Science > Physics > Current Electricity > Temperature Dependence of Resistance
In this article, we shall study the effect of temperature on the value of resistance and thermistors and their uses.
A metallic conductor consists of a large number of free electrons. These electrons are always in a state of random motion. When a potential difference is applied across the ends of the conductor. These free electrons start moving in the definite direction i.e. towards the positive end of the conductor. During this process, the electrons flow through the crowd of vibrating atoms. These electrons collide with the atoms. Thus vibrating atoms offer obstruction to the flow of electrons. This obstruction to the flow of electrons is called the resistance of the conductor.
If the temperature of the conductor is increased, the kinetic energy of vibrating atoms is increased, due to which the atoms start vibrating with higher amplitude. Thus the obstruction to the flow of electrons increases and hence the resistance of the conductor also increases.
Expression for Temperature Coefficient of Resistance:
Let Ro be the initial resistance at 0° C. Let R be the resistance at t° C.
∴ Change in resistance = R – Ro
∴ Change in temperature (Δt) = t2 – t1
Experimentally it is found that the change in resistance is directly proportional to
- the original resistance.
- to change in temperature.
R – Ro ∝ Ro ——— (1)
R – Ro ∝ t2 – t1 ——— (2)
From (1) & (2)
R – Ro ∝ Ro (t2 – t1)
R – Ro = α Ro (t2 – t1)
Where α is constant called temperature coefficient of resistance.
But t2 – t1 = Δ t
R – Ro = α Ro Δ t ……….. (3)
R = Ro + α Ro Δ t
R = Ro (1 + α Δ t)
This is an expression which gives the value of resistance at the new temperature.
From equation (3), we have
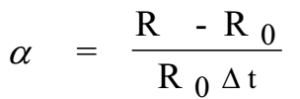
This is an expression for the temperature coefficient of the resistance of a material of a conductor.
Temperature Coefficient of Resistance:
Temperature coefficient of resistance is defined as the change in resistance per unit resistance at 0° C per degree rise in temperature
Notes:
For good conductors value of temperature coefficient of resistance is positive hence the value of resistance increases as temperature increases and the value of resistance decreases if its temperature decreases
For semiconductors value of temperature coefficient of resistance has a negative value. Hence the value of resistance decreases as temperature increases and the value of resistance decreases if its temperature increases.
Thermistors:
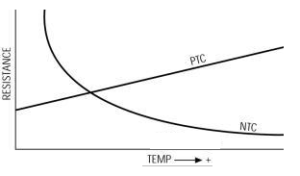
A thermistor is a special case of a semiconductor having a large negative temperature coefficient of resistance. Thermistors are also called as temperature-sensitive resistance. As they have a large negative value of alpha the value of resistance decreases very fast, as the temperature increases. Thermistors are very sensitive.
Thermistors are made up of oxides of copper, manganese, nickel, cobalt, iron, lithium, etc. These oxides are mixed and are powdered. After this, they are given the desired shape and are heated to very high temperatures. Thus ceramic thermistors are formed. Thermistors are used in the temperature controlling devices or as temperature sensors.
Previous Topic: Introduction to Current Electricity
Next Topic: Kirchhoff’s Laws of Current Electricity