Science > Physics > Gravitation > Acceleration Due to Gravity
In this article, we shall study the concept of acceleration due to gravity and its characteristics. Also, we shall derive an expression for the same and solve some numerical problems.
Weight of a Body:
Weight of a body is the force with which the body is attracted towards the centre of the earth (planet).
Its unit is newton (N) and dimensions are the same as that of the force [M1L1 T-2]. Mathematically the weight of a body on the surface of the Earth (Planet) is given by
W = F = mg
Where m = mass of the body and
g = acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the earth
Force of Gravitation:
The force of attraction between two material bodies in the universe is known as the force of gravitation. If one of the body is the earth or some other planet or natural satellite then the force of gravitation is called the force of gravity.
Acceleration Due to Gravity:
When a body is released from a height, it gets accelerated towards the earth with constant acceleration, this constant acceleration is called the acceleration due to gravity.
Expression for Acceleration Due to Gravity on the Surface of the Earth (Planet):
Let us consider a body of mass ‘m’ be at rest on the surface of the earth on which the acceleration due to gravity is ‘g’. If ‘M’ and ‘R’ are mass and radius of the earth (planet) respectively
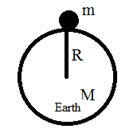
Now the force of attraction on the body is equal to its weight ‘mg’

This is the expression for acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the earth. Thus acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the earth (planet) is directly proportional to the mass of the earth (planet) and inversely proportional to the square of the radius of the earth (planet).
Characteristics of Acceleration Due to Gravity:
- It is on account of the gravitational force acting on the body.
- Average acceleration due to gravity on the surface is different for different planets.
- At a given place, the value of acceleration due to gravity is the same for all bodies irrespective of their masses.
- It changes from place to place. i.e. it changes with the change in latitude or altitude or depth.
- The acceleration due to gravity at a small height ‘h’ from the surface of the earth is the same as the acceleration due to gravity at the depth, ‘d = 2h’ below the surface of the earth. It means that the value of acceleration due to gravity at a small height from the surface of the earth decreases faster than the value of the acceleration due to gravity at the depth below the surface of the earth.
Notes:
- The value of acceleration due to gravity at the sea level and latitude 45° is taken as the standard.
- The value of acceleration due to gravity at the equator is 9.7804 m/s2 and at poles is 9.8322 m/s2.
- Unless otherwise stated, the value of ‘g’ is taken as 9.81 m/s2 in S.I. system and 981 cm/s2.
- The values of ‘g’ for Delhi, Kolkata, and Mumbai are 9.7914 m/s2, 9.7876 m/s2, 9.7863 m/s2 respectively.
Difference Between Universal Gravitation Constant (G) and Acceleration Due to Gravity (g):
- Universal gravitation constant ‘G’ is a scalar quantity while acceleration due to gravity ‘g’ is a vector quantity.
- Universal gravitation constant ‘G’ is universal constant, while acceleration due to gravity ‘g’ changes from place to place and from planet to planet.
- Dimensions of Universal gravitation constant ‘G ‘are [M-1L3 T-2], while dimensions of acceleration due to gravity ‘g’ are [M0L1 T-2].
Expression for acceleration due to gravity At a Height ‘h’ From the Surface of the Earth:
Let us consider a body of mass ‘m’ at rest at height ‘h’ from the surface of the earth. Let the acceleration due to gravity at this height be is ‘gh’. Let ‘r’ be the distance of the body from the centre of the earth. If ‘M’ and ‘R’ are mass and radius of earth respectively then, r = R + h


Where r = R + h
This is the expression for the acceleration due to gravity at height h from the surface of the earth.
Relation Between g and gh:

Numerical Problems on Acceleration Due to Gravity:
Example – 01:
Taking G = 6.67 × 10-11 N m2/kg2, the radius of the earth as 6400 km and mean density of earth as 5500 kg/m3, calculate g at the surface of the earth.
Given: Radius of the Earth = R = 6400 km = 6.4 × 106 m, Density of material of earth = ρ = 5500 kg/m3, G = 6.67 × 10-11 N m2/kg2
.To find: Acceleration due to gravity = g =?
Solution:

Ans: Acceleration due to gravity = 9.83 m/s2.
Example – 02:
At what height will be the acceleration due to the gravity of the earth fall off to one half that at the surface? At what height will the value of g be 8 m/s2? Take radius of earth = 6400 km.
Solution Part – I:
Given: R = 6400 km and gh = g/2
To find: Height above the surface of the earth = h =?

Now, r = R + h
∴ h = r – R = 9050 – 6400 = 2650 km
Solution Part – II:
Given: R = 6400 km and gh = 8 m/s2
To find: Height above the surface of the earth = h =?

Now, r = R + h
∴ h = r – R = 7084 – 6400 = 684 km
Ans: At height of 2650 km, the acceleration due to gravity of the earth fall off to one half that at the surface and at a height of 684 km the acceleration due to gravity is 8 m/s2.
Example – 03:
How far from the centre of the earth does the acceleration due to gravity reduce by 5 per cent of its value at the surface of the earth? Take the radius of the earth as 6.4 x 106 m.
Given: , R = 6.4 x 106 m and gh = g – 5% g = 0.95 g
To find: Distance of point from centre of the earth =r =?
Solution:

Ans: At the distance of 6566 km from the centre of the earth does the acceleration due to gravity reduce by 5 percent of its value at the surface of the earth
Example – 04:
At a certain height above the surface of the earth, the gravitational acceleration is 90 % of its value on the surface of the earth. Determine the height if the radius of the earth is 6400 km.
Solution:
Given: R = 6400 km and gh = 90% g = 0.9 g
To find: Height above the surface of the earth =h =?

Now, r = R + h
∴ h = r – R = 6746 – 6400 = 346 km
Ans: At a height of 346 km from the surface of the earth acceleration due to gravity be 90% of the value at the surface of the earth
Example – 05:
At what height above the earth’s surface will the acceleration due to gravity be 4% of the value at the surface of the earth? R= 6400 km.
Given: R = 6400 km and gh = 4% g = 0.04 g
To find: Height above the surface of the earth =h =?
Solution:

Now, r = R + h
∴ h = r – R = 32000 – 6400 = 25600 km
Ans: At height of 25600 km from the surface of the earth acceleration due to gravity be 4% of the value at the surface of the earth
Note:
When solving this type of problem, take care of the phrases reduced by and reduced to. For e.g. if the acceleration is reduced by 5 % data is gh = g – 5% g = 0.95 g and if the acceleration reduces to 5 % data is gh = 5% g = 0.05 g.
Example – 06:
The mass of the body on the surface of the earth is 100 kg. What will be its mass and weight at an altitude of 1000 km?
Given: Mass of body = 100 kg, R = 6400 km and altitude = h = 1000 km
To find: Mass and weight at altitude of 1000 km =?
Solution:
r = R + h = 6400 + 1000 = 7400 km

Now weight of body at altitude 100 km = Wh = m gh = 100 x 7.33 = 733 N
The mass is always constant, hence mass at altitude of 100 km = 100 kg
Ans: At an altitude of 1000 km the mass of the body is 100 kg and its weight is 733 N.
Example – 07:
A body weights 1.8 kg on the surface of the earth. How much will it weigh on the surface of a planet whose mass is 1/9 that of earth and whose radius is half that of earth
Given: Weight of body on earth = WE = 1.8 kg, mass of planet = 1/9 mass of earth i.e MP = 1/9 ME, radius of planet = 1/2 radius of earth i.e. RP = 1/2 RE.
To find: Weight of body on the planet = WP =?
Solution:

Ans: The weight of the body on the surface of the planet is 0.8 kg or 0.8 kg wt.
Example – 08:
A body weights 4.5 kg on the surface of the earth. How much will it weigh on the surface of a planet whose mass is 1/9 that of earth and whose radius is half that of the earth?
Given: Weight of body on earth = WE = 4.5 kg, mass of planet = 1/9 mass of earth i.e MP = 1/9 ME, radius of planet = 1/2 radius of earth i.e. RP = 1/2 RE.
To find: Weight of body on the planet = WP =?
Solution:

Ans: The weight of the body on the surface of the planet is 2 kg or 2 kg wt
Example – 09:
A body weights 3.5 kg wt, on the surface of the earth. How much will it weigh on the surface of a planet whose mass is 1/7 that of earth and whose radius is half that of earth
Given: , Weight of body on earth = WE = 1.8 kg, mass of planet = 1/9 mass of earth i.e MP = 1/7 ME, radius of planet = 1/2 radius of earth i.e. RP = 1/2 RE.
To find: Weight of body on the planet = WP = ?
Solution:

Ans: The weight of the body on the surface of the planet is 2 kg wt.
Example – 10:
The radius of a planet is half that of the earth. The acceleration due to gravity on the planet’s surface is half that on earth’s surface. Find the mass of the planet in terms of mass M of earth
Given: Acceleration due to gravity on planet = 1/2 Acceleration due to gravity on earth i.e gP = 1/2 gE, radius of planet = 1/2 radius of earth i.e. RP = 1/2 RE.
To find: Mass of the planet = MP =?
Solution:

Ans: The mass of planet in terms of the mass of earth is M/8
Example – 11:
Find the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the moon. Given that the mass of the moon is 1/80 times that of the earth and the diameter of the moon is 1/4 times that of the earth. g = 9.8 m/s2.
Given: Mass of Moon = 1/80 mass of earth i.e MM = 1/80 ME, diameter of Moon = 1/4 diameters of earth i.e. RM = 1/4 RE. , acceleration due to gravity on surface of earth = gE = 9.8 m/s2.
To find: acceleration due to gravity on the surface of moon = gM =?
Solution:

Ans: The acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the moon is 1.96 m/s2,
Example – 12:
A star having a mass 2.5 times that of the sun and collapsed to a size of radius 12 km rotates with a speed of 1.5 rev/s (Extremely compact stars of this kind are called neutron stars. Astronomical objects pulsars belong to this category). Will object placed on its equator remain stuck to its surface due to gravity? Mass of sun is 2 x 1030 kg.
Given: Mass of Star = 2.5 times mass of Sun i.e MStar = 2.5 MSun, Radius of star = 12 km = 12 x 103 m, mass of sun = MSun = 2 x 1030 kg. Number of revolutions of star = n = 1.5 rev per second.
Solution:

As the gravitational acceleration on the surface of the star is greater than the centripetal acceleration, the weight of the body will be much larger than the centrifugal force acting on the body. Thus body remains stuck to the surface of the star.
Example – 13:
The mass of the Hubble telescope is 11600 kg. What is its weight and mass when it is in an orbit 598 km above the surface of the earth? Mass of earth is 5.98 x 1024 kg, Radius of earth = 6400 km,
Given: Mass of telescope = m = 11600 kg, Mass of earth = M = 5.98 x 1024 kg, Radius of earth = 6400 km, Height of telescope above the surface of earth = h = 598 km, G = 6.67 x 10-11 N m2/kg2
To find: Weight of telescope = W =?
Solution:
r = R + h = 6400 + 598 = 6998 km = 6.698 x 106 m

The mass is always constant, hence mass at an altitude of 598 km = 11600 kg
Ans: The weight of Hubble telescope in its orbit is 9.447 x 104 N and mass at an altitude of 598 km = 11600 kg
Example – 14:
Find the value of Universal gravitational Constant G from the following data: M = 6 x 1024 kg, R = 6400 km, g = 9.774 m/s2,
Given: M = 6 x 1024 kg, R = 6400 km = 6.4 x 106 m, g = 9.774 m/s2,
To find: G = ?
Solution:

Ans: The value of G is 6.672 x 10-11 N m2/kg2.
Example – 15:
Assuming the earth to be homogeneous sphere, find the density of material of the earth from the following data.g = 9.8 m/s2, G = 6.673 x 10-11 Nm2/kg2 , R = 6400 km,
Given: g = 9.8 m/s2, Universal gravitational Constant = G = 6.673 x 10-11 Nm2/kg2 ,R = 6400 km = 6.4 x 106 m,
To find: Density = r = ?
Solution:

Ans: Density of material of the earth = 5483 kg/m3
Previous Topic: Concept of Gravitational Potential
Next Topic: Variation in Acceleration Due to Gravity
3 replies on “Acceleration Due to Gravity”
Best physics online site with so many real examples. Thanks for this.
The explanation is very clear and helpful… Thanks for such a detailed explanation!!
Thank you so much for this masterpiece 😁