Science > Chemistry > Solid State > Numerical Problems on Type of Crystal Structure
In this article, we shall study to solve problems to calculate the atomic radius, the distance between atoms in the unit cell and to decide the type of crystal structure.
Example – 01:
A naturally occurring gold crystallizes in face centred cubic structure and has a density of 19.3 g cm-3. Calculate the atomic radius of gold. (Au = 197 g mol-1)
Given: Density of gold = 19,3 g cm-3, Avogadro’s number N = 6.022 x 1023 mol-1.Atomic mass of gold = M = 197 g mol-1.Type of crystal structure = fcc
To Find: Atomic radius of gold =?
Solution:
The number of atoms in the unit cell of a face centred cubic structure is n = 4

Ans: The atomic radius of gold is 144 pm
Example – 02:
Sodium metal crystallizes in the bcc structure with an edge length of unit cell 4.29 x 10-8 cm. Calculate the atomic radius of sodium metal.
Given: Edge length = a = 4.29 x 10-8 cm, Type of crystal structure = bcc
To Find: Atomic radius of sodium =?
Solution:
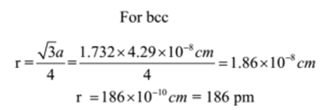
Ans: The atomic radius of sodium is 186 pm
Example – 03:
Niobium crystallizes in bcc structure and has a density of 8.55 g cm-3. Calculate its atomic radius, if its atomic mass is 93.
Given: Density of niobium = 8.55 g cm-3, Avogadro’s number N = 6.022 x 1023 mol-1.Atomic mass of niobium = M = 93 g mol-1.Type of crystal structure = bcc
To Find: Atomic radius of niobium =?
Solution:
The number of atoms in the unit cell of body centred cubic structure is n = 2
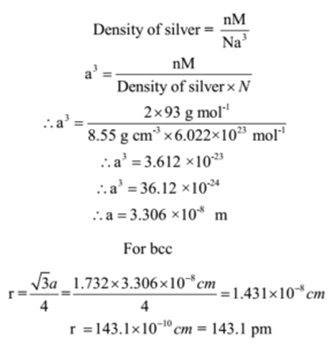
Ans: Atomic radius of niobium is 143.1 pm
Example – 04:
Sodium metal crystallizes in the body-centred cubic unit cell. If the distance between the nearest Na atom is 368 pm, calculate the edge length of the unit cell.
Given: the distance between nearest Na atom is 368 pm,
To Find: Edge length of unit cell =?
Solution:
The nearest atoms in bcc crystal structure are along the body diagonal of the cube and they are in contact with each other.
2r = 368 pm
∴ r = 184 pm

Ans: The edge length of the cell is 424.9 pm
Example – 05:
Copper crystallizes in fcc structure. If two neighbouring Cu atoms are at a distance of 234 pm, find a) edge length, b) volume of a unit cell. Also, find the distance between the next neighbouring atoms.
Given: the distance between nearest Cu atom is 234 pm,
Solution:
The nearest atoms in fcc crystal structure are along the face diagonal of the cube and they are in contact with each other.
2r = 234 pm
∴ r = 117 pm

a = 331 x 10-10 m = 3.31 x 10-8 m
Volume of unit cell = a3 = (3.31 x 10-8 m)3
Volume of unit cell = (3.31) 3 x 10-24 m3 = 36.24 x 10-24 m3
The next neighbouring atom is along the edge of the cell. Thus the distance between next neighbouring atom is ‘a’ i.e. 331 pm
Ans: The edge length = 331 pm, the volume of unit cell = 36.24 x 10-24 m3, the distance between next neighbouring atom is 331 pm
Example – 06:
A metal occurs as body centred cube and has a density of 7.856 g cm-3. Calculate the atomic radius of metal. Atomic mass of metal = 58 g/mol
Given: Density of metal = 7.856 g cm-3, Avogadro’s number N = 6.022 x 1023 mol-1.Atomic mass of metal = M = 58 g mol-1.Type of crystal structure = bcc
To Find: Atomic radius of metal =?
Solution:

Ans: The atomic radius is 125.7 pm
Example – 07:
An element germanium crystallizes in the bcc type crystal structure with an edge of unit cell 288 pm and the density of the element is 7.2 g cm-3. Calculate the number atoms present in 52 g of the crystalline element. Also, calculate the atomic mass of the element.
Given: Density of germanium = 7.2 g cm-3, edge length = 288 pm = 288 x 10-12 m = 288 x 10-10 cm = 2.88 x 10-8 cm, Avogadro’s number N = 6.022 x 1023 mol-1. Given mass of germanium = 52 g, Type of crystal structure = bcc
To Find: the number atoms present in 52 g of the crystal =? atomic mass of the element = M = ?
Solution:
The number of atoms in the unit cell of bcc structure is n = 2


For bcc there are 2 atoms in a unit cell
Number of atoms in given mass = 2 x 3.023 x 1029 = 6.046 x 1029

Example – 08:
An atom crystallises in fcc crystal lattice and has a density of 10 g cm-3 with unit cell edge length of 100 pm. Calculate the number atoms present in 1 g of the crystal.
Given: Density = 10 g cm-3, edge length = 100 pm = 100 x 10-12 m = 100 x 10-10 cm = 10-8 cm, Avogadro’s number N = 6.022 x 1023 mol-1. Given mass of crystal = 1 g, Type of crystal structure = fcc
To Find: the number atoms present in 1 g of the crystal
Solution:
The number of atoms in the unit cell of fcc structure is n = 4

For fcc there are 4 atoms in a unit cell
Number of atoms in given mass = Number of atoms in unit cell x Number of unit cells
Number of atoms in given mass = 4 x 1023
Ans: Number of atoms in given mass = 4 x 1023
Example – 09:
Aluminium having atomic mass 27 g mol-1, crystallizes in face centred cubic structure. Find the number of aluminium atom in 10 g of it. Also, find the number of unit cells in the given quantity.
Given: Atomic mass = 27 g mol-1, Avogadro’s number N = 6.022 x 1023 mol-1. Given mass = 10 g, Type of crystal structure = fcc
To Find: the number of aluminium atom in 10 g =? Number of unit cells =?
Solution:
Mass of each atom = Atomic mass / Avogadro’s number
Mass of each atom = 27 g mol-1/ 6.022 x 1023 mol-1 = 4.483 x 10-23 g
The number of atoms in unit cell of fcc structure is n = 4
Hence mass of unit cell = 4 x 4.483 x 10-23 g = 1.793 x 10-22 g
Number of unit cells = Given mass/ mass of unit cell = 10 g/ 1.793 x 10-22 g = 5.58 x 1022
Number of aluminium atom = 4 x number of unit cell
Number of aluminium atom = 4 x 5.58 x 1022 = 2.23 x 1023
Ans: Number of aluminium atoms = 2.23 x 1023 and number of unit cells = 5.58 x 1022
Example – 10:
A unit cell of iron crystal has edge length 288 pm and density 7.86 g cm-3. Find the number of atoms per unit cell and type of crystal lattice. Given the molar mass of iron 56 g/mol.
Given: Density = 7.86 g cm-3, edge length = 288 pm = 288 x 10-12 m = 288 x 10-10 cm = 2.88 x 10-8 cm, Avogadro’s number N = 6.022 x 1023 mol-1. Molecular mass of iron = M = 56 g mol-1,
To Find: the number of atoms per unit cell and type of crystal lattice
Solution:

Number of atoms per unit cell = 2,
Now body centred cubic structure has 2 atoms in the unit cell. Hence the crystal structure must be bcc
Ans: The crystal structure is bcc
Example – 11:
The edge length of a unit cell of a cubic crystal is 4.3 A°, having atomic mass 89 g/mol. If the density of crystal is 9.02 g cm-3, find the number of atoms in a unit cell.
Given: Density = 9.02 g cm-3, edge length = 4.3 A0 = 4.3 x 10-10 m = 4.3 x 10-8 cm, Avogadro’s number N = 6.022 x 1023 mol-1. Molecular mass = M = 89 g mol-1,
To Find: the number of atoms in a unit cell.
Solution:

Ans: Number of atoms per unit cell = 5
Example – 12:
The density of silver having atomic mass 107.8 g /mol is 10.7 g cm-3. If the edge length of a cubic unit cell is 405 pm, find the number of silver atoms in a unit cell and predict its type.
Given: Density = 10.7 g cm-3, edge length = 405 pm = 405 x 10-12 m = 405 x 10-10 cm = 4.05 x 10-8 cm, Avogadro’s number N = 6.022 x 1023 mol-1. Molecular mass = M = 107.8 g mol-1,
To Find: the number of silver atoms in a unit cell and predict its type.
Solution:

The number of atoms per unit cell = 4,
Now face centred cubic structure has 4 atoms in the unit cell. Hence the crystal structure must be fcc
Ans: The crystal structure is fcc
Example – 13:
A crystalline solid is made up of two elements ‘A’ and ‘B’. Atoms of A are present at the corners and atoms of B are present at face centres. One atom of A is missing from the corner. Find the simplest formula of the solid.
Solution:
Atoms of A are present at 7 corners
Hence the number of atoms of A in the lattice = 7 x 1/8 = 7/8
Atoms of B are present at 6 face centres
Hence the number of atoms of B in the lattice = 6 x 1/2 = 3
Thus the ratio of atoms of A to atoms of B in crystal = 7/8 : 3 = 7 : 24
Hence the simplest formula of the solid is A7B24
Example – 14:
A solid has a structure in which ‘W’ atoms are located at the corners of the cube, ‘O’ atoms are at the centre of the edges and Na atoms at the centre of the cube. Find the formula of the compound.
Solution:
Atoms of W are present at 8 corners
Hence the number of atoms of W in the lattice = 8 x 1/8 = 1
Atoms of O are present at 12 edge centres
Hence the number of atoms of O in the lattice = 12 x 1/4 = 3
Atoms of Na are present at the centre
Hence the number of atoms of Na in the lattice = 1
Thus the ratio of atoms of W to atoms of O to atoms of Na in crystal = 1:3:1
Hence the simplest formula of the solid is WO3Na i.e. NaWO3
One reply on “Numerical Problems on Type of Crystal Structure”
very interested problems.
many thanks for helping me.