Science > Physics > Motion in a Straight Line > Motion in a Straight Line True and False Questions
In last few articles, we have seen the concept of a motion in a straight line. From this article we shall apply the concept. In this article we shall study true and false type questions based on a motion in a straight line.
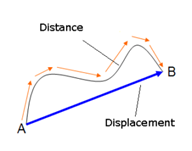
State whether the following statements are true or false. If false correct the statement.
- The travel of a train from one station to another is an example of translatory motion.
True
In translational motion every particle of the body has the same displacement.
- Motion of an ant along one of the edge of table is translatory motion.
True
In translational motion every particle of the body has the same displacement.
- The magnitude of displacement can be equal to or lesser than the distance travelled.
True
The shortest distance from the initial position to the final position of the body is called the magnitude of the displacement. Thus in case of body moving in a straight line in the same direction, the maximum displacement can be equal to the distance travelled. In all other case, it will be less than the distance travelled.
- Ddistance covered by a moving body is always greater than zero.
True.
- Displacement of a particle can be less than or greater than or equal to zero.
True
- Uniform speed is a vector quantity
False
Correction: Speed is a scalar quantity
Speed = distance / time, in this formula, both the dstance travelled and time are scalar quantities, hence speed is a scalar quantity.
- A particle moving with a uniform velocity must be along a straight line.
True.
Since velocity is a vector quantity it has both the magnitude and direction and if direction changes it is not uniform velocity. In case of circular motion there is a continuous change in direction leading to accelarated motion which results in non uniform velocity.
- A body can have a constant speed and still have varying velocity.
True.
In a uniform circular motion, the speed of the body is constant but due to continuous change in direction, the velocity is varying. A body can not have its velocity constant, while its speed varies.
- The magnitude of average velocity is always equal to the average speed.
False.
Correction: The magnitude of average velocity ned not be equal to the average speed.
In a uniform circular motion, the speed of the body is constant but due to continuous change in direction, the velocity is varying. The magnitude of the average velocity of an object is equal to its average speed, only in one condition when an object is moving in a straight line.
- Average velocity can be calculated by taking the average of initial and final velocities for a given time interval irrespective of the type of acceleration.
True
- For a body moving along a circular path, the average velocity and average speed can never be equal.
True.
In a uniform circular motion, the speed of the body is constant but due to continuous change in direction, the velocity is varying. Thus in case of uniform ciercular motion, average speed is constant and equal to the magnitude of the instantaneous velocity of the body, but average velocity is zero.
- Average velocity can be zero, but average speed of a moving body can not be zero in any finite time interval.
True
uniform ciercular motion, average speed is constant and equal to the magnitude of the instantaneous velocity of the body, but average velocity is zero.
- If a body moves with constant velocity, its displacement depends on depends on square of time
False
Correction: If a body moves with constant velocity, its displacement depends on depends on time
v = ds/dt = k = constant
Integrating both sides with time t
s = kt
Thus displacement varies directly with time (t)
- A particle speed is constant, acceleration of the particle must be zero.
False
Correction: A particle speed is constant, acceleration of the particle need not be zero.
In a uniform circular motion, the speed of the body is constant but due to continuous change in direction, the velocity is varying. Thus particle possesses acceleration.
- When a particle moves with a constant speed in the same direction, neither the magnitude nor the direction of velocity changes and so acceleration is zero.
True
Since velocity is a vector quantity it has both the magnitude and direction. In this case both the speed and direction are the same. Hence the particle is moving with a constant velocity and has zero acceleration.
- A particle is known to be at rest at time t = 0. If its acceleration at t = 0 is zero.
False
Correction: A particle is known to be at rest at time t = 0. If its velocity at t = 0 is zero.
A body is said to be at rest if it does not change its position with respect to its immediate surroundings. Thus the velocity of the body decides its state of motion.
- An object covers distances in direct proportion to the square of the time elapsed. Its acceleration is increasing.
False
An object covers distances in direct proportion to the square of the time elapsed. Its acceleration is constant
s = kt2 (given)
Differentiating both sides w.r.t. time t
velocity = v = ds/dt = 2kt
Differentiating both sides again w.r.t. time t
acceleration = a = dv/dt = 2k = constant
Thus in this case acceleration is constant. i.e. the object is moving with constant acceleration.
- A particle in one-dimensional motion with a positive value of acceleration must be speeding up.
False
A particle in one-dimensional motion with a positive value of acceleration may or may not be speeding up.
If the initial velocity of a body is negative then even in case of positive acceleration, the body speeds down.
- There can be a motion in which speed is constant but velocity is variable.
True
In uniform circular motion, speed is constant but velocity is variable.
- A body moves with retardation when it is projected vertically upward.
True
Every body on the earth surface is acted upon by gravitational force acting in downward direction. When a body is projected vertically upward, due to the action of the gravitational force, its velocity goes on decreasing. Thus the body moves with retardation. at the highest point of its journey its velocity is zero.
- A body is projected vertically up. On reaching maximum height, its velocity becomes zero.
True
Every body on the earth surface is acted upon by gravitational force acting in downward direction. When a body is projected vertically upward, due to the action of the gravitational force, its velocity goes on decreasing. Thus the body moves with retardation. at the highest point of its journey its velocity is zero.
- A stone dropped from a height moves with constant velocity
False
Correction: A stone dropped from a height moves with constant acceleration.
When the body falls freely under gravity, the acceleration produced in the body due to the gravitational force of attraction of the earth, then the acceleration by which the body falls down is called the acceleration of gravity.
- When two balls of different masses are thrown vertically upwards with the same initial speed, the heavier body rises to greater height then the lighter body.
False
Correction: When two balls of different masses are thrown vertically upwards with the same initial speed, both the bodies will rise to the same maximum height.
When the body falls freely under gravity, the acceleration produced in the body due to the gravitational force of attraction of the earth, then the acceleration by which the body falls down is called the acceleration of gravity. The height reached by the body epends on the initial speed by which they are thrown ipwards and the acceleration due to gravity at that place. Both the bodies will be acted upon by the same acceleration due to gravity and they are projected with same initial speed. hence both the bodies will rise to the same height.
- The distance travelled by a freely falling body in every successive second is the same.
False:
Correction: The distance travelled by a freely falling body in every successive second increases.
When the body falls freely under gravity, the acceleration produced in the body due to the gravitational force of attraction of the earth, then the acceleration by which the body falls down is called the acceleration of gravity. Thus freely falling body moves with acceleration due to gravity in downward direction i.e. in the direction of motion, hence its speed increases continuously and thus it covers more distance in every successice second.
- The area under the velocity-time diagram shows the displacement of the body
True
- Velocity-time graph cannot be used to find the instantaneous velocity
False
Correction: Velocity-time graph can be used to find the instantaneous velocity
- Velocity-time graph can be used to find displacement of the body.
True
The area under the velocity-time diagram shows the displacement of the body
- Equations of motion are applicable only when a body moves with uniform velocity.
False
Correction: Equations of motion are applicable only when a body moves with uniform acceleration.
- Direction of motion is decided by the displacement of a body.
False
Direction of motion is decided by the velocity of a body. Positive value of velocity indicates body is moving in the direction of the displacement while neghative value of velocity indicates the body is moving in the opposite direction to that of displacement.