Science > Physics > Introduction to Measurements > Other Important Units
The quantity to be measured may be very large so that the SI unit of that quantity may be smaller to use or the quantity to be measured is so small that the SI unit of that quantity is very large to use. Hence other units were defined. Many of them are used with SI system of units. Examples: Light year is used to measure the distance between stars. unit fermi is used for measuring size of the nucleus of an atom. The radius of orbit of electrons in atom is measured in angstrom, etc.
- 1 fermi or femtometer (F) = 10-15 m
- 1 angstrom (A0) = 10-10 m
- 1 micron or micrometre = 10-6 m
- 1 X-ray unit = 10-13 m
Measuring Distances and Sizes:
- Lightyear: It is defined as a distance travelled by light in a vacuum in one year. 1 light year = 9.46 x 1015 m
- One astronomical unit: It is a mean distance between the sun and the earth. 1 AU or 1 astronomical unit = 1.496 x 1011 m
- 1 parsec: It is the distance at which an arc of length one astronomical unit subtends an angle of 1 second of an arc. 1 parsec or parallactic second = 3.086 x 1016 m
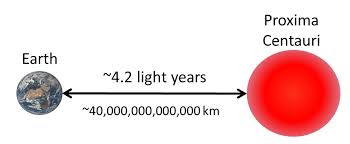
Note that light-year (ly) and parsec (pc) are units of distances and not of time. A light-year (ly), parsec (pc) are used to measure the distance between stars and the astronomical unit is used to measure the distance between planets.
Measuring Masses:
- One a.m.u.: It is defined as 1/12 th of the mass of one atom. 1 a.m.u. = 1.66 x 10-27 kg.
- Chandra Shekhar unit is practical unit of measuring large masses. 1 chandrashekhar unit = 1.4 times mass of the Sun.
- Mass is measured in slug, metric ton, quintal. 1 slug = 14.57 kg, 1 metric ton = 1000 kg, 1 quintal = 100 kg.
Measuring Small Areas:
- Extremely small areas are measured in barn. 1 barn = 10-28 m2
Measuring Small Time:
- shake is used to measure very small time. 1 shake = 10-8 s
Units outside SI but Frequently Used in Physics:
| Name | Symbol | Value in SI units |
| minute (time) | min | 1 min = 60 s |
| hour | h | 1 h = 60 min = 3600 s |
| day | d | 1 d = 24 h = 86 400 s |
| degree (angle) | ° | 1° = ( π/180) rad |
| minute (angle) | ‘ | 1′ = (1/60)° = (π/10 800) rad |
| second (angle) | ” | 1”= (1/60)’= (π/648 000) rad |
| liter | L | 1 L = 1 dm3 = 10-3 m3 |
| metric ton | t | 1 t = 103 kg |
| neper | Np | 1 Np = 1 |
| bel | B | 1 B = (1/2) ln 10 Np (c) |
| unified atomic mass unit | u | 1 u = 1.660 54 x 10-27 kg, approximately |
| astronomical unit | ua | 1 ua = 1.495 98 x 1011 m, approximately |
| astronomical unit | ua | 1 ua = 1.495 98 x 1011 m, approximately |
Units Currently Accepted for Use with the SI System:
| Name | Symbol | Value in SI units |
| nautical mile | 1 nautical mile = 1852 m | |
| knot | 1 nautical mile per hour = (1852/3600) m/s | |
| are | a | 1 a = 1 dam2 = 102 m2 |
| hectare | ha | 1 ha = 1 hm2 = 104 m2 |
| bar | bar | 1 bar = 0.1 MPa = 100 kPa = 1000 hPa = 105 Pa |
| angstrom | Å | 1 Å = 0.1 nm = 10-10 m |
| barn | b | 1 b = 100 fm2 = 10-28 m2 |
| curie | Ci | 1 Ci = 3.7 x 1010 Bq |
| roentgen | R | 1 R = 2.58 x 10-4 C/kg |
| rad | rad | 1 rad = 1 cGy = 10-2 Gy |
| electron volt | eV | 1 eV = 1.602 18 x 10-19 J, approximately |
Calculation of number of kilometers in 20 miles:
Conversion factors a mile = 5280 ft, 1 ft = 12 in, 1 in = 2.54 cm, 1 m = 100 cm, 1 km = 1000 m.
20 miles = 20 × 5280 ft = 20 × 5280 × 12 inches
20 miles = 20 × 5280 × 12 × 2.54 cm
20 miles = 20 × 5280 × 12 × 2.54 ÷ 100 m
20 miles 20 × 5280 × 12 × 2.54 ÷ 100 ÷ 1000 km = 32.197 km
Calculation of the number of light years in one metre:
1 light year = distance travelled by light in one year
1 light year = 299, 792, 458 × 60 × 60 × 24 × 365 m
1 light year =9.46 × 1015 m
∴ 1 m = 1/(9.46 × 1015 ) light year
∴ 1 m = 1.057 × 10-16 light year
Expression of 1 parsec in terms of light year:
1 parsec = 3.086 × 1016 m
∴ 1 parsec = 3.086 × 1016 × 1.057 × 10-16 light year = 3.262 lightyears
The mass of an electron is 9.1 x 10-31 kg. How many electrons would make 1 kg?
mass of electron = 9.1 x 10-31 kg
∴ the number of electrons in 1 kg = 1/ (9.1 x 10-31) = 1.099 x 1030
The mass of an electron is 9.1 x 10-31 kg. How many electrons would make 1 g?
mass of electron = 9.1 x 10-31 kg = 9.1 x 10-28 g
∴ the number of electrons in 1 g = 1/ (9.1 x 10-28) = 1.099 x 1027
The mass of a proton is 1.67 x 10-27 kg. How many protons would make 1 g?
mass of proton = 1.67 x 10-27 kg = 1.67 x 10-24 g
∴ the number of protons in 1 g = 1/ (1.67 x 10-24) = 5.99 x 1023
Express the distance between the sun and earth in parsec and light year.
Distance between the sun and the earth = 1.5 x 1011 m
Distance between the sun and the earth = (1.5 x 1011 m) ÷ (3.086 × 1016 ) = 4.861 × 10-6 parsec
Distance between the sun and the earth = 1.5 x 1011 × 1.057 × 10-16 light year = 1586 × 10-5 light year
Derive the S.I. unit of joule (J) in terms of fundamental units.
Joule is the unit of work
Work = Force × Displacement = mass × acceleration × displacement
∴ 1 J = kg × ms-2 × m
∴ 1 J = kg m2s-2
A new unit of length is chosen such that the speed of light in a vacuum is unity. What is the distance between the sun and the earth in terms of a new unit if it takes 8 minutes and 20 seconds to cover the distance
Time taken by light = 8 min and 20 seconds = 8 × 60 + 20 = 480 + 20 = 500 seconds
Now 1 second of light corresponds to 1 new unit
Hence 500 seconds corresponds to 500 new units.
Hence the distance between the sun and the earth is 500 new units.
If x = a + bt + ct2, where x is in metres and t is in seconds. Find units of a, b and c.
Physical quantities can only be added if they have the same unit.
Now, the unit of L.H.S. = The unit of R.H.S.
Hence unit of a, bt and ct2 is metre
Hence unit of a is metre
Unit of b × s = m
∴ Unit of b = m/s
Unit of c × s2 = m
Unit of c = m/s2
Related Topics:
- 1.2.1 Introduction to Measurements
- 1.2.2 Meassurement of Length, Area and Volume
- 1.2.3 Measurement of Mass, Weight, and Density
- 1.2.4 Measurement of Time
- 1.2.5 Dimensional Analysis
- 1.2.6 Error Analysis