Carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and other “greenhouse gases” trap heat that would otherwise escape Earth’s atmosphere. In the right proportion, these gases do a critical job ensuring the atmosphere holds onto enough heat to support every kind of life on the planet. Without them, the Earth would lose so much heat that life as we know it would be impossible.
The problem arises when greenhouse gas levels get too high because of human activities, trapping too much of the sun’s energy as heat and upset the natural systems that regulate our climate. Things keep getting hotter and hotter and we start seeing more and more extreme weather and other impacts.
Industrial compounds known as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are mainly responsible for greenhouse effect.
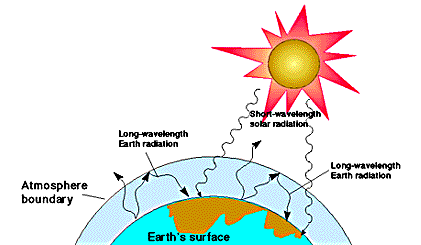
The greenhouse effect refers to the phenomenon by which the earth’s atmosphere traps infrared radiation or heat. Gases that causes the greenhouse effect are for the most part natural compounds—water vapour, CO2, methane and nitrous oxide that keep the earth habitable. But human activity is increasing the concentration of these and other gases, for example, the industrial compounds known as chlorofluorocarbons(CFCs). The trend, if continues, is expected by atmospheric scientists to lead to global climate change with uncertain but potentially grave long-term effects.
Greenhouse Gases:
Carbon dioxide (CO2):
Carbon dioxide enters the atmosphere through burning fossil fuels (coal, natural gas, and oil), solid waste, trees and other biological materials. It is certain chemical reactions (e.g., manufacture of cement). Carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere by plants as part of the biological carbon cycle during photosynthesis.
Methane (CH4):
Methane is emitted during the production and transport of coal, natural gas, and oil. Methane emissions also result from livestock and other agricultural practices and by the decay of organic waste in municipal solid waste landfills.
Nitrous oxide (N2O):
Nitrous oxide is emitted during agricultural and industrial activities, combustion of fossil fuels and solid waste, as well as during treatment of wastewater.
Fluorinated gases:
Hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons, sulfur hexafluoride, and nitrogen trifluoride are synthetic, powerful greenhouse gases that are emitted from a variety of industrial processes. These gases are typically emitted in smaller quantities, but because they are potent greenhouse gases, they are sometimes referred to as High Global Warming Potential gases (“High GWP gases”).
Each of these gases can remain in the atmosphere for different amounts of time, ranging from a few years to thousands of years. .
Greenhouse effect is main cause of global warming.