Science > Physics > Magnetism > Magnets
About 600 to 800 BC the people living in Magnesia in Asia Minor found a stone (an ore of iron Magnetite Fe2O3) which was capable of attracting iron pieces towards it. They called this stone as magnetite. During the course of time, the name changed to a magnet. Certain substances have a tendency to attract iron filings towards them, such substances are called magnetic substances and the property is known as magnetism. e.g. Iron, Steel, Cobalt, Nickel.
The pieces of loadstone, which show magnetism are called natural magnets. The natural magnets are of irregular and odd shapes. They don’t have strength. Magnetized iron pieces of iron or other magnetic material are called artificial magnets. They can be made of different shapes.
A magnet creates around it what is called a magnetic field. Thus the region around the magnet in which it exerts a force on other magnets or other magnetic materials is called a magnetic field. The magnetic force is a non-contact force.
Characteristics of Magnet:
Attractive Property:
A magnet attracts small pieces of iron. The magnetic field is stronger at the ends of a magnet and thus the ends of the magnet are the centres of attraction. These centres of attraction are called poles of the magnet.
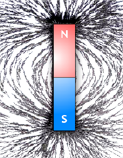
Magnetic lines of force are crowded at the ends of a bar magnet. Actually, the poles are not at the ends of the geometric length of the magnet but they are slightly inside. The points of a magnet where the attraction appears to be maximum are called the poles of the magnet.
Directive Property:
When a bar magnet is suspended in the air such that it is free to rotate about the transverse axis passing through its centre, then it is found that the bar magnet always aligns itself in a north-south direction. The end of the magnet which is pointing towards the geographical north is called north-seeking pole or simply north pole, while the end of the magnet pointing towards the geographical south is called south-seeking pole or simply south pole.
Law of Magnetic Poles:
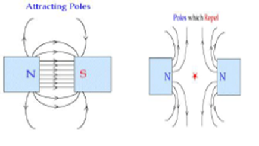
Like poles of magnets repel each other and unlike poles attract each other.
Pair Property:
When we cut a magnet into two parts two new magnets are formed. Thus it is impossible to separate the poles of a magnet. Isolated magnetic poles do not exist. i.e. magnetic poles always exist in pairs. Hence the magnets have to be necessarily regarded as dipoles.

Sure Test of Magnetization:
Repulsion is a sure test of attraction because an iron rod is always attracted towards the magnet and unlike poles always attract. Thus if a given rod is repelled we can definitely say that the rod is magnetized.
Types of Magnets:
Bar Magnet:

A bar magnet is a rectangular parallelepiped body which exhibits magnetic properties. Actually, the poles are not at the ends of the geometric length of the magnet but they are slightly inside.

- The length of the edge parallel to the magnetic axis is called the geometric length of the bar magnet.
- The line joining the poles of the bar magnet to called an axis of the magnet.
- The distance between the poles of the bar magnet is called magnetic length.
- Magnetic length of bar magnet × 1.2 = Geometric length of the bar magnet.
- A vertical plane passing through the magnetic axis of the freely suspended magnet is called magnetic meridian.
- A vertical plane passing through the magnetic equator of the freely suspended magnet is called equatorial meridian.
Magnetic Needle:
It is a magnet tapered towards both ends and pivoted at the centre.

It is used to check the direction of the magnetic field and to map magnetic lines of force of other magnets.
Horse Shoe Magnet:
It is in the shape of a horseshoe. This magnet is usually more powerful than a bar magnet. As both the poles of horseshoe magnet face each other, the attractive power is doubled.

The two poles can be made closer than any other type, hence these magnets can be used when a strong magnetic field is required in a small space. They are used in electronic valves of RADAR, electric motors, electric generators and moving coil galvanometers.
Disc Magnet:
It is in the shape of a disc.

Its poles are located each on its circular faces. i.e. if one face is acting as a north pole, other face will act as a south pole.
Magnetic Keepers:
If two magnets are placed side by side there will be mutual repulsion or attraction. This weakens the strength of the magnet. Similarly, a magnet is kept for a long time it loses its magnetic property. It is due to self-inductance and due to Earth’s magnetic field. To prevent this, bar magnets are placed side by side with opposite poles near. A soft iron piece called a keeper is placed across the poles as shown in the figure.

The magnet induces opposite polarity at the ends of the keeper. Thus this soft iron piece provides a path for the magnetic field lines to form a continuous loop. Thus it helps in preserving the magnetic field.
Advantages of Artificial Magnets:
- Artificial magnets can be made up of different (convenient) shapes and sizes.
- Artificial magnets can be made of different strengths.
- Strong magnetism can be obtained by artificial magnets only.
Uses of Magnets:
- Its directive property is used to construct magnetic needles and mariner’s compass.
- Permanent magnets are used in dynamos, electric motors, generators, electrical accelerators, door locks.
- Electromagnets are widely used in electric bells, electric cranes, tape recorders and speakers.
- Magnets are used in separating iron particles from solid mixtures using the method of magnetic separation.
- It is used in pin holder to stock pins and makes easy to pick them when required.
- They are used as a magnetic lock to keep shutters of doors and cupboards to shut tightly.
Magnetic Compass OR Mariner’s Compass:

A magnetic compass consists of a small magnetic needle pivoted at the centre of a small brass box which has a glass top. Generally, the north end is painted in red.
It works on the principle that when a magnet is free to rotate about a transverse axis then under the action of Earth’s magnetic field, the needle aligns itself in North-South direction. Thus using Compass the North and South direction can be located and thus other directions can be obtained.
Uses of the magnetic compass are.
- To decide North-South directions.
- To find the direction of the magnetic field at a place.
- To plot or draw magnetic lines of force
- To test the polarity of a magnet.
- It is very useful for travellers, mariners a, d navigators to find direction when they sail through the unknown location.
Pin Holder:

Pin holder is used on writing tables to hold pins. It consists of a thin round magnet fitted at its mouth. When the pin holder is turned upside down, the pins at the bottom of the holder stick to the inside of the mouth of the holder. Now they can be easily picked out and be used.
Magnetic Locks for Shutters of Cupboards:

The magnetic lock is fitted on the frame of the cupboard, while a thin iron strip is fixed on the shutter, exactly opposite to the magnetic lock.
When the shutter is brought near the frame, the magnetic attraction between the iron strip and magnet click shut the shutter tightly to the frame.
Next Topic: Properties of Magnet

One reply on “Magnets”
Ah think I got all information that I required for my science project