Karl Landsteiner in 1900 discovered that blood in all persons is not alike and hence clumping or agglutination occurs on the mixing of blood of certain persons. Blood group is determined by the antigens present on the surface of RBC’s. An antigen is a molecule (in this case a carbohydrate) that acts as a signal, enabling the body to recognize foreign substances in the body.
Human blood is classified into 4 main groups: A, B, AB and O. Each can be either Rhesus + ve or Rhesus – ve, giving 8 groups in all. Blood grouping is the identification of the antigens in a blood sample. This system is called the ABO system.
The ABO system is based on the A and B antigens. It classifies blood by the antigens on the surface of the RBCs and the antibodies circulating in the plasma. An individual RBC may carry an ‘A’ antigen, a ‘B’ antigen, both ‘A’ and ‘B’ antigens, or no antigen at all. These antigen patterns are called blood types A, B, AB, and O, respectively.
| Blood Group | Antigen |
|---|---|
| A | Has only A antigen on red cells (and B antibody in the plasma) |
| B | Has only B antigen on red cells (and A antibody in the plasma) |
| AB | Has both A and B antigens on red cells (but neither A nor B antibody in the plasma) |
| O | Has neither A nor B antigens on red cells (but both A and B antibody are in the plasma) |
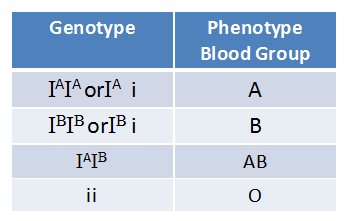
Genetic Basis of Blood Groups:
- The gene I control ABO blood groups it has three alleles; IA , IB and i.
- The allele IA and IB produce slightly different types of sugar and allele i does not produce any sugar.
- As humans are diploid organisms each person possesses any two of the three I genes.
- IA and IB are co-dominant and completely dominant on i.
Blood Group of Children:

Donating Blood by Compatible Type:
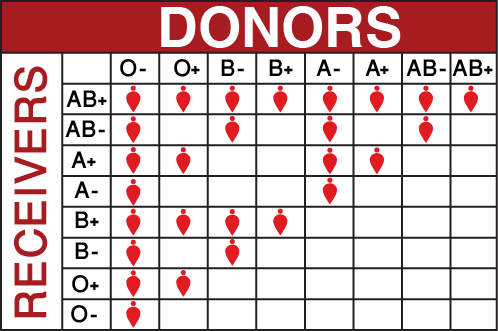
Blood types are very important when a blood transfusion is necessary. In a blood transfusion, a patient must receive a blood type compatible with his or her own blood type. If the blood types are not compatible, red blood cells will clump together, making clots that can block blood vessels and cause death. Therefore, it is important that blood types be matched before blood transfusions take place. In an emergency, type O blood can be given because it is most likely to be accepted by all blood types. However, there is still risk involved.
Type AB is known as a universal recipient, meaning that they can receive any type of blood, while O is the universal donor, meaning they can donate blood to anyone. The universal red cell donor has Type O negative blood type. The universal plasma donor has Type AB positive blood type.
Rhesus System:
An antigen that is sometimes on the surface of RBC is the Rh factor named after the Rhesus monkey in which it was first discovered. If this factor is present then the blood is Rh + ve, and if it is absent the blood is Rh – ve.
If an Rh – ve person receives a transfusion of blood that has Rh + ve antigens, anti-Rh + ve antibodies will be formed and will react with the Rh + ve antigen and agglutination (clumping i.e. The antibody or other molecule binds multiple particles and joins them, creating a large complex) will occur.
Seriousness of Rhesus System:

The most serious problem with Rh incompatibility occurs during pregnancy. If the mother is Rh – and the father is Rh+, the child may inherit the dominant Rh+ allele (gene) from the father. The baby’s Rh+ blood will then get into the mother’s blood during delivery, causing her to develop antibodies to the Rh factor.
If a second Rh+ child is later conceived, the mother’s antibodies will cross the placenta and attack the blood of the foetus, causing a condition known as rhesus baby syndrome. The symptoms include damaged liver and so fewer RBCs, less developed brain (due to lack of oxygen) and skin.
To prevent this, any Rh mother will automatically be given an injection of anti-Rh+ antibodies (known, confusingly, as anti-D) at childbirth. These antibodies attack and destroy all Rh+ antigens in the mother’s blood, thus preventing her from becoming sensitized to the Rh+ antigen.
This tricks her body into believing she has not had an Rh +ve child, and so the next pregnancy will be protected from attack since she will have no antibodies to Rh +ve blood
Health Benefits Of Donating Blood
Blood donation is a voluntary procedure. You agree to have blood drawn so that it can be given to someone who needs a blood transfusion. Millions of people need blood transfusions each year. Some may need blood during surgery.
Hemochromatosis
It reduces the risk of hemochromatosis. Hemochromatosis is a health condition that arises due to excess absorption of iron by the body. This may be inherited or may be caused due to alcoholism, anemia or other disorders. Regular blood donation may help in reducing iron overload.
Anti-cancer benefits
Blood donation may also help in lowering the risk of cancer. By donating blood the iron stores in the body are maintained at healthy levels. And the reduction in iron levels in the body is linked with low cancer risk.
Healthy heart and liver
Blood donation is beneficial in reducing the risk of heart and liver ailments caused by iron overload in the body. Intake of iron-rich diet may increase the iron levels in the body and since only limited proportions can be absorbed excess iron gets stored in the heart, liver, and pancreas. This, in turn, increases the risk of cirrhosis, liver failure, damage to the pancreas, and heart abnormalities like irregular heart rhythms. Blood donation helps in maintaining iron levels and reduces the risk of various health ailments.
Weight Loss:
Regular blood donation reduces the weight of the donors. This is helpful to those who are obese and are at higher risk of cardiovascular diseases and other health disorders. However, blood donation should not be very frequent and you may consult your doctor before donating blood to avoid any health issues.
New Blood Cells
After donating blood, the body works to replenish the blood loss. This stimulates the production of new blood cells and in turn, helps in maintaining good health.