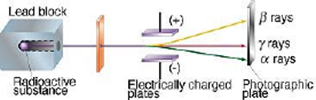
Science > Physics > Nuclear Physics > Natural Radioactivity Radioactivity was discovered by French physicist Antoine Becquerel in 1896. He found that certain compounds of uranium emitted invisible radiations which affected photographic plates. It is also found that Thorium and its compounds also show these properties. Madame Curie and Piere Curie discovered two elements namely […]
Natural Radioactivity