Science > Biology > Human Population and Population Control > Surgical Methods of Contraception
Sterilization is a permanent method of birth control. Sterilization procedures for women are called tubal ligation or tubectomy or Hysterectomy in a rare case. The procedure for men is called vasectomy. Sterilization is considered a permanent and sure method of contraception. In certain cases, sterilization can be reversed, but the success of this procedure is not guaranteed. For this reason, sterilization is meant for men and women who do not intend to have children in the future. Sterilization includes surgical methods of contraception.
Sterilization does not protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs), including human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). A male or female condom should be used to protect against these infections if there is a risk of getting an STI
Tubal Ligation or Tubectomy:
This is one of the surgical methods of contraception is used in case of females. Tubal ligation closes off the fallopian tubes. This prevents the egg from moving down the fallopian tube and keeps the sperm from reaching the egg. Tubal ligation is performed under general, regional, or local anesthesia. The procedure takes anywhere from 10 to 45 minutes.
Sterilization is a highly effective way to prevent pregnancy. Fewer than 1 out of 100 women will become pregnant within 1 year of having the procedure. In the rare chance, pregnancy does occur after tubal sterilization, this is likely caused by an incomplete closure of the tubes. There is an increased risk that it will be an ectopic pregnancy (pregnancy in a location other than the anticipated position within the uterus). But the risk of ectopic pregnancy occurring in women after tubal sterilization is lower than in women who do not use any birth control.
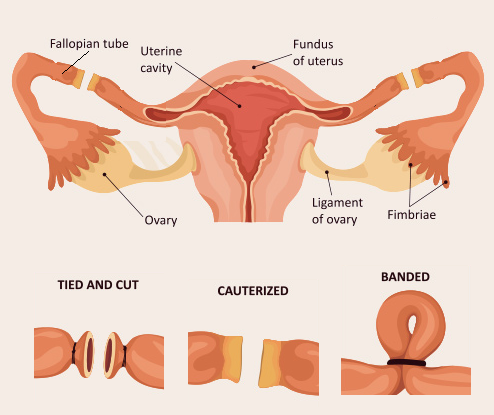
There are two ways that sterilization for women can be performed: mini-laparotomy and laparoscopy.
Mini-laparotomy:
A small incision (cut) is made in the abdomen. The fallopian tubes are brought up through the incision. A small section of each tube is removed, or both tubes can be removed completely. Less often, clips are used to close off the tubes. This approach often is used for postpartum sterilization i.e. sterilization carried out following childbirth.
Laparoscopy:
A device called a laparoscope is inserted through a small incision made in or near the belly button (navel). The laparoscope allows the pelvic organs to be seen. The fallopian tubes are closed off using instruments passed through the laparoscope or with another instrument inserted through a second small incision.
Side Effects:
Side effects of a tubal ligation may include infection, bleeding (hemorrhage), and any effects or complications associated with being under general anesthesia.
Advantages:
- The female can have menstrual periods after a sterilization procedure.
- The procedure is of short duration. Female sterilization does not involve hormones. It is a permanent form of birth control.
- There are no changes in libido (sexual desire), menstrual cycle, or breastfeeding ability.
Disadvantages:
- It is a permanent form of birth control, and some women may regret their decision at a later date. The regret may due to change in marital status or death of a child or external pressure by the clinician, spouse, relatives, or significant others.
- The procedure does not prevent a man from contracting sexually transmitted diseases.
Vasectomy:
This is one of the surgical methods of contraception is used in case of men. The vas deferens is one of two tubes that carry sperm from the testicles. Sperm becomes part of a man’s semen. In a vasectomy, the vas deferens tubes are tied, cut, clipped, or sealed to prevent the release of sperm into the semen. This prevents a woman’s egg from being fertilized with the man’s sperm.

A vasectomy is usually performed by either a urologist or a general surgeon. Under local anesthesia, a small incision is made in the scrotal sac, and the vas deferens from each testicle is severed. The open ends are then closed off. Each vas deferens then is placed back into the scrotum. There also is a “no-scalpel” technique that does not require incisions in the skin. It can be done with local anesthesia by a specialist health care professional.
Confirmation of Sterility:
After a vasectomy, the man may feel tenderness or bruising around the incision site due to the presence of some sperm may remain in the vas deferens for several months after the procedure. A man is not considered sterile until he has produced sperm-free ejaculations. This usually requires 15 to 20 ejaculations. It takes about 2–4 months for the semen to become totally free of sperm. The couple should use another form of birth control during this period. Semen is tested in the lab several weeks after the procedure to determine if the semen is free of sperm.
Side Effects:
Vasectomy generally is considered to be safer than female sterilization. It requires only local anesthesia. There is no increased risk of ectopic pregnancy if the vasectomy fails. Risks of vasectomy include minor bleeding and infection. Major complications are rare.
Advantages:
- Vasectomy involves no hormones.
- It is permanent.
- The procedure is quick with few risks.
- It is performed as an outpatient procedure in a clinic or doctor’s office.
Disadvantages:
- Men may regret the decision later.
- Vasectomy does not prevent a man from contracting sexually transmitted diseases.
- Short-term discomfort usually follows the procedure. After a vasectomy, the man may feel tenderness or bruising around the incision site due to the presence of some sperm may remain in the vas deferens for several months after the procedure.
Hysterectomy:
This is one of the surgical methods of contraception is used in case of females. A hysterectomy is the surgical removal of a woman’s uterus. Sometimes depending on the overall health status of the woman undergoing a hysterectomy, the surgery includes removal of one or both ovaries and fallopian tubes. Then the procedure is called a radical hysterectomy with salpingo-oophorectomy.

For practical purposes, no woman who has had a hysterectomy can become pregnant. It is an irreversible method of birth control and absolute sterilization. The hysterectomy can be abdominal, vaginal. It can also be done by laparoscopy.
If a woman has other chronic medical problems like excessive menstrual bleeding, uterine fibroids, uterine growths, gynecologic cancer, Chronic pelvic pain, Endometriosis, Uterine Prolapse. Descent of the uterus into your vagina can happen when supporting ligaments and tissues weaken.
- A hysterectomy is the only certain, permanent solution for fibroids.
- In endometriosis, the tissue lining the inside of the uterus (endometrium) grows outside the uterus on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, or other pelvic or abdominal organs.
- In Uterine Prolapse the uterus descends into the vagina. It can happen when supporting ligaments and tissues weaken.
Previous Topic: Intrauterine Devices (IUDs)
Next Topic: Other Methods of Contraception