point of journey is P and the end point is at Q
Distance travelled = 3/4 x Circumference = 3/4(2πr) = 3πr/2 units
Applying Pythagoras theorem to Δ POQ
Displacement = PQ = √2 r units
Q6. A boy starts moving from a point in the north. after moving 5 m, he turns right and travels 2m straight, after which he again turns right. Finally he stops after travelling 5 m. What is the path length, he travels? Also find his displacement.

Path length =AB = BC + CD = 5 m + 2 m + 5 m = 12 m
Displacement = AD = 2 m
Q7. A particle moves 5 m towards the east and then moves 8 m towards the West. What is the total distance traveled and the magnitude of the displacement?

Distance travelled = OA + AB = 5m + 8 m = 13 m
Displacement = OB = 3 m towards the west
Q8. A horse runs straight north and covers a distance of 5 m, then turns east and travels a distance of 12 m. Draw the diagram showing the displacement and from the diagram, calculate distance travelled and displacement of the horse.

Distance travelled = OA + AB = 5 m + 12 m = 17 m
By pythagoros theorem
OB2 = OA2 + AB2 = 52 + 122 = 25 + 144 = 189
Displacement = OB = √189 = 13.75 m from O to B
Q9. Redraw the following figure to scale and find out the distance and displacement of a particle moving along the path A-B-C-D.

Drawn to the scale on the graph paper
Scale 1 cm = 1m
Displacement = AD from A to D
Displacement = 9.8 m from A to D