Science > Biology > Human Population and Population Control > Intrauterine Devices (IUDs)
The Intrauterine Devices are ideal contraceptives for females. IUD is a tiny device that is put into the uterus by the health service provider to prevent pregnancy. It is long-term, reversible, and one of the most effective birth control methods available. These devices are made up of plastics or metal or a combination of the two. These are called lops, spirals, rings, bows, shields, Copper Ts. Depending upon shapes IUDs are of three types. They are used for temporary avoidance of pregnancy.
Inert Intrauterine Devices:
Inert IUDs do not have a bioactive component. These devices are made of plastic or stainless steel only. Lippes loop made of plastic (polyethylene) impregnated with barium sulphate is still used in many parts of the world. Stainless steel rings are widely used in China only. They are less effective than copper or hormonal IUDs, with a side effect profile similar to copper IUDs. Inert IUDs mainly work by changing the intra-uterine environment and making it spermicidal. Non-medicated IUD causes a sterile inflammatory response by producing a tissue injury of minor degree but sufficient enough to be spermicidal. This primary mechanism of action induces a local foreign body reaction, which makes the uterine environment hostile both to sperm and to implantation of an embryo.

They work on the following principles:
- There is impairment of sperm ascent.
- There is a quick tubal motility resulting in premature migration of fertilized egg into the uterus before it is ready for receiving the egg.
- Histological and biochemical changes have spermicidal effect.
Copper Ts ( Copper Releasing Intrauterine Devices):
It is a non-hormonal IUD consisting of a small piece of flexible plastic shaped like a T that has copper wrapped around it. Hence it is also called the copper IUD. They include CuT, Multiload 375 and CuT 360. Copper Ts have ionized copper which slowly diffuses at the rate of 50 micrograms per day. Free copper and copper salts that have both a biochemical and morphological impact on the endometrium and also produce alteration in cervical mucus and endometrial secretions. Sperm doesn’t like copper. it changes the way sperm cells move so they can’t swim to an egg. Thus the motility and fertilizing capacity of the sperm is suppressed. These devices should be replaced after 3 to 5 years when the rate of copper diffusion decreases. CuT 380 has a replacement period of 7-10 years. Copper Ts should be placed by health practitioners only.
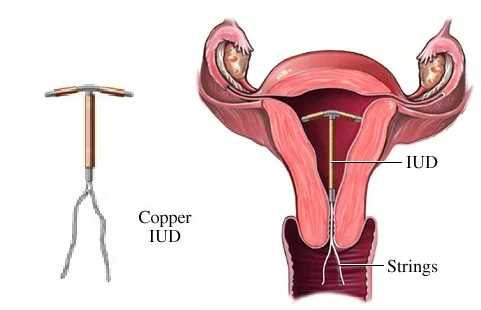
Available Copper Ts:
- CuT 380A: It is a T shaped device with a polyethylene frame holding 380 mm2 of the exposed surface area of copper. The IUD frame contains barium sulfate thus making it radio-opaque.
- CuT-380Ag: It is identical to 380 A except that the copper wire on the stem has a silver core to prevent fragmentation and extend the life span of the copper.
- CuT 380 slimline: It has copper sleeves flushed at the ends of horizontal arms to facilitate easier loading and insertion. The performance of CuT-380 Ag and the CuT-380 slimline is equal to that of CuT-380 A.
- Multiload 375: It has 375 mm2 of copper wire wound around its stem. The flexible arms are designed to minimize expulsions. The multiload 375 and T Cu-380 A are similar in their efficacy and performance.
- Nova T: It is similar to the CuT-200, containing 200 mm2 of copper. However, the Nova T has a silver core to the copper wire, flexible arms, and a large flexible loop at the bottom to prevent cervical perforation.
The copper IUD is good at preventing pregnancy and is totally hormone free. So it’s a good option for people who prefer non-hormonal birth control or can’t use methods with hormones due to medical reasons.
Remedy Against Unprotected Sex:
To prevent pregnancy after unprotected sex if the Copper T is inserted within 120 hours (5 days), then in more than 99.99% cases it prevents pregnancy.
Side Effects of Copper Ts:
The side effects include Pain when the IUD is placed, and cramping or back aches for a few days after, spotting between periods, irregular periods, heavier or longer periods, vaginal discharge, cramping during your periods, pain during sex.
Hormone Releasing Intrauterine Devices :
The hormonal IUD releases a small amount of the hormone progestin into the body over several years. Progestin released is very similar to the hormone progesterone that our bodies make naturally. The released progesterone effect on endometrium to the foreign body reaction. The endometrium becomes decidualized with atrophy of glands. The progesterone IUD does not increase the serum progesterone level and mainly acts by inhibition of implantation, sperm-capacitation and survival.
The hormones in the IUD prevent pregnancy in two ways:
- Hormonal IUDs make the mucus on your cervix thicker. This mucus blocks sperm so it can’t get to an egg.
- The hormones in the IUD can also stop eggs from leaving your ovaries (called ovulation), which means there’s no egg for a sperm to fertilize. They can also reduce or even prevent menstrual bleeding. As a result, they are used to treat menorrhagia i.e. heavy menses, once pathologic causes of menorrhagia (such as uterine polyps) have been ruled out.

Available Hormone Releasing IUDs :
- Progestasert: It is a T shaped IUD made of ethylene and vinyl acetate copolymer containing titanium dioxide. The vertical stem contains a reservoir of 38 mg progesterone together with barium sulfate dispersed in silicone fluid. The progesterone is released at the rate of 65 µg per day.
- LNG – 20 (Mirena): This T shape & device has a collar attached to a vertical arm containing 52 mg of levonorgestrel dispersed in poly dimethyl siloxane. It releases 15µg of levonorgestrel per day in vivo and is effective for 7-10 years. The LNG-20 IUD decreases the blood loss (by about 40-50%) and dysmenorrhoea. Levonorgestrel IUD produces serum concentrations of the progestin half those of Norplant and therefore, ovarian follicular development and ovulation is not inhibited.
Previous Topic: Barrier Methods of Contraception
Next Topic: Surgical Methods of Contraception