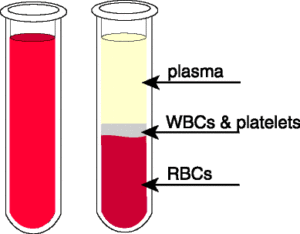
Science > Biology > Human Anatomy and Physiology > Cardiovascular System > Composition of Blood: Erythrocytes When a human blood sample is prevented from clotting and spun in a test tube (centrifuged), in a machine called a centrifuge, the blood separates into a straw coloured liquid called plasma and a dark brown mass of blood […]
Erythrocytes