Management > Managerial Statistics > Index Number By Simple Aggregative Method In Simple Aggregative Method, the total price of commodities in a given (current) year is divided by the total price of commodities in a base year and expressed as a percentage. Steps involved in Simple Aggregative Method: Add the prices of all the commodities […]
Categories
Index Number By Simple Aggregative Method
- Post author By Hemant More
- Post date June 27, 2019
- 3 Comments on Index Number By Simple Aggregative Method
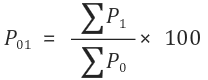
- Tags Arithmetic mean, Base year, Chain base, Choice of average, Commodities, Different Weighted Index Method, Dorbish and Browley's Method, Explicit method, Fisher's Ideal Index Number, Fixed base, Geometric mean, Implicit method, Index Number, Lapeyre's Index Number, Managerial Statistics, Marshall Edgeworth Method, Paasche's Index Number, Price index, Price Index by Dorbish and Browley's Method, Price Index by Fisher's Method, Price Index by Laspeyre’s Method, Price Index by Marshall Edgeworth Method, Price Index Number by Paasche's Method, Quantity index, Quantity Index by Dorbish and Browley's Method, Quantity Index by Fisher's Method, Quantity Index by Laspeyre’s Method, Quantity Index by Marshall Edgeworth Method, Quantity Index by Paasche's Method, Selection of Weights, Simple Aggregative Method, Simple Average of Relative Method, Statistics, Value index