Science > Biology > Management of Crop Production > Irrigation
All living beings need water to live. Water is important for proper growth and development of flowers, fruits, and seeds of plants. Plants contain nearly 90% water.
Importance of Water for Plants
- Water is essential because germination of seeds does not take place under dry conditions.
- Water helps in some physiological processes like the process of photosynthesis by which plants prepare their food.
- Water is absorbed by the plant roots. Along with water, nutrients, minerals, and fertilizers required for the growth of the plant are also absorbed.
- Nutrients dissolved in the water get transported to each part of the plant.
- Water helps in the maintenance of the plant structure by providing the appropriate turgor pressure to the plant tissues.
- Water also protects the crop from both frost and hot air currents.
- Water provides habitat in the form of ponds, rivers, lakes, and sea for a large number of plants.
Irrigation:
Irrigation essentially means the watering of land to make it ready for agricultural purposes. To maintain the moisture of the soil for healthy crop growth, fields have to be watered regularly. The supply of water to crops at different intervals is called irrigation. The time and frequency of irrigation vary from crop to crop, soil to soil and season to season. In the summer, the frequency of watering is higher.
Importance of Irrigation in India:
- In India, most of the farmers depend on rain for farming. In India, the period of rain is restricted to only four months in a year, June to September, when the monsoon arrives. The remaining eight months are dry. Besides the nature of rain in India is uncertain and irregular. Sometimes it gets delayed. It causes uncertainty in agriculture and may result in drought conditions in large areas. Hence to overcome the uncertainty of the rain the irrigation is important in India.
- The productivity of irrigated land is considerably more than the productivity on un-irrigated land.
- Due to a tropical and sub-tropical climate, it is possible for farmers to take crops round the year. In India, the period of rain is restricted to only four months in a year, June to September, when the monsoon arrives. The remaining eight months are dry. Besides the rain is uncertain and irregular. Hence multiple cropping is generally not possible. Irrigation provides for the growth of two or three crops in a year in most areas of the country. Thus the productivity of land can be improved.
- The success of the High Yielding variety Programme (HYV) depends on good irrigation facilities.
- Using irrigation more land can be brought under cultivation.
- Irrigation helps in stabilizing the output and yield levels. It gives chance to Government to create buffer stock which can be used during drought years.
- It can give rise to waterways and inland water transport.
Sources of Irrigation:
The sources of irrigation are wells, tube-wells, ponds, lakes, rivers, dams, and canals.
Traditional Methods of Irrigation:
Most of the farmers use surface irrigation. Surface methods include flooding and furrow irrigation, as well as basins around trees and shrubs. Smooth, graded, gravity-driven slopes suit surface irrigation best. The water available in wells, lakes, and canals is lifted up by different methods in different regions, for taking it to the fields. Cattle or human labour is used in these methods. So these methods are cheaper but less efficient. The various traditional ways are:
Moat (pulley-system)
Also called the pulley system, it involves pulling up water from a well or other such source to irrigate the land. For pulling up water cattle or human labour is used. It is an extremely time-consuming and labor-intensive system. It is very cost-efficient and wastage of water is avoided when using a moat system of irrigation.

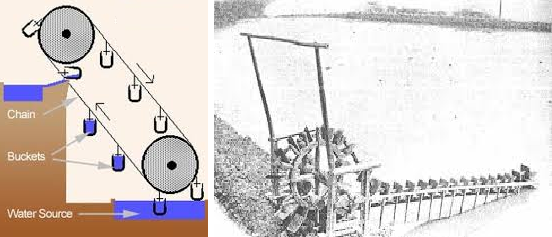
Chain Pump:
A chain pump consists of two large wheels connected by a chain. There are buckets attached to the chain. One part of the chain dips into the water source. As the wheel turns, the bucket picks up water. The chain later lifts them to the upper wheel where the water gets deposited into a source. And the empty bucket gets carried back down.
Dhekli:
It is a system of drawing water from a well or such similar source. Here rope and bucket are tied to a pole. At the other end, a heavy object as a counterbalance is fixed. The pole is used to draw up water.

Rahat (Lever System):
Rahat system of irrigation uses animal labour. Above the well, a large wheel is tied. An ox or cow would turn the wheel to draw the water from the well using a belt fitted with buckets passing over the wheel.

Advantages of Traditional Methods of Irrigation:
- They are the simplest and most economic methods of irrigation.
- They do not require any technical knowledge or experty.
- They are suitable for irrigation of leveled fields.
- As the water remains in the reservoir, less erosion is caused.
- As human observation is their water is used with less wastage and proper water is made available to the crop.
Disadvantages of Traditional Methods of Irrigation:
- They are time-consuming and labourious in nature.
- Due to seepage in drains, there is a wastage of water.
- After the growth of crops, water reaches the basins in disproportionate quantity thereby causing wastage of water.
- If not done properly can cause waterlogging.
- There is a possibility of overwatering and wasteful runoff.
- If the soil lacks proper sloping or doesn’t absorb readily, then the water can’t move through the field. Standing water damages plants and reduces yields of edible crops.
Water Logging:
When too much of water stands in a field and accumulates around the roots, then it is called waterlogging. It damages crops because
- It reduces air in the space between soil particles. This results in a decrease in the supply of oxygen to the roots. It results in the damage of the roots.
- It increases the salinity of the soil which reduces the fertility of the soil.
Pumps:
- Pumps are commonly used for lifting water. Diesel, biogas, electricity and solar energy is used to run these pump
Modern Methods of Irrigation:
Modern methods of irrigation help us to use water economically. The main methods used are as follows:
Sprinkler System:
This system mimics the phenomenon of rain. The system is more useful on the uneven land where sufficient water is not available. The perpendicular pipes, having rotating nozzles on top, are joined to the main pipeline at regular intervals. When water is allowed to flow through the main pipe under pressure with the help of a pump, it escapes from the rotating nozzles. It gets sprinkled on the crop as if it is raining. The sprinkler is very useful for sandy soil. Sprinkler system also provides the best coverage regardless of the size of the farm.

Drip system :
In this system plastic pipes having holes in them are laid in rows near the crops or plants. Water seeps from these holes drop by drop just at the position of the roots. So it is called a drip system. Drip irrigation delivers water directly to plants rather than areas and keeps soil evenly moist, yet full of oxygen. It is the best technique for watering fruit plants, gardens and trees. The system provides water to plants drop by drop. Water is not wasted at all. It is very effective in regions where the availability of water is poor. Setting a drip irrigation system is costly, hence it is not used by all farmers.

Previous Topic: Sowing of Seeds

2 replies on “Irrigation”
Nice!! Thank you so much. It helped me a lot in finalizing my project.
yeah……………………………………………………………………
it helped me a lot as i can’t understand from where to start my project but ……….. your site helped me a lot ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; thank you from bottom of the heart