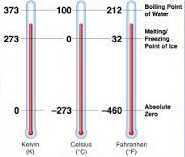
Science > Biology > Introduction to Biology > Biology and Nature Biology and nature are two intertwined realms that encapsulate the essence of life on Earth. While biology delves into the scientific study of living organisms, nature embodies the entirety of the physical world, comprising both living and non-living entities. This article seeks to unravel […]
Biology and Nature