Science > Chemistry > Everyday Chemistry > Use of Chemicals in Food
In the last two articles, we have studied the use of chemicals as everyday medicines. In this article, we shall study the use of chemicals in food. The use of chemicals in food is in the form of food additives, food preservatives, artificial sweeteners, and antioxidants.
Food Additives:
To increase shelf life and to make food attractive various chemicals are added to food. Main categories of food additives are food colours, flavours and sweeteners, antioxidants, fat emulsifiers, stabilizing agents, flour improvers, food preservatives, and nutritional supplements like minerals, vitamins, and amino acids. Except for nutritional supplement, no other additive has any nutritional value.
Food Preservatives:
Food preservatives are the substances when added to food is capable of inhibiting, retarding or arresting the process of fermentation, acidification or other decomposition of food by the growth of microbes.
Examples: Sodium benzoate, salt of the ascorbic acid and propionic acid etc.
Food preservatives are classified into two groups – Class I and Class II.
- Class – I preservatives include table salt, sugar, and vegetable oils.
- Class- II preservatives include chemical preservatives like sodium benzoate, sodium meta-sulphide.
In India chemical preservatives like benzoic acid or its sodium salt and potassium metabisulphite or sodium metal sulphide are permitted.
Characteristics of Food Preservatives:
- It should not be harmful to human being.
- It should inhibit the growth of microorganism even if it is used in traces.
The Necessity of Food Preservation:
- To make the food available during the days of scarcity.
- To make fruit palatable, attractive and to increase its shelf life.
- To prevent spoilage of food by retarding or inhibiting the growth of microorganisms due to fermentation or acidification.
- To avoid undesirable changes that occur in colour, taste, flavour of the food.
Physical Methods of Food Preservation:
- By Removal of Heat (Cooling): This method involves refrigeration, freezing, dehydro-freezing, or carbonation. At low temperatures, the growth of the organism is inhibited. Cooling lowers the temperature of the substance which prevents the growth of the microorganisms. Fresh fruits, vegetables are preserved by this method.
- By Addition of Heat: This method involves pasteurization or sterilization. This process is also called as canning or heat processing. Heating kills microorganisms. Hence solid and liquid foods can be preserved by heating it. Pasteurization is a sterilization process for preserving food by the addition of heat or by increasing temperature. Pasteurization of milk is an example of this process.
- By Removal of Water (Dehydration): This process involves sun drying, freeze-drying, and puff drying. As water is removed the growth of the organisms is prevented. Fishes, fruits, vegetables, and food grains are preserved by this method.
- By Irradiation: This method involves ultraviolet or ionizing radiation. Irradiation controls the growth of microorganisms. High energy electromagnetic radiation produces desired effects without inducing radioactivity in food. Bakery products are preserved by this method.
Chemical Methods of Food Preservation:
- By Addition of Sugar: In this method, sugar is added to the food which is to be preserved and is then heated. This method is simple and cheap. This method is used to preserve fruit jams, jellies, and marmalades.
- By the addition of salt: Salt is added during the preparation of the product. Making pickles of raw mango, lemon, chilies, and preservation of fish products involve this method.
- By Addition of Vinegar: Dilute acetic acid commonly known as vinegar is added to food for preservation. This method is used for the preservation of pickles of raw mango, lemon, chilies salad dressing, and preservation of fishes.
- By Addition of Chemicals: Sodium benzoate, salt o the ascorbic acid and propionic acid, etc. are used as food preservatives. They inhibit the growth of microorganisms. These are added in small quantities to food like jams, jellies, and juices.
Chemicals Used in Food Preservations:
Sodium benzoate:
Benzoic acid or its salt of sodium benzoate are used as common food preservatives. It is soluble in water and also soluble in food products. 3. 0.06 % to 0.1 % concentration of sodium benzoate is sufficient for the preservation of fruit juices and squashes. Sodium benzoate is metabolized by conversion to hippuric acid which is finally excreted in the urine.
Potassium metabisulphite and Sodium meta sulphide:
It is used for preservation of colourless food materials such as fruit juices, squashes, apples, litchies and raw mango chutney. These preservatives react with the acid in the fruit juice producing sulphur dioxide which is very effective in killing the harmful microorganisms present in the food and thus prevents it from getting spoiled.
These are not used for preservation of coloured food material because the sulphur dioxide produced from these chemicals act as a bleaching agent and decolourises the food material.
Latest Methods of Food Preservation:
- The latest methods of food preservation are vacuum packing, freeze drying, ultraviolet or ionizing radiation. Using these methods microorganisms are destroyed.
- Irradiation by gamma rays prevents spoilage of potatoes and onions.
Artificial Sweeteners:
Natural sweeteners, e.g., sucrose add to calorie intake and therefore many people prefer to use artificial sweeteners. Natural sweeteners are metabolized in the body. Excess consumption of sugar leads to many diseases such as obesity, diabetes, coronary heart diseases.
The chemical compounds which do not occur in nature but are synthesized in the laboratory have a sweet taste, but they have no food value (they have very low-calorie value) are called artificial sweeteners. They are imparting sweetness but not adding any calorie value to the food. They pass through the human digestive system without being digested. Hence they are used for making sweets. Such sweets can be consumed by the diabetic patient also.
Saccharin:
Ortho-sulphobenzimide, also called saccharin, is the first popular artificial sweetening agent. It has been used as a sweetening agent ever since it was discovered by Constantine Fahlberg and Era Ramsen in 1879.
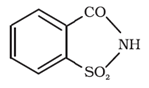
It is about 550 times as sweet as cane sugar. It is excreted from the body in urine unchanged. It appears to be entirely inert and harmless when taken. Its use is of great value to diabetic persons and people who need to control the intake of calories.
Aspartame:
Aspartame is the most successful and widely used artificial sweetener. It is roughly 100 times as sweet as cane sugar. 2. It is methyl ester of dipeptide formed from aspartic acid and phenylalanine.
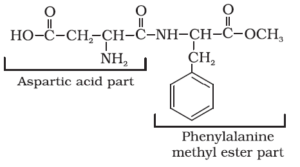
Use of aspartame is limited to cold foods and soft drinks because it is unstable at cooking temperature.
Alitame:
Alitame is high potency sweetener, Hence it is difficult to control the sweetness of food while using this sweetener.

It is more stable than aspartame, the control of the sweetness of food is difficult while using it. It is 2000 times sweeter than sucrose.
Sucralose:
Sucralose is a trichloro derivative of sucrose. Its appearance and taste are like sugar.

It is stable at cooking temperature. It does not provide calories. It is 600 times sweeter than sugar.
Note: The use of cyclamates as sweetening agent has been banned in many countries in view of suspected carcinogenic effects.
Edible Colours:
Adding colours to the food makes the food more attractive, more acceptable and palatable. Colour has therapeutic value. The edible colours are classified into three types a) natural colours, b) browning colours produced during cooking and c) additives. Natural colours are
- carotenoids – yellow to red colours
- chlorophyll – green colour flavonoids (anthocyanins) – red to blue colour
- Anthocyanins are widely used in the food and their sources are grapes, beetroot, sweet potato, cabbage etc.
- Natural colour carotene is safe to be used in food.
Chemical dyes i.e. additives have stronger colours than the natural colours. Generally, they are azo dyes. They are not good for health. Tetrazine is a dye used in food for giving it colour.
Some additives are Chocolate Brown, Quinoline yellow WS, Sunset yellow, Allura red AC, Patent Blue V, Green S, Red 2G etc.
Antioxidants:
Antioxidants are the substances which when added to food, retard or prevents oxidative deterioration of food.
Examples: Butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA) and Butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT), Vitamin E is a natural antioxidant.
During the oxidation of food free radicals are generated. Antioxidants when added to food, react with these free radicals and prevent further oxidation and food becoming rancid.
Butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA):
Its chemical name is 2-tertbutyl-4-methoxy phenol. Its molecular formula is C11H16O2.

It is found in butter, meats, cereals, chewing gum, snack foods, baked foods, beer and dehydrated potatoes. It is also found in rubber products, cosmetics, and petroleum products. It is used to preserve food. It is used in cosmetics, pharmaceutical, animal feed.
Butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT):
Its chemical name is 2,6-Di-tertbutyl-p-cresol. Its molecular formula is C15H24O.

Fat reacts with oxygen to form free radicals which react further with BHT to form stable BHT radical. This radical does not further react with molecules of fat and thus the chain reaction is stopped. By this way, BHT prevents rancidity of fats and hence it is used to preserve colour, odour and taste of foodstuff.
Sulphur dioxide and Sulphite:
The salts of sodium and potassium sulphite and bisulphites are used as antioxidants. Sulphur dioxide is widely used as preservative and antioxidant in food and beverage industries. Sulphites are used as antioxidants. They reduce discolorization of fruits, vegetables, and dehydrated potatoes.
Sulphites are used to preserve wine, dairy products, sauces, jams jellies etc. They are used as food additives as antimicrobial agents, structure modifiers, enzyme inhibitors.
In the next article, we shall study about cleansing agents: Soaps and detergents
Previous Topic : Antimicrobials, Antibiotics, Sulpha Drugs, Antiseptics, Disinfectants
Next Topic: Cleansing Agents: Soaps and Detergents
One reply on “Use of Chemicals in Food”
Nice to read and learn.