In this article, we shall study to prepare the forward difference table from the given data. Example – 1: If f(x) = x2 + x + 1, construct a forward difference table by taking x = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 i.e. 0(1)5. Hence find Df(o), D2f(1) and D3f(2). Solution: Given f(x) = x2 […]
Author: Hemant More
Reactions of Alkenes
In the last article, we have studied methods of preparation of alkenes. In this article, we shall study the reactions of alkenes Stability of Alkenes: The stability of alkenes is measured in terms of its heat of hydrogenation. The heat of hydrogenation of an alkene is defined as the amount of heat evolved when one […]
Preparation of Alkenes
In the last article, we have studied what are alkenes and isomerism in them. In this article, we shall study different methods of preparation of alkenes. Preparation of Alkenes By Dehydration of Alcohols: Alcohols on heating in the presence of dehydrating agents Iike concentrated sulphuric acid or phosphorous pentoxide or anhydrous alumina etc. undergoes a loss […]
Alkenes: Introduction
In this article, we shall learn about alkanes, isomerism in alkenes. Compounds containing carbon and hydrogen only are called hydrocarbons. Examples: Methane (CH4), Ethane (C2H6), Benzene (C6H6), etc. Aliphatic Hydrocarbons: The hydrocarbons in which carbon atoms are joined form an open chain are called aliphatic hydrocarbons. Examples: Methane (CH4), Ethane (C2H6), etc. Aliphatic hydrocarbons are […]
Alkanes
In this article, we shall learn about alkanes, isomerism in alkanes. Compounds containing carbon and hydrogen only are called hydrocarbons. Examples: Methane (CH4), Ethane (C2H6), Benzene (C6H6), etc. Aliphatic Hydrocarbons: The hydrocarbons in which carbon atoms are joined form an open chain are called aliphatic hydrocarbons. Examples: Methane (CH4), Ethane (C2H6), etc. Aliphatic hydrocarbons are […]

Science > Mathematics > Statistics and Probability > Probability > Binomial Distribution In this article, we shall study to solve problems of probability based on the concept of the binomial distribution. Example – 01: An unbiased coin is tossed 5 times. Find the probability of getting a) three heads b) at least 4 heads Solution: […]
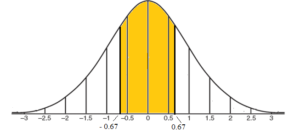
Science > Mathematics > Statistics and Probability > Probability > Normal Distribution 02 In this article, we shall study to find the probability of an event when data normally distributed is given. Area Under Normal Curve (0 < x< z) Example – 01: A sample of 100 dry battery cells tested to find the length […]

Science > Mathematics > Statistics and Probability > Probability > Normal Distribution 01 The normal distribution refers to a family of continuous probability distributions described by the normal equation. on the domain x ∈ (- ∞, ∞) where x is a normal random variable, μ is the mean, σ is the standard deviation, Thus the normal distribution can be completely specified by two […]

Science > Mathematics > Statistics and Probability > Probability > Checking of Probability Mass Function In this article, we shall study to check whether the given function is a probability mass function or not. Example – 01: X = x 1 2 3 4 P(X=x) 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 Verify whether the function can be […]

Science > Mathematics > Statistics and Probability > Probability > Probability Distribution In this article, we shall study to write probability mass function and to write probability distribution for the given event. Example – 01: If a coin is tossed two times and X denotes the number of tails. Find the probability distribution of X. […]