Science > Physics > Wave Motion > Numerical Problems on Wave Motion Set – 02
Wave velocity in medium does not depend on the frequency. It depends upon the Elasticity and inertia of the medium. When medium changes the wavelength and velocity of wave changes but the frequency remains the same. Thus n1 = n2.
Example 01:
A body vibrating with certain frequency sends waves 1.5 m long through a medium a and 2.0 m long through medium B. The velocity of waves in A is 120 m s-1. Find the velocity in medium B.
Given: Wavelength in medium A = λA = 1.5 m, Wavelength in medium B = λB = 2.0 m, Velocity in medium A = vA = 120 m s-1,
To Find: Velocity in medium B = vB =?
Solution:
When medium changes the wavelength and velocity of wave changes but the frequency remains the same. Thus nA = nB.
Velocity of wave is given by
v = n λ
∴ vA = nA λA
∴ vB = nB λB
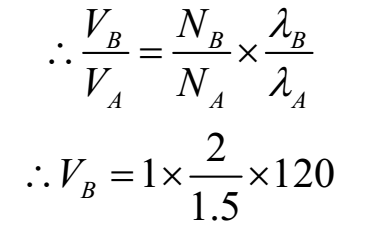
∴ vB = 160 m s-1
Ans: Velocity of wave in medium B is 160 m s-1.
Example 02:
A body vibrating with certain frequency sends waves 100 mm long through a medium a and 0.25 m long through medium B. The velocity of waves in A is 80 cm s-1. Find the velocity in medium B.
Given: Wavelength in medium A = λA = 100 mm = 0.1 m, Wavelength in medium B = λB = 0.25 m, Velocity in medium A = vA = 80 cm s-1 = 0.8 m s-1.
To Find: Velocity in medium B = vB =?
Solution:
When medium changes the wavelength and velocity of wave changes but the frequency remains the same. Thus nA = nB.
Velocity of wave is given by
v = n λ
∴ vA = nA λA
∴ vB = nB λB
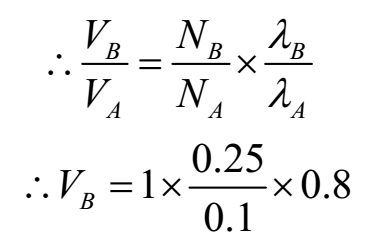
∴ vB = 2 m s-1
Ans: Velocity of wave in medium B is 2 m s-1.
Example 03:
A source of sound vibrating with certain frequency sends waves of wavelengths 0.80 m through air and 4.0 m long through water. The velocity of sound in air is 332 m s-1. Find the velocity of sound in water.
Given: Wavelength in air = λA = 0.80 m, Wavelength in water = λW = 4.0 m, Velocity in air = vA = 332 m s-1.
To Find: Velocity in water = vW =?
Solution:
When medium changes the wavelength and velocity of wave changes but the frequency remains the same. Thus nA = nB.
Velocity of wave is given by
v = n λ
∴ vA = nA λA
∴ vW = nW λW
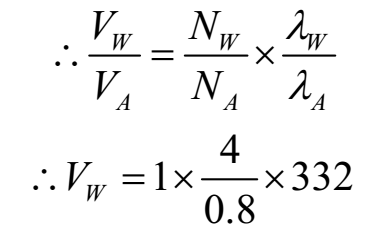
∴ vW = 1660 m s-1
Ans: Velocity of wave in water is 1660 m s-1.
Example 04:
A bat emits ultrasonic sound of frequency 100 kHz ibn air. If this sound meets a water surface, what is the wavelength of (i) the reflected sound (ii) the transmitted sound? Speed of sound in air is 340 m s-1 and in water is 1486 m s-1.
Given: Frequency = nA = 100 kHz = 100 x 103 Hz, Velocity in air = vA = 340 m s-1, Velocity in water = vA = 1486 m s-1
To Find: Wavelengths λA =? and λW =?
Solution:
When medium changes the wavelength and velocity of wave changes but the frequency remains the same. Thus nA = nW.
Velocity of wave is given by
v = n λ
vA = nA λA
∴ λA = vA/nA = 340/100 x 103 = 3.4 x 10-3 m
vW = nW λW
∴ λW = vW/nW = 1486/100 x 103 = 1.486 x 10-2 m
Ans: Wavelength of reflected wire is 3.4 x 10-3 m and wavelength of transmitted sound is 1.486 x 10-2 m.
Example 05:
A stone is dropped into a well 19.6 m deep and the impact of sound in heard after 2.056 seconds. Find the velocity of sound in air.
Given: Depth of well = h = 19.6 m, Impact heard after dropping ti = 2.056 s, Acceleration due to gravity = g = 9.8 m s-2.
To Find: Velocity of sound in air = v =?
Solution:
Considering downward journey of stone.
h = ut + ½ gt2
∴ – 19.6 = (0)t + ½ (- 9.8) t2
∴ -19.6 = – 4.9 t2
∴ t2 = 4
∴ t = 2 s (only positive value considered)
Thus, time taken by stone for downward journey = 2 s
Time taken by sound to travel from water surface to point of drop
= 2.056 – 2 = 0.056 s
Now Velocity = Displacement/Time = 19.6/0.056 = 350 m s-1.
Ans: Velocity of sound in air is 350 ms-1.
Example 06:
A stone is dropped into a well 78.4 m deep and the splash is heard after 4.23 seconds. Find the velocity of sound in air.
Given: Depth of well = h = 78.4 m, Impact heard after dropping ti = 4.23 s, Acceleration due to gravity = g = 9.8 m s-2.
To Find: Velocity of sound in air = v =?
Solution:
Considering downward journey of stone.
h = ut + ½ gt2
∴ -78.4 = (0)t + ½ (- 9.8) t2
∴ -78.4 = – 4.9 t2
∴ t2 = 16
∴ t = 4 s (only positive value considered)
Thus, time taken by stone for downward journey = 4 s
Time taken by sound to travel from water surface to point of drop
= 4.23 – 4 = 0.23 s
Now Velocity = Displacement/Time = 78.4/0.23 = 340.9 m s-1.
Ans: Velocity of sound in air is 340.9 ms-1.
Example 07:
A stone is dropped into a well and its splash is heard at the mouth of the well after an interval of 1.45 s. Find the depth of the well. Given that velocity of sound in air at room temperature is equal to 332 ms-1.
Given: Impact heard after dropping ti = 1.45 s, Acceleration due to gravity = g = 9.8 m s-2.
To Find: Depth of well = h =? Velocity of sound = v = 332 m s-1.
Solution:
Let t be the time taken by stone to travel from point of dropping to the water surface.
Considering downward journey of stone.
h = ut + ½ gt2
∴ -h = (0)t + ½ (- 9.8) t2
∴ h = 4.9 t2 ………… (1)
Now Velocity = Displacement/Time
∴ 332 = h/(1.45 -t)
∴ h = 332(1.45 – t) …….. (2)
From (1) and (2)
4.9 t2 = 332(1.45 – t)
∴ 4.9 t2 = 481.4 – 332t
∴ 4.9 t2 + 332t – 481.4 = 0

Depth of well = h = 4.9 t2 = 4.9 x (1.418)2
∴ Depth of well = h = 9.9 m
Ans: Depth of well is 9.9 m.
Example 08:
A source of sound is placed at one end of an iron bar two kilometre long and two sounds are heard at the other end at an interval of 5.6 s. If the velocity of sound in air is 330 m s-1, find the velocity of sound in air.
Given: Interval between two sounds = 5.6 s, Velocity in air = vA = 330 m s-1, Distance travelled by sound = 2 km = 2000 m.
To Find: Velocity of sound in iron = vI =?
Solution:
One sound is heard through air and other through iron bar.
Consider sound travelling through air.
Velocity = Displacement/Time
∴ 330 = 2000/tA
∴ tA = 2000/330 = 6.06 s
Sound travels faster in iron than water
Thus tA – tI = 5.6 s
∴ tI = tA – 5.6 = 6.06 – 5.6 = 0.46 s
Velocity of sound in iron = Distance/Time = 2000/0.46 = 4348 m s-1
Ans: Velocity of sound through iron is 4348 m s-1.
Example 09:
A sinusoidal wave is travelling along a rope. The oscillator that generates wave completes 40.0 vibrations in 30.0 s. Also, given maximum travels 425 cm along the rope in 10.0 s. What is the wavelength of the wave.
Given: Frequency = n = 40.0 vibrations in 30.0 s = 4/3 vibrations per second, Distance travelled = 425 cm = 4.25 m, Time taken to cover this distance = t = 10.0 s
To Find: Wavelength of the wave =?
Solution:
Velocity of wave = Distance travelled/ Time = 4.25/10 = 0.425 m s-1
Velocity of wave is given by
v = n λ
∴ λ = v/n = 0.425/(4/3) = 0.319 m
Ans: Wavelength of wave is 0.319 m