Science > Physics > Wave Motion > Effect of Temperature on the Speed of Sound
In the last article, we have studied the factors affecting the velocity of sound. In this article, we shall solve numerical problems to study the effect of change of temperature on the velocity of sound.
Example 01:
At what temperature will the speed of sound be double its value at 273 K.
Given: v2 = 2v1, T1 = 273 K.
To Find: T2 =?
Solution:
We have
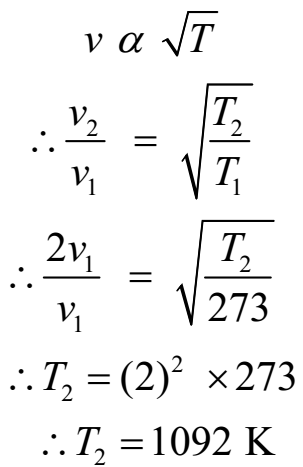
Ans: At 1092 K (819 oC), the speed of sound be double its value at 273 K.
Example 02:
At what temperature will the speed of sound be half its value at 273 K.
Given: v2 = ½ v1, T1 = 273 K.
To Find: T2 =?
Solution:
We have
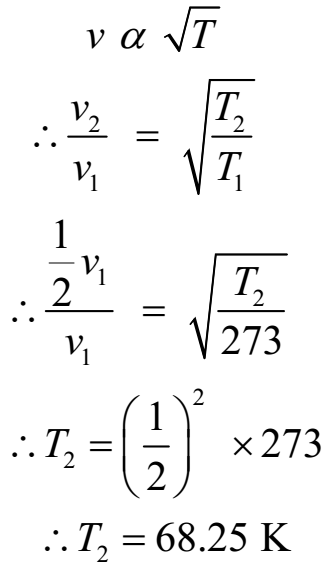
Ans: At 68.25 K (- 204.75 oC), the speed of sound be half its value at 273 K.
Example 03:
Find the temperature at which the velocity of sound in air is 1½ times the velocity at 11 oC.
Given: v2 = 1.5 v1, T1 = 11 oC = 11 + 273 = 284 K.
To Find: T2 =?
Solution:
We have
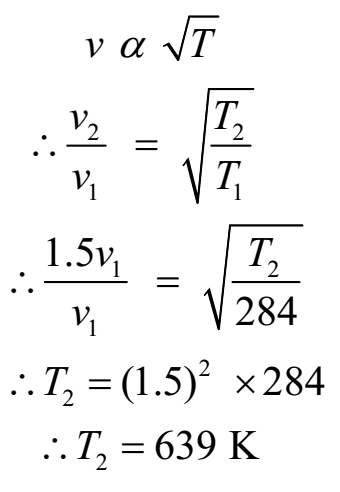
Ans: At 693 K (366 oC), the speed of sound be 1½ times its value at 11 oC.
Example 04:
Find the temperature at which the velocity of sound in air is twice the velocity at 27 oC.
Given: v2 = 2 v1, T1 = 27 oC = 27 + 273 = 300 K.
To Find: T2 =?
Solution:
We have

Ans: At 1200 K (927 oC), the speed of sound be twice its value at 27 oC.
Example 05:
The velocity of sound at 0 oC is 332 m s-1. Calculate the velocity when the temperature rises to 91 oC and pressure is doubled.
Given: T1 = 0 oC = 0 + 273 = 273 K, T2 = 91 oC = 91 + 273 = 364 K, v1 = 332 m s-1, P2 = 2 P1.
To Find: Velocity at 91 oC = v2 =?
Solution:
We have

Since velocity of sound is not affected by the change in pressure, therefore we have to see the effect of temperature alone.
Ans: The new velocity of sound is 362.8 m s-1.
Example 06:
The speed of sound in air at 15 oC is 340 m s-1. Find the speed of sound at 0 oc and 30 oC.
Given: v15 = 340 m s-1, T15 = 15 + 273 = 288 K, T0 = 0 + 273 = 273 K, T30 = 30 + 273 = 303 K,
To Find: v0 =? v30 =?
Solution:
Speed at 0 oC:

Speed at 30 oC:

Ans: The speed of sound at 0 oC is 331 m s-1 and at 30 oC is 348 m s-1.
Example 07:
Calculate the ratio of the speeds of sound at 0 oC and 1092 K
Given: T1 = 0 + 273 = 273 K, T2 = 1092 K
To Find: v1/v2 =?
We have

Ans: The ratio of the speeds of sound at 0 oC and 1092 K is 1: 2.
Example 08:
If the speed of sound at 0 oC is 330 m s-1, then at what temperature will its value becomes 495 m s-1.
Given: T1 = 0 + 273 = 273 K, v1 = 330 m s-1, v2 = 495 m s-1.
To Find: Temperature = T2 =?
Solution:
We have

Ans: At temperature of 614.25 K (341.25 oC) the speed of sound is 495 m s-1.
Example 09:
A tuning fork of frequency 220 Hz produces sound waves of wavelength 1.5 m in air at N.T.P. Calculate the increase in the wavelength when the temperature of air is 27 oC.
Given: Frequency of tuning fork = n1 = n2 = 220 Hz, Wavelength of wave = λ = 1.5 m, T1 = 273 K, T2 = 27 oC = 27 + 273 = 300 K
To Find: | λ1 – λ2| =?
Solution:
Velocity of a wave is given by
v = n λ
Thus, v1 = n1 λ1
v1 = 220 x 1.5 = 330 m s-1

Now, v2 = n2 λ2
345.9 = 220 x λ2
λ2 = 345.9/220 = 1.57 m
Increase in wavelength = λ2 – λ1 = 1.57 – 1.5 = 0.07 m
Ans: The increase in wavelength is 0.07 m.
Example 10:
A sound wave propagates in air with frequency 4000 Hz. Calculate the percentage change in a wavelength when wave front moves from a region of temperature 27 oC to region of temperature 10 oC.
Given: Frequency of tuning fork = n1 = n2 = 4000 Hz, T1 = 27 oC = 27 + 273 = 300 K, T2 = 10 oC = 10 + 273 = 283 K
To Find: Percentage change in wavelength =?
Solution:
Velocity of a wave is given by
v = n λ
Thus, v1 = n1 λ1 and v2 = n2 λ2


From equations (1) and (2)

Percentage in wavelength = 0.03 x 100 = 3
Ans: The change in wavelength is 3%.
Example 11:
Speed of sound in air is 332 m s-1 at S.T.P. What will be its value in hydrogen at S.T.P., if density of hydrogen at S.T.P. is 1/16 th that of air?
Given: vA = 332 m s-1, ρH = 1/16 ρA,
To Find: Velocity of sound in hydrogen = vH =?
Solution:
The velocity of sound in gas is given by

Assuming γ and P same for air and hydrogen

Ans: Speed of sound in hydrogen is 1328 m s-1.
Example 12:
The speed of sound in hydrogen is 1270 m s-1. Calculate the speed of sound in a mixture of oxygen and hydrogen mixed in a volume ratio 1: 4:
Given: vH = 1270 m s-1, VO/VH = ¼
To Find: vMixture =?
Solution:

The velocity of sound in gas is given by

Assuming γ and P same for mixture and hydrogen

Ans: Speed of sound in mixture is 635 m s-1.
Example 13:
The speed of sound in dry air at S.T.P. is 332 m s-1. Assuming air as composed of 4 parts of nitrogen and one part of oxygen, calculate velocity of sound in oxygen under similar conditions, when the densities of oxygen and nitrogen at S.T.P. are in the ratio 16:14.
Given: vMixture = 332 m s-1, VN/VO = 4/1 = 4, ρO/ρN = 16/14
To Find: vMixture =?
Solution:

The velocity of sound in gas is given by

Assuming γ and P same for mixture and hydrogen

Ans: Speed of sound in oxygen is 315 m s-1.
Example 14:
A gas is a mixture of two parts by volume of hydrogen and one part by volume of nitrogen. If velocity of sound in hydrogen at 0 oC is 1300 m s-1, find the velocity of sound in gaseous mixture at 27 oC.
Given: vH = 1300 m s-1, VH/VN = 2/1 = 2
To Find: vMixture at 27 oC=?
Solution:

The velocity of sound in gas is given by

Assuming γ and P same for mixture and hydrogen

Now,

Ans: The velocity of sound in gaseous mixture at 27 oC is 590.1 m s-1.