Science > Physics > Wave Motion > Factors Affecting Speed of Sound in a Gas
In the last article, we have seen expression for speed of sound in a gas. In this article, we shall study different factors affecting the speed of sound.
Laplace assumed that the process of propagation of sound as an adiabatic process. He said that the formation of compression and rarefaction is so rapid that there is not enough time to exchange heat between compression and rarefaction. In the adiabatic process, the heat of the system remains the same. Thus no heat is lost to the surroundings and no heat is gained from the surroundings.
The velocity of the sound wave in the air is given by
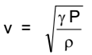
Where, v = Velocity of sound in air
γ = Ratio of specific heats of medium (air)
P = Pressure of the medium (air)
ρ = Density of medium (air)
Effect of Change of Pressure on the Speed of Sound in Air at Constant Temperature:
The speed of sound in air is given by Laplace’s formula

Where, P = Pressure of medium (air), γ = Ratio of specific heats of medium (air)
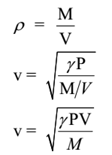
Let V1 be the volume of the gas at pressure P1. Let ρ1 be the density of a gas at this pressure. Let v1 be the velocity of sound under these conditions. Let V2 be the volume of the gas at pressure P2. Let ρ2 be the density of a gas at this pressure. Let v2 be the velocity of sound under these conditions.

Thus there is no effect of the change in pressure on the speed of sound in air at a constant temperature.
Effect of Density on the Speed of Sound in Air:
The velocity of sound in air is given by Laplace’s formula

Where, P = Pressure of medium (air), γ = Ratio of specific heats of medium (air)
Let ρ1 be the density of dry air and ρ2 be the density of moist air

Correction: In equation (2) read as suffix 2 instead of suffix 1
Thus the velocity of sound in air is inversely proportional to the square root of the density.
Effect of Humidity on the Velocity of Sound in Air:
We have proved that the velocity of sound in air is inversely proportional to the square root of the density. Humidity or moisture in the air is due to water vapours present in the medium. The density of vapour is very much less than that of dry air. Hence the density of moist air is less than that of dry air.
Now ρ1 > ρ2. Therefore v2 > v1
Thus the velocity of sound in moist air is more than that in dry air.
Effect of Temperature on the Velocity of Sound:
The velocity of sound in air is given by Laplace’s formula

Where, P = Pressure of medium (air), γ = = Ratio of specific heats of medium (air)
Consider one mole of atmospheric air having pressure P, volume V, density ρ at temperature T K then we have
PV = RT ………………. (1)

Thus the velocity of sound in air is directly proportional to the absolute temperature of the air.
Temperature Coefficient for Speed of Sound in Air:
We have

Where vo is speed of sound at 0 oC i.e., 273 K and vt is speed of sound at t oC i.e. (273 + t) K.

Expanding binomially

At 0 oC, vo = 332 m s-1

Hence velocity of sound in air increases by 0.61 m s-1 for every 1 oC rise of temperature. This is known as temperature coefficient for sound in air.
Effect of Wind on Speed of Sound in Air:
The wind is the movement of air caused by the difference in atmospheric pressure between two zones. velocity of sound is affected by the velocity of the wind. Let ω be the velocity of wind making an angle with the direction of the velocity of sound as shown. The component of the wind velocity along the direction of the velocity of sound is ω cos θ.

Thus, resultant velocity of sound = v + ω cos θ
Case 1: When wind blows in the same direction as that of sound (θ = 0o):
Resultant velocity of sound = v + ω cos 0o = v + ω (1) = v + ω
Case 2: When wind blows in the opposite direction as that of sound (θ = 180o):
Resultant velocity of sound = v + ω cos 180o = v + ω (-1) = v – ω
Effect of Frequency on Speed of Sound in Air:
The speed of a sound wave depends on the properties of the medium through which it moves and the only way to change the speed is to change the properties of the medium. Thus the speed of sound in air is independent of its frequency. Sound waves of different frequencies travel with the same velocity, but their wavelengths are different.
Effect of Amplitude on Speed of Sound in Air:
Generally, the speed of sound in air is independent of the amplitude of the sound wave. But if the amplitude of sound wave is very large, the compression and rarefaction may cause large temperature variation which may affect the speed of sound.
Effect of Media on Speed of Sound:
The speed of a sound wave depends on the properties of the medium through which it moves and the only way to change the speed is to change the properties of the medium. Thus media changes the speed of sound changes.