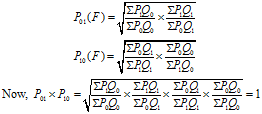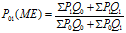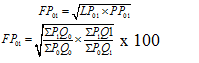Several formulae have been suggested for constructing index numbers and the problem is that of selecting the most appropriate one in a given situation. The different tests are the unit test, time reversal test, factor reversal test, and circular test. Unit Test: This test states that the formula for constructing an index number should be […]
Tests for Adequacy of Index Number