Science > Chemistry > Halogen Derivatives of Alkanes > Nomenclature of Alkyl Halides
In this article, we shall study isomerism in alkyl halides and their nomenclature.
Isomerism in Haloalkanes:
Isomers are the organic compounds, which have the same molecular formula but different structural formula and properties. The phenomenon is called isomerism. Haloalkanes can exhibit the following type of isomerism.
Chain Isomerism:
The haloalkanes with four or more carbon atoms exhibit this type of isomerism. This isomerism is exhibited due to the difference in the carbon chains.
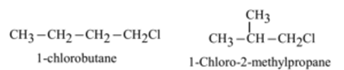
Position Isomerism:
The haloalkanes with three or more carbon atoms exhibit this type of isomerism. This isomerism is exhibited due to the difference in the position of halogen group.
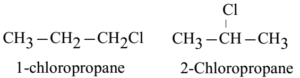
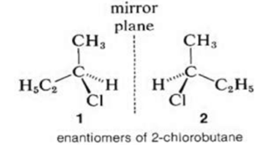
Optical Isomerism:
The haloalkanes which have the same molecular and structural formula, but have a different arrangement of the atoms or group of atoms in space and have a tendency to rotate the plane of polarised light are called optical isomers and the phenomenon is called optical isomerism.
More Examples:
Isomers of monochloro derivatives of 2,3-Dimethylbutane:
Structure of 2,3-Dimethylbutane is

The isomers of monochloro derivatives of 2,3-Dimethylbutane are

Isomers of C5H11Br and their classification:


Note: 2 – Bromo-2-methylbutane, 2 – Bromo-3-methylbutane, 1 – Bromo-3-methylbutane are enantiomers. i.e. they are optically active compounds
Isomers of C4H9Br and their classification:

Classification of alkyl halides:
1-Bromopropane

Bromine atom is attached to a primary carbon i.e. this carbon is attached to only one carbon atom. Hence it is primary alkyl halide.
2-Bromopropane

Bromine atom is attached to a secondary carbon i.e. this carbon is attached to two other carbon atoms. Hence it is secondary alkyl halide.
2-Bromo-2-methylpropane

Bromine atom is attached to a tertiary carbon i.e. this carbon is attached to three other carbon atoms. Hence it is tertiary alkyl halide.
Nomenclature:
Trivial or Common System of Nomenclature:
In the trivial system, haloalkanes are named as alkyl halides. The name is derived by adding the word halide to the name of the corresponding alkyl group. The trivial name is always written as two separate words.
e.g. CH3Br (Methyl bromide), CH3CH2Br (Ethyl bromide), CH3CH2Cl (Ethyl chloride).
Different Alkyl Groups With Examples:
|
Sr. |
Alkyl Group |
Name of Group |
Example |
Compound Name |
|
1 |
CH3– |
Methyl |
CH3Cl |
Methyl chloride |
|
2 |
CH3CH2– or C2H5– |
Ethyl |
C2H5Br |
Ethyl bromide |
|
3 |
CH3CH2CH2– |
n-Propyl |
CH3CH2CH2I |
n-Propyl iodide |
|
4 |
iso-Propyl |
CH3CHBrCH3 |
iso-Propyl bromide |
|
|
5 |
CH3CH2CH2CH2– |
n-Butyl |
CH3CH2CH2CH2I |
n-Butyl iodide |
|
6 |
sec-Butyl |
CH3CHClCH2CH3 |
sec-Butyl iodide |
|
|
7 |
iso-Butyl |
iso-Butyl chloride |
||
|
8 |
 |
tert-Butyl |
 |
tert-Butyl bromide |
|
9 |
 |
neo-Pentyl |
 |
neo-Pentylbromide |
IUPAC Nomenclature:
| No. | Formula | Common Name | IUPAC Name |
| 1 | CH3Br | methyl bromide | Bromomethane |
| 2 | CH3CH2Br | ethyl bromide | Bromoethane |
| 3 | CH3CH2CH2Cl | n-propyl chloride | 1-Chloropropane |
| 4 | CH3CHClCH3 | isopropyl chloride | 2-Chloropropane |
| 5 | CH3CH2CH2CH2Cl | n-butyl chloride | 1-Chlorobutane |
| 6 | CH3CHClCH2CH3 | sec-butyl chloride | 2-Chlorobutane |
| 7 | (CH3)2CHCH2I | isobutyl iodide | 1-Iodo-2-methylpropane |
| 8 | (CH3)3CBr | tert-butyl bromide | 2-Bromo-2-methylpropane |
| 9 | (CH3)3CCH2Br | neo-pentyl bromide | 1-Bromo-2,2-dimethylpropane |
| 10 | CH2=CHCl | vinyl chloride | Chloroethene |
| 11 | CH2=CHCH2Cl | allyl chloride | 3-Chloroprop-1-ene |
To Draw Structure From IUPAC Name:
|
No. |
IUPAC Name |
Structure |
|
1 |
2-Iodo-3-methylpentane |
|
|
2 |
3-Chlorohexane |
|
|
3 |
1-Chloro-2,2-dimethylpropane |
 |
|
4 |
3-Bromo-2-methylpentane |
|
|
5 |
2-Bromo-3-ethyl-2-methylhexane |
 |
|
6 |
1-Chlorobutane |
CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2Cl |
|
7 |
2-Bromo-2-methylpentane |
 |
|
8 |
1-chloro-2,2-dimethylpropane |
 |