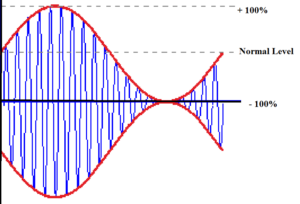
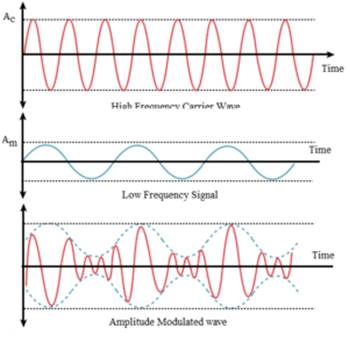
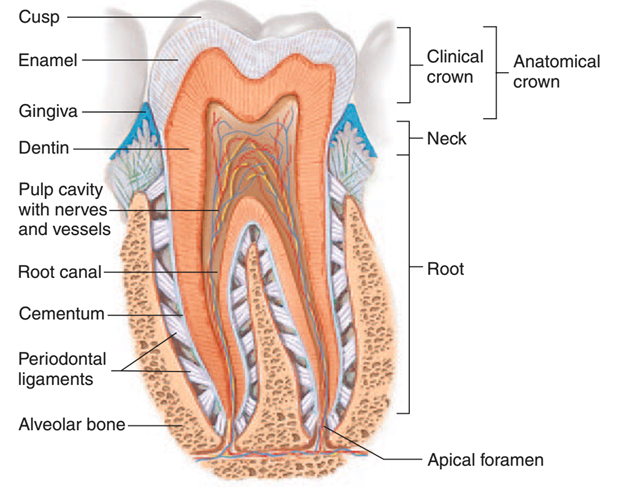
Science > Physics > Communication > Amplitude Modulation The first amplitude modulated signal was transmitted in 1901 by a Canadian engineer named Reginald Fessenden. He used a continuous spark transmission and placed a carbon microphone in the antenna lead. This transmission was very crude, signals were audible over a distance of a few hundred metres. The […]
Amplitude Modulation