Science > Physics > Surface Tension > Numerical Problems on Capillary Action
In this article, we shall study to solve problems on capillary action.
Important Formulae:

and Jurin’s law, hr = constant
where h = height of liquid level in the capillary
T = Surface tension
ρ = Density of liquid
r = Radius of the bore of the capillary tube
g = Acceleration due to gravity
θ = Angle of contract
Example – 1:
A capillary tube of a uniform bore is dipped vertically in water which rises by 7 cm in the tube. Find the radius of the capillary if the surface tension is 70 dynes/cm g= 9.8 m/s2.
Given: Rise in the tube = h = 7 cm = 7× 10-2 m, Surface tension = T = 70 dynes/cm = 70 × 10-3 N/m, Acceleration due to gravity = g = 9.8 m/s2, Density of water = ρ = 1 ×10³ kg/m³, Angle of contact = θ = 0°
To Find: Radius of the tube = r =?
Solution:
The rise in the tube is given by
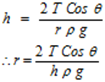
∴ r = (2 × 70 × 10-3 × cos 0°) / (7× 10-2 × 1 ×10³ × 9.8)
∴ r = 2 × 10-4 m = 0.2 × 10-3 m = 0.2 mm
Ans: The radius of the capillary is 0.2 mm
Example – 2:
Water rises to a height of 4.5 cm in a capillary tube of radius r. Find r assuming the surface tension of water is 72 dynes/cm. Take the angle of contact of water in the glass as 15°. Density of water=1000 kg/m³, g = 9.8 m/s².
Given: Rise in the tube = h =4.5 cm = 4.5 × 10-2 m, Surface tension = T = 72 dynes/cm = 72 × 10-3 N/m, Acceleration due to gravity = g = 9.8 m/s2, Density of water = ρ = 10³ kg/m³, Angle of contact = θ = 15°
To Find: Radius of the tube = r =?
Solution:
The rise in the tube is given by

∴ r = (2 × 72 × 10-3 × cos 15°) / (4.5× 10-2× 1 ×10³ × 9.8)
∴ r = (2 × 72 × 10-3 × 0.9659) / (4.5× 10-2× 1 ×10³ × 9.8)
∴ r = 3.15 × 10-4 m = 0.315 × 10-3 m = 0.315 mm
Ans: The radius of the tube is 0.315 mm
Example – 3:
A liquid rises to a height of 9 cm in a glass capillary of radius 0.02 cm. What will be the height of the liquid column in a similar glass capillary of radius 0.03 cm?
Given: Rise in first tube = h1 = 9 cm, Radius of first tube = r1 = 0.02 cm, Radius of second tube = r2 = 0.03 cm,
To Find: Radius in second tube = h2 =?
Solution:
For a particular liquid-solid interface by Jurin’s law, hr = constant
∴ h1 r1 = h2 r2
∴ h2 = h1 r1 / r2
∴ h2 = 9 × 0.02 / 0.03 = 6 cm
Ans: The height of the liquid column in a similar glass capillary is 6 cm
Example – 4:
A liquid rises to a height of 4.5 cm in a glass capillary of radius 0.01 cm. What will be the height of the liquid column in a similar glass capillary of radius 0.02 cm?
Given: Rise in first capillary tube = h1 = 4.5 cm, Radius of first capillary tube = r1 = 0.01 cm, Radius of second capillary tube = r2 = 0.02 cm,
To Find: Radius in second capillary tube = h2 =?
For a particular liquid-solid interface by Jurin’s law, hr = constant
∴ h1 r1 = h2 r2
∴ h2 = h1 r1 / r2
∴ h2 = 4.5 × 0.01 / 0.02 = 2.25 cm
Ans: The height of the liquid column in a similar glass capillary is 2.25 cm
Example – 5:
Water rises to height 3.2 cm in glass capillary tube. Find height to which same water rises in another capillary having half area of cross-section.
Given: Rise in first capillary tube = h1 = 3.2 cm, Area of cross-section of first capillary tube = A1, Area of cross-section of second capillary tube = A2 , A2 = ½ A1,
To Find: Rise in second capillary tube = h2 =?
Solution:
Given A2 = ½ A1
∴ π r2² = ½ π r1²
∴ r2² = ½ r1²
∴ r2 = 0.707 r1
For a particular liquid-solid interface by Jurin’s law hr = constant
∴ h1 r1 = h2 r2
∴ h2 = h1 r1 / r2
∴ h2 = 3.2.5 × r1 / 0.707 r1 = 4.525 cm
Ans: The height of the liquid column in the second glass tube is 4.525 cm
Example – 6:
A liquid of density 900 kg/m³ rises to a height of 7 mm in a capillary tube of 2 mm internal diameter. If the angle of contact of the liquid in the glass is 25°, find the surface tension of the liquid. g=9.8 m/s².
Given: Rise in capillary tube = h = 7 mm = 7× 10-3 m, Internal diameter = 2 mm, Radius of capillary tube = r = 2/2 = 1 mm = 1 × 10-3 m, Acceleration due to gravity = g = 9.8 m/s2, Density of liquid = ρ =900 kg/m³, Angle of contact = θ = 25°
To Find: Surface tension = T =?
Solution:
The rise in the capillary tube is given by

∴ T = (7× 10-3 × 1 × 10-3 × 900 × 9.8) / (2 × cos 25°)
∴ T = (7× 10-3 × 1 × 10-3 × 900 × 9.8) / (2 × 0.9063)
∴ T = 0.064 N/m
Ans: The surface tension of the liquid is 0.064 N/m
Example – 7:
When a capillary tube of radius 0.45 mm is dipped into water, the level inside the capillary tube rises to height 3 cm above the surface of the water. Calculate the surface tension of water, if its angle of contact is zero and its density is 1 g/cm³, g = 9.8 m/s².
Given: Rise in capillary tube = h =3 cm = 3 × 10-2 m, Radius of capillary tube = r = 0.45 mm = 0.45 × 10-3 m, Acceleration due to gravity = g = 9.8 m/s2, Density of water = 1 g/cm³ = 1 × 103 kg/m³, Angle of contact = θ = 0°
To Find: Surface tension = T =?
Solution:
The rise in the capillary tube is given by

∴ T = (3× 10-3 × 0.45 × 10-3 × 1 × 103 × 9.8) / (2 × cos 0°)
∴ T = (3× 10-3 × 0.45 × 10-3 × 1 × 103 × 9.8) / (2 ×1)
∴ T = 0.006615 N/m
Ans: The surface tension of the liquid is 0.066615 N/m
Problem – 8:
The capillary rise when a glass capillary tube of diameter 0.4 mm is dipped vertically in olive oil is 3.82 mm. If the angle of contact of olive oil with glass is 0°and the density of olive oil is 920 kg/m³, find the surface tension of olive oil.
Given: Rise in capillary tube = h =3.82 mm = 3.82 × 10-3 m, Radius of capillary tube = r = 0.4 mm = 0.4 × 10-3 m, Acceleration due to gravity = g = 9.8 m/s2, Density of olive oil = 920kg/m³, Angle of contact = θ = 0°
To Find: Surface tension = T =?
Solution:
The rise in the tube is given by

∴ T =(3.82× 10-3 × 0.4 × 10-3 × 920 × 9.8) / (2 × cos 0°)
∴ T =(3.82 × 10-3 × 0.4 × 10-3 × 920 × 9.8) / (2 ×1)
∴ T = 6.889 × 10-3 N/m
Ans: The surface tension of olive oil is 6.889 × 10-3 N/m
Example – 9:
A mercury barometer tube is 2.5 mm in internal radius. Find the error introduced in the observed reading because of surface tension. g = 9.8 m/s², T=0.540 N/m. Density of mercury = 13600 kg /m³, angle of contact of mercury in glass = 135°.
Given: Radius of capillary tube = r =2.5 mm = 2.5 × 10-3 m, Surface tension = T = 0.540N/m, Acceleration due to gravity = g = 9.8 m/s2, Density of mercury = ρ = 13600 kg/m³, Angle of contact = θ = 135°
To Find: Error introduced in the observation = h =?
Solution:
The rise in capillary tube is given by

∴ h= (2 × 0.540× cos 135°) / (2.5× 10-3× 13600 × 9.8)
∴ h= (2 × 0.540× (-0.707)) / (2.5× 10-3× 13600 × 9.8)
∴ h= – 2.29 × 10-3 m = – 2.29 mm
Ans: The error introduced in the observation is – 2.29 mm
Hence 2.29 mm should be added to height of mercury measurement.
Example – 10:
The tube of a mercury barometer is 3 mm in diameter. What error is introduced in the reading because of surface tension? Angle of contact of mercury in glass = 135° and S.T. of mercury = 0.460 N/m. Density of mercury = 13.6 g/cc, g=9.8 m/s²
Given: Diameter of capillary tube = 3 mm, Radius of capillary tube = r =3/2 = 1.5 mm = 1.5 × 10-3 m, Surface tension = T = 0.460N/m, Acceleration due to gravity = g = 9.8 m/s2, Density of mercury = ρ = 13.6 g/cc= 13.6 × 103 kg/m³, Angle of contact = θ = 135°
To Find: Radius of capillary tube = r =?
Solution:
The rise in capillary tube is given by

∴ h= (2 × 0.460× cos 135°) / (1.5× 10-3× 13.6 × 103 × 9.8)
∴ h= (2 × 0.460× (-0.707)) / (1.5× 10-3× 13.6 × 103 × 9.8)
∴ h= – 3.25 × 10-3 m = – 3.25 mm
Ans: The error introduced in the observation is – 3.25 mm
Hence 3.25 mm should be added to height of mercury measurement.
Example – 11:
A mercury barometer tube is 1 cm in diameter. Find the error introduced in the observed reading because of surface tension. g = 9.8 m/s², T=435.5 dyne/cm. The density of mercury = 13600 kg /m³, angle of contact of mercury in glass = 140°.
Given: Diameter of capillary tube = 1 cm, Radius of capillary tube = r =1/2 = 0.5 cm = 0.5 × 10-2 m, Surface tension = T =435.5 dyne/cm = 435.5 × 10-3 N/m, Acceleration due to gravity = g = 9.8 m/s2, Density of mercury = ρ = 13600 kg/m³, Angle of contact = θ = 140°
To Find: Correction due to capillary action = h =?
Solution:
The rise in capillary tube is given by

∴ h= (2 × 435.5 × 10-3 × cos 140°) / (0.5× 10-2× 13600 × 9.8)
∴ h= (- 2 × 435.5 × 10-3 × sin 140°) / (0.5× 10-2× 13600 × 9.8)
∴ h= (- 2 × 435.5 × 10-3 × 0.766) / (2.5× 10-3× 13600 × 9.8)
∴ h= – 1.01 × 10-3 m = – 1.01 mm
Ans: The correction due to capillary action is – 1.01 mm
Hence 1.01 mm should be added to height of mercury measurement.
Example – 12:
A capillary tube of radius 0.5 mm is dipped vertically in a liquid of surface tension 0.04 N/m and density 0.8 g/cc. Calculate the height of capillary rise, if the angle of contact is 10°.
Given: Radius of capillary tube = r =0.5 mm = 0.5 × 10-3 m, Surface tension = T =0.04 N/m, Acceleration due to gravity = g = 9.8 m/s2, Density = ρ = 0.8 g/cc = 0.8 × 103 kg/m³, Angle of contact = θ = 10°
To Find: Height of capillary rise = h =?
Solution:
The rise in capillary tube is given by

∴ h= (2 × 0.04× cos 10°) / (0.5× 10-3× 0.8 × 103 × 9.8)
∴ h= (2 × 0.04× 0.9848) / (0.5× 10-3× 0.8 × 103 × 9.8)
∴ h= 2.01 × 10-2 m = 2.01 cm
Ans: The height of capillary rise is 2.01 cm
Problem – 13:
A capillary tube 0.12 mm in diameter has its lower end immersed in a liquid of surface tension 0.054 N/m. If the density of the liquid is 860 kg/m³, find the height to which the liquid rises in the tube. Given the angle of contact 30° and g = 9.8 m/s².
Given: Radius of capillary tube = r =0.12 mm = 0.12 × 10-3 m, Surface tension = T =0.054 N/m, Acceleration due to gravity = g = 9.8 m/s2, Density = ρ = 860 kg/m³, Angle of contact = θ = 30°
To Find: Height of capillary rise = h =?
Solution:
The rise in the tube is given by

∴ h= (2 × 0.054× cos 30°) / (0.12× 10-3×860 × 9.8)
∴ h= (2 × 0.054× 0.5) / (0.12× 10-3 × 860 × 9.8)
∴ h= 5.34 × 10-2 m = 5.34 cm
Ans: The height of capillary rise is 5.34 cm
Example – 14:
A capillary tube of radius 0.5 mm is immersed in a beaker of mercury. The mercury level inside the tube is found to be 0.80 cm below the level of the reservoir. Determine the angle of contact between mercury and glass. Surface tension of mercury = 0.465 N/m and density is 13.6 × 103 kg/m³, g = 9.8 m/s2.
Given: Radius of capillary tube = r =0.5 mm = 0.5 × 10-3 m, Height of capillary rise = h = – 0.80 cm = – 0.80 × 10-2 m, Surface tension = T =0.465 N/m, Acceleration due to gravity = g = 9.8 m/s2, Density = ρ =13.6 × 103 kg/m³,
To Find: Angle of contact = θ =?
Solution:
The rise in capillary tube is given by

∴ cos θ = (- 0.80 × 10-2 × 0.5 × 10-3 × 13.6 × 103 × 9.8)/ (2× 0.465)
∴ cos θ = – 0.5732
∴ cos (π – θ) = 0.5732
∴ (π – θ) = cos-1 (0.5732)
∴ (180° – θ) =55°2′
∴ θ = 180° – 55°2′ = 124°58′
Ans: The angle of contact is 124°58′
Example – 15:
Calculate the density of paraffin oil, if glass capillary of diameter 0.25 mm dipped in a paraffin oil of the surface tension 0.0245 N/m rises to a height of 4 cm. Angle of contact of paraffin oil with glass is 28°, g = 9.8 m/s2,
Given: Diameter of capillary tube = 0.25 mm, Radius of capillary tube = r = 0.25/2 = 0.125 mm = 0.125 × 10-3 m, Height of capillary rise = h = 4 cm = 4 × 10-2 m , Surface tension = T =0.0245 N/m, Acceleration due to gravity = g = 9.8 m/s2, Angle of contact = θ = 28°
To Find: Density = ρ =?
Solution:
The rise in capillary tube is given by

∴ ρ = (2 × 0.0245 × cos 28°) / (0.125 × 10-3 × 4 × 10-2 × 9.8)
∴ ρ = (2 × 0.0245 × 0.8829) / (0.125 × 10-3 × 4 × 10-2 × 9.8)
∴ ρ = 882.9 kg/m³
Ans: The density of paraffin oil is 882.9 kg/m³
Example – 16:
Water rises to a height of 4 cm in a certain capillary tube. If the same capillary tube is dipped in mercury, the level of mercury decreases to 3 cm. Compare the surface tension of water and mercury, if densities of mercury and water are 13.6 × 103 kg/m³ and 103 kg/m³ respectively. The angle of contact for water and mercury are 0° and 135° respectively.
Given:
For water: The rise in tube = hw =4 cm, Density = ρw = 103 kg/m³, Angle of contact = θw =0°, Radius of capillary = rw= r.
For mercury: The rise in tube = hm = – 3 cm, Density = ρm = 13.6 × 103 kg/m³, Angle of contact = θm =135°, Radius of capillary = rm = r
To Find: Tw / Tm =?
Solution:
The rise in the tube is given by

Ans: The ratio of the surface tension of water to the surface tension of mercury 0.06932:1
Example – 17:
A U tube has one limb of radius 0.5 cm and the other limb of radius 0.1 cm. Water is poured in the tube. Find the difference in the level of water in the two tubes. S.T. of water = 0.070 N/m. g = 9.8 m/s2.
Given: Radius of first limb = r1 =0.5 cm = 0.5 × 10-2 m , Radius of second limb = r2 =0.1 cm = 0.1 × 10-2 m , Surface tension = T = 0.070 N/m, Acceleration due to gravity = g = 9.8 m/s2, Density = ρ = 1 × 103 kg/m³, Angle of contact = θ = 0°
To Find: Differene in levels = |h2 – h1| =?
Solution:
The rise in the capillary tube is given by

Hence h ∝ 1/r
Now r1 > r2, hence h2 > h1

Ans: The difference in the level of water in the two tubes is 1.142 cm
Previous Topic: The Concept of Capillary Action (Capillarity)
For More Topics in Physics Click Here
6 replies on “Numerical Problems on Capillary Action”
Nice
Thanks u so much for in this physics problem.
Your help has helped me more
Perfect problem solutions
Best of all
Thanks 🥰
Thanks so much for helping me understand capillary calculations very well.