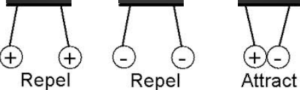
Science > Physics > Electrostatics > Introduction to Static Electricity Electricity is a very important form of energy which can be easily converted into other forms of energy. Electricity can be produced at one place and can be transmitted to long distances. Electricity is a branch of Physics which deals with charges, stationary and moving. […]
Introduction to Static Electricity