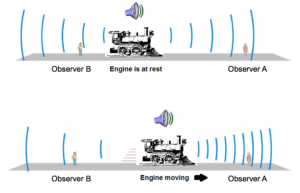
Science > Physics > Wave Motion > Doppler Effect In this article, we shall study the Doppler effect in case of sound waves and a brief idea of the Doppler effect in case of light. Doppler Effect: The apparent change in the frequency of the sound heard by an observer, due to relative motion between […]
Categories
Doppler Effect
- Post author By Hemant More
- Post date January 18, 2020
- 1 Comment on Doppler Effect
- Tags all hamonics, Antinode, Displacement antinode, Displacement node, end correction, First overtone, Fundamental frequency, Fundamental mode, harmonic, Mechanical wave, Node, odd harmonics, overtone, pipe open at both end, pipe open at one end, Pressure antinode, Pressure node, Progressive wave, Reflection of wave, Second harmonic, Second overtone, Stationary wave, Stationary waves, Third harmonic, Vibrating string, Vibration of air column, Wave