Science > Chemistry > Concept of Atomic Mass and Equivalent Mass > Equivalent Masses of Acids, Bases, and Salts
In this article, we shall study the determination of the equivalent mass of acid, base, and salt.
Equivalent Mass of Acids:
One gram equivalent mass of an acid is that mass of it which contains one gram equivalent mass of replaceable hydrogen atoms.
Thus the equivalent mass of an acid depends on the replaceable hydrogen atoms it contains per mole. The number of replaceable hydrogen atoms present in a molecule of acid is called the basicity of the acid.

Illustration – 1:
Molecular mass of HCl = 1 + 35.5 = 36.5

Illustration – 2:
Molecular mass of H2SO4 = 2 + 32 + 64 = 98
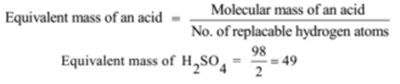
Equivalent Mass of Base:
One gram equivalent mass of a base is that mass of it which contains one gram equivalent mass of the hydroxyl radical.
Thus the equivalent mass of a base depends on the number of hydroxyl radicals it contains per mole. The number of hydroxyl radical present in a molecule of a base is called the acidity of the base.

Illustration – 1:
Molecular mass of NaOH = 23 + 16 + 1 = 40

Illustration – 2:
Molecular mass of Ca(OH)2= 40 + (16+1) x 2 = 74

Equivalent-Mass of Salts:
Equivalent mass of a simple salt is that mass of it which contains one gram equivalent of the metal or a radical
Illustration – 1:
Molecular mass of KCl = 39 + 35.5 = 74.5
In this case, KCl contains 1 gram equivalent of K and 1 gram equivalent of Cl. Hene equivalent mass of KCl is 74.5 / 1 = 74.5.
Illustration – 2:
Molecular mass of AlCl3 = 27 + 35.5 x 3 = 133.5
In this case AlCl2 contains 1 gram equivalent of Al and 3 gram equivalent of Cl. Hene equivalent mass of KCl is 133.5 / 3 = 44.5.
Illustration – 3:
Equivalent mass of a salt is also that mass of it, which will combine with one gram equivalent of another substance.
To find equivalent mass of Na2CO3
Na2CO3 reacts with HCl as
Na2CO3 + 2HCl → 2 NaCl + CO2 + H2O
Molecular mass of Na2CO3 = 23 x 2 + 12 x 1 + 16 x 3 = 106
one gram equivalent of Na2CO3 reacts with 2 gram equivalent of HCl. Hence equivalent mass of Na2CO3 is 106 / 2 = 53.
Equivalent Mass of Oxidising and Reducing Agents:

Note:
Metals with variable valency show variable equivalent masses depending upon their valency in the compound. For e.g. in oxides FeO, Fe2O3 and Fe3O4 the equivalent masses of Fe are 28.18.6 and 21 respectively.
Gram Equivalent:
The equivalent mass expressed in grams is called gram equivalent mass (GEM)
Milliequivalent:
A milliequivalent is one-thousandth of an equivalent mass of any substance is the equivalent mass expressed in milligrams. It is the unit which is used to express the concentration of electrolytes in tissue fluids of animals and plants.