Science > Physics > Electrostatics > Charging a Body and Detection of Charge
In this article, we shall study methods of charging of body and different apparatus used for detection of charge on the body.
Charging of Body:
Charging by Friction:
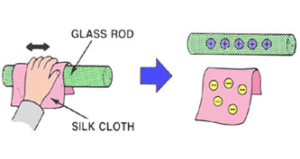
When a body is rubbed to another, there is a transfer of electrons from one body to another due to friction. The body losing electrons is positively charged and the body gaining electrons is negatively charged. The amount of gained and the lost electrons is equal to each other. Hence the total charge of the system is conserved.
When a glass rod is rubbed with a silk cloth, the glass loses electrons and gets positively charged while the silk cloth gains electrons and gets negatively charged.
Charge Producers:
The charge producers consist of two wands, one with dark coloured material and one with white coloured material attached to a conductive disk. After rubbing the dark and white surfaces of the two charge producers together. The disk with the white surface will acquire a positive charge; the disk with the dark surface will acquire a negative charge.
Charging by Conduction:
In the electrically neutral body, there are equal numbers of electrons and protons. The body can be charged by changing this balance by some external agency.
When a negatively charged rod touches the neutral body mounted on an insulating stand, then some of the electrons from the rod pass to the neutral body. As a result, the neutral body is negatively charged by contact due to the conduction of electrons from the negatively charged rod to the neutral body.
If the rod is positively charged, then some of the electrons from the neutral body pass to the rod and the neutral body becomes electron-deficient and acquires a positive charge by contact due to the conduction of electrons from the neutral body to the positively charged rod.

When a charged object touches to a neutral object, they both have the same charge. after contact, they start repelling each other due to the same nature of the charge. When two charged bodies touch each other, the total charge of the system is conserved and they share the total charge according to their capacities.
Charging by Induction:
Conductors can also be charged without contact. Let us consider a negatively charged rod is brought near (without contact) a neutral body mounted on an insulating stand, which is a good conductor of electricity. The rod repels the electrons in the conductors. Hence electrons move towards the far end and protons stay at near end Thus, the near end acquires positive charge while the far end acquires a negative charge. The total charge is zero. Now the far end is grounded. The negative charge on the far end is a free charge it moves towards the earth, while the positive charge is a bound charge remains on the body. Now earthing is removed at the negatively charged rod moved away, the body retains the positive charge.

Let us consider a positively charged rod is brought near (without contact) a neutral body mounted on an insulating stand, which is a good conductor of electricity.The rod attracts the electrons in the conductors. Hence electrons move towards the near end and protons stay at the far end Thus, the near end acquires negative charge while the far end acquires a positive charge. The total charge is zero. Now the far end is grounded. The positive charge on the far end is a free charge it is neutralized, while the negative charge is a bound charge remains on the body. Now earthing is removed at the negatively charged rod moved away, the body retains the negative charge.

Detection of Charge on a Body:
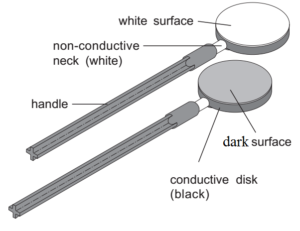
Proof Plane:
A proof plane is used for detection of charge. If the size of a body to be tested is very large, then an instrument called proof plane is used. The proof plane is brass or an aluminium-covered conductive disk attached to an insulated handle. It is used to carry the sample of the charge on charged conductive surfaces to transfer to the electroscope.

To collect a sample, the proof plane is rested on the surface of a charged body. When the proof plane is detached it carries the same nature of charge as that carried by the charged body.

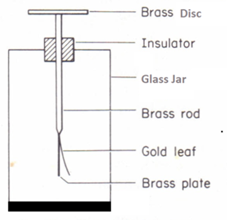
Gold Leaf Electroscope:
This instrument is used for the detection of charge and measuring static electricity. It works on the principle that the like charges repel each other.

It consists of an evacuated glass jar placed on a nonconducting surface like wood. The mouth of the jar is sealed. A brass rod passes through the seal. inside the jar, at the lower end of the brass rod, two flattened gold foils are fixed parallel to each other. Sometimes only one gold foil is fixed and thin brass plate at the lower end of the brass rod acts as a parallel plate. At the bottom and lower lateral sides of the jar, tin foils are fixed (optional), which help the gold foils to retain their charge for a longer time. A brass disc is provided at the top of the brass rod.
When a charge is put on the disc at the top it spreads down to the plate and the gold leaves. Now both the leaves and plate will have the same charge. Similar charges repel each other and hence the leaves diverge from each other. Bigger the charge the more is the divergence of the leaves.
After the use of electroscope, the gold leaves can be made to come together by touching the disc or earthing the disc of the electroscope.
The electroscope can be charged in two ways: (a) by contact – a charged rod is touched on the surface of the disc and some of the charges are transferred to the electroscope. This is not a very effective method of charging the electroscope. or (b) by induction – a charged rod is brought up to the disc and then the electroscope is earthed, the rod is then removed. The two methods give the gold leaf opposite charges.
Pith Ball Electroscope:
A pith ball electroscope is a pith ball hanging from a copper hook by help pf a silk thread. It is used to test whether an object is charged or not.

When a non-charged object is brought near a non-charged pith ball electroscope, the pith ball will not move. If the object is charged then the pith ball will move towards the charged object because it is attracted to it. Now both the pith ball and charged object has same nature of charge hence the pith ball moves away from the charged object. Now if the oppositely charged body is brought near the pith ball it gets attracted. The extent of repulsion or attraction depends on the strength of a charge on the charged body.