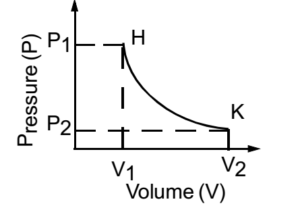
Science > Physics > Themodynamics > Introduction In this article, we shall study the concept of thermodynamics and thermodynamic state. Thermodynamics is a branch of physics that deals with the inter-conversion between heat energy and any other form of energy. Thermodynamic State: The simplest example of a system to which thermodynamics can be applied is […]
Introduction to Thermodynamics