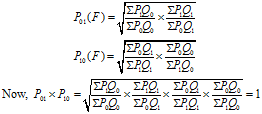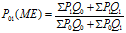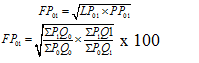Science > Biology > Human Population and Population Control > Natural Methods of Contraception Birth control also known as contraception is the use of various devices, drugs, agents, sexual practices, or surgical procedures to prevent conception or pregnancy. It enables people to choose when they want to have a baby. Contraception may be a temporary […]
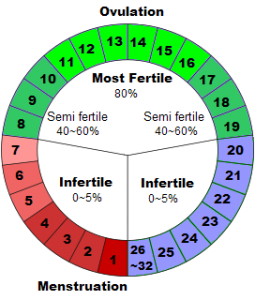
Natural Methods of Contraception