Science > Chemistry > Atomic Structure > Problems Based on Atomic Number, Mass Number, and Neutron Number In this article, we shall study to solve problems based on the calculation of atomic number, atomic mass number, and neutron number Atomic number (Z) : The number of protons (positive charge) present in the nucleus of an […]
Tag: Atomic number
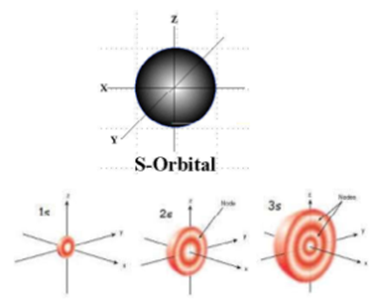
Science > Chemistry > Atomic Structure > Quantum Numbers and Quantum Model of an Atom In this article, we shall study the concept of quantum numbers and the model of an atom based on the quantum numbers. Concept of Quantum Numbers: In 1926, Erwin Schrodinger put forward a theory of atom called as a quantum […]
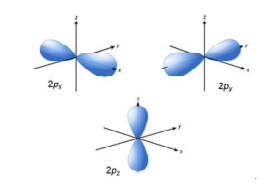
Science > Chemistry > Atomic Structure > Quantum Numbers and Shapes of Orbitals In this article, we shall study the concept of quantum numbers and different types of orbitals and their shapes. Difference Between Shell, Subshell, and Orbital: All electrons that have the same value for n (the principal quantum number) are in the same […]
Electronic Configuration
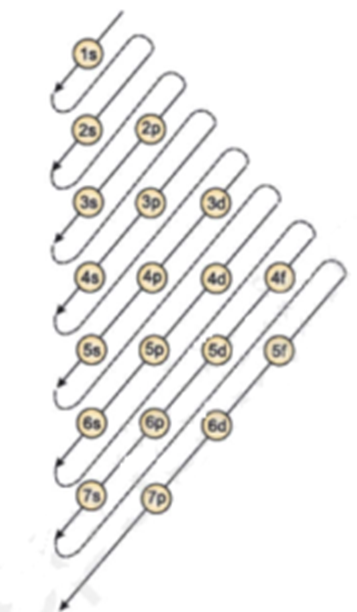
Science > Chemistry > Atomic Structure > Electronic Configuration The distribution of electrons in various shells and orbitals of an atom is known as electronic configuration. Generally electronic configuration is given by nlx. Where n is shell number, l is subshell and x are the number of electrons. Aufbau Principle: The arrangement of the electrons […]
Rutherford’s Atomic Model

Science > Chemistry > Atomic Structure > Rutherford’s Atomic Model In this article, we shall study Thomson’s model of an atom and its deficiencies and Rutherford’s atomic model and its deficiencies. Thomson’s Model of an Atom: J. J. Thomson, in 1898, proposed that an atom possesses a spherical shape (radius approximately 10–10 m) in which the positive charge […]

Science > Chemistry > Atomic Structure > Discovery of Proton and Neutron In last article, we have discussed, the discovery of electron and characteristics of electron. In this article, we shall discuss the discovery of proton and neutron and their characteristics. Discovery of Proton: Proton was discovered by E. Goldstein in 1886. He performed the […]
Discovery of Electron

Science > Chemistry > Atomic Structure > Discovery of Electron In this article, we shall study earlier concepts of an atom, discovery of electron, and its characteristics. 600 B.C. Indian saint and philosopher Maharshi Kanad proposed that matter is made up of the smallest individual particles. He called these particles ‘paramanu’. Around 400 B.C. The […]
Radioactivity

Science > Chemistry > Atomic Structure > Radioactivity Radioactivity was discovered by French physicist Antoine Becquerel in 1896. The phenomenon of spontaneous and continuous and uncontrollable disintegration of an unstable nucleus accompanied by the emission of active radiations is called natural radioactivity. The substance which exhibits radioactivity is called a radioactive substance. e.g. Uranium, thorium, […]

Science > Chemistry > Physical Chemistry > Nature of Chemical Bond > Formation of Covalent Bonds In previous articles, we have seen formation of ionic bonds. In this article, we shall study the concept of the formation of a covalent bond. Covalent Bonds or Electron Pair Bonds: A bond established between two identical or different atoms […]

Science > Chemistry > Physical Chemistry > Nature of Chemical Bond > Properties of Ionic Compounds In this article, we shall study the properties of ionic compounds. Physical State: Due to strong electrostatic force present between the oppositely charged ions, they are held closer and fixed at specified positions in the crystal lattice. Hence ionic […]