Science > Chemistry > Organic Chemistry > Halogen Derivatives of Alkanes > Introduction
In this article, we shall study halogen derivatives of alkanes or haloalkanes.
Organic Compounds Containing Halogens:
If one or more hydrogen atom is replaced in hydrocarbon by an equivalent number of halogen, the compounds obtained are called halogen derivatives of hydrocarbons. Halogen derivatives of hydrocarbons are further classified as aliphatic halogen compounds and aromatic halogen compounds. Aliphatic halogen compounds are obtained by replacing one or more hydrogen of aliphatic hydrocarbons (alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes).
Aliphatic Halogen Compounds:
Aliphatic halogen compounds are further classified as haloalkanes, haloalkenes and haloalkynes.
Haloalkanes:
- CH3Cl (Chloromethane)
- CH2Cl2 (Dichloromethane)
- CHCl3 (Trichloromethane / Chloroform)
- CCl4 (Tetrachloromethane / Carbon tetrachloride)
- CH3-CH2-CH2I (1-Iodopropane )
- CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-Cl (1-Chlorobutane)
Haloalkenes:
- CH2= CH-Cl (Chloroethene)
- CH2= CH-CH2-I (3-Iodoprop-1-ene)
- CH3-CH = CH-CH2-Br (4-Bromobut-2-ene)
Haloalkynes:
- CH≡C-Cl (Chloroethyne)
- CH≡C-CH2I ( 3-Iodoprop-1-yne)
- CH3-C≡C-CH2-Br (4-Bromobut-2-yne)
Aromatic Halogen Compounds:
Aromatic hydrocarbons are called arenes. Halogen derivatives of arenes are called aromatic halogen compounds. Aromatic halogen compounds are further classified as nuclear halogen derivatives and side chain halogen derivatives.
When a hydrogen atom is directly attached to an aromatic ring is replaced by a halogen atom, the compound obtained is called nuclear halogen derivative of arene or halo arene or aryl halide.
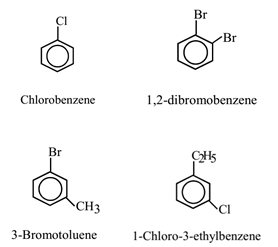
When a hydrogen atom present in a side chain attached to an aromatic ring is replaced by a halogen atom, the derivative obtained is called side chain derivative. The side chain halogen derivatives are regarded as the aryl derivatives of haloalkane.

Halogen Derivatives of Alkanes:
Saturated aliphatic hydrocarbons are called alkanes. Their general formula is CnH2n + 2. When one or more hydrogen atoms of saturated aliphatic hydrocarbons or aromatic hydrocarbons are replaced by the corresponding number of halogen atoms, (Cl, Br, I), then the new compounds obtained are called, halogen derivatives of alkanes or of arenes. In haloalkanes, the halogen atom is attached to the sp3 hybridized carbon atom.

Examples of Halogen Derivatives of Alkanes:
- CH3Cl (Methyl chloride) (Chloromethane),
- C2H5Br (Ethyl bromide) (Chloroethane).
Examples of Halogen Derivatives of Arenes:

In haloarenes, halogen atom is attached to the sp2 hybridized carbon atom.
Classification Halogen Derivatives of Alkanes:
Classification on the Basis of Number of Halogen Atoms:
Depending upon the number of halogen atoms in halogen derivatives of alkanes are classified as monohalogen derivatives of alkanes and polyhalogen derivatives of alkanes. Polyhalogen derivatives of alkanes are further classified as dihalogen, trihalogen, tetrahalogen derivatives of alkanes and so on.
Monohalogen Derivatives of Alkanes:
When one hydrogen atom of an alkane is replaced by one halogen atom, then the compound obtained is called a monohalogen derivative of alkanes. They are commonly called as alkyl halides or haloalkenes. Their general formula is CnH2n + 1X. e.g. CH3Cl (Methyl chloride), C2H5Br (Ethyl bromide)
Dihalogen Derivatives of Alkanes:
When two hydrogen atoms of alkane are replaced by two halogen atoms, then the compound obtained is called a dihalogen derivative of alkanes. Their general formula is CnH2nX2. e.g. C2H4Cl2 (Dichloroethane).
Trihalogen Derivatives of Alkanes:
When three hydrogen atoms of an alkane are replaced by three halogen atoms, then the compound obtained is called a trihalogen derivative of alkanes. Their general formula is CnH2n-1X3. e.g. CHCl3 (Chloroform)
Tetrahalogen Derivatives of Alkanes:
When four hydrogen atoms of an alkane are replaced by four halogen atoms, then the compound obtained is called a tetrahalogen derivative of alkanes. Their general formula is CnH2n-2X4. e.g. CCl4 (Carbon tetrachloride)
Monohalogen Derivatives of Alkanes OR Alkyl Halides:
When one hydrogen atom of an alkane is replaced by one halogen atom, then the compound obtained is called a monohalogen derivative of alkanes. They are commonly called as alkyl halides or haloalkenes. Their general formula is CnH2n + 1X. Where X is either Cl, Br or I. They are also represented by a general formula R-X, where R is an alkyl group and X is a halogen. e.g. CH3Cl (Methyl chloride), C2H5Br (Ethyl bromide)
Classification of Monohalogen Derivatives of Alkanes:
Classification on the Basis of Type of Carbon Atom:
Depending upon the type of carbon atom to which halogen is attached alkyl halides are classified into three types.
Primary Alkyl Halides:
A primary carbon atom is an atom which is bonded to only one other carbon or to none. The primary carbon atom is denoted by 1°. In primary alkyl halide, the halogen is attached to primary (1°) carbon atom.

CH3-CH2-CH2-I CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-Cl
1-Iodopropane 1-Chlorobutane

Secondary Alkyl Halides:
A secondary carbon atom is an atom which is bonded to two other carbon atoms. The secondary carbon atom is denoted by 2°. In secondary alkyl halide, the halogen is attached to secondary (2°) carbon atom.

R and R’ may be same or different

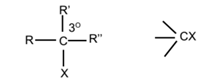
Tertiary Alkyl Halides:
A tertiary carbon atom is an atom which is bonded to three other carbon atoms. The tertiary carbon atom is denoted by 3°. In tertiary alkyl halide, the halogen is attached to tertiary (3°) carbon atom.

R, R’ and R’’ may be same or different

Classification of Monohalo Compounds on the Basis of Hybridization State of the carbon in C-X Bond:
Compounds containing Csp3 – X Bond:
In this type of monohalo compounds, the halogen atom is directly bonded to an sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Such compounds are further classified as follows
Haloalkanes or Alkyl Halides:
In this type, the halogen atom is attached to the alkyl group denoted by R. Their general formula is CnH2n + 1X. They are further classified as primary, secondary and tertiary alkyl halides.
If R is alicyclic, then R-X is called halocycloalkane or cycloalkyl halide. Such compounds are either secondary or tertiary.

Allylic Halides:
The halides in which halogen is attached to an sp3 hybridized carbon atom next to carbon-carbon double bond are called allylic halides. Such carbon is called allylic carbon.

Note: Allylic halides may be primary, secondary or tertiary.
Benzylic Halides:
The halides in which halogen is attached to sp3 hybridized carbon atom next to aromatic ring are called benzylic halides. Such carbon is called benzylic carbon.

Note: Benzylic halides may be primary, secondary or tertiary.
Compounds containing Csp2 – X Bond:
In this type of monohalo compounds, the halogen atom is directly bonded to an sp2 hybridized carbon atom. Such compounds are further classified as
Vinylic Halides:
The halides in which halogen is attached to one of the sp2 hybridized carbon atoms of carbon double bond are called vinylic halide. Such carbon is called vinylic carbon. The halogen atom is attached to one of the carbon atoms of carbon-carbon double bond.

Aryl Halides:
In aryl halides, halogen is directly attached to one of the sp2 hybridized carbon atoms of the benzene ring.

Compounds containing Csp – X Bond:
In this type of monohalo compounds, the halogen atom is directly bonded to an sp hybridized carbon atom.
CH-C≡Cl CH3-C≡C-I
Chloroethyne 1-Iodoprop-1-yne
One reply on “Introduction to Halogen Derivatives of Alkanes”
Sir it’s to good 🙏 thanks