Science > Chemistry > Everyday Chemistry > Everyday Medicines 01
In the last article, we have studied the mechanism of action of a drug. In this article, we shall study some everyday medicines like analgesics, antipyretics, antihistamines, antifertility, and tranquilizers.
Antipyretics:
Chemical substances that are used to bring down body temperature with high fevers are called antipyretics. They don’t have any effect on the human body when it is at normal temperature. This causes the body to lose heat and thus the temperature of the body decreases. Aspirin, Paracetamol, Analgin, Phenacetin acts as antipyretics.
Aspirin is common antipyretic. But it has the side effect. on hydrolysis, it gives salicylic acid which causes bleeding in the stomach. It should not be taken on an empty stomach. Some persons are allergic to aspirin. The usual allergic reactions are rashes on the skin, lowering of blood pressure, profuse sweating, intense thirst, nausea, and vomiting.
Calcium and sodium salts of aspirin are more soluble hence are less harmful. Aspirin has anti-blood clotting action. Hence it is used in the prevention of heart attacks. Other antipyretics used are novalgin, phenyl butazone, methacetin and butazolidine.
Chemical Names:
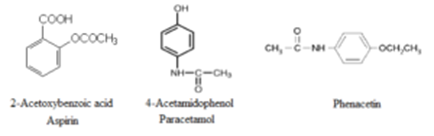
- Aspirin: 2-Acetoxybenzoic acid
- Paracetamol: 4-Acetamidophenol
- Phenacetin: N-(4-Ethoxyphenyl)acetamide
- Methacetin: 4-Methoxy acetanilide.
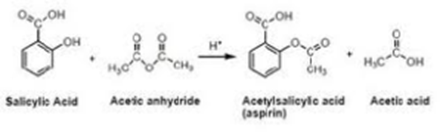
Preparation of Aspirin:
When salicylic acid is treated with the mixture of acetic anhydride and glacial acetic acid in presence of concentrated sulphuric acid, acetylation of salicylic acid takes place and aspirin is obtained.
Analgesics:
Analgesics are drugs which reduce or abolish pain without causing impairment of consciousness, mental confusion, incoordination or paralysis or some other disturbances of the nervous system.
Note: Aspirin, novalgin, phenacetin and combiflam act both as antipyreic as well as analgesic.
Analgesics are classified as follows:(i) Non-narcotic (non-addictive) analgesics(ii) Narcotic drugs
Non-narcotic (non-addictive) Analgesics:
Aspirin and paracetamol belong to the class of non-narcotic analgesics. Aspirin inhibits the synthesis of chemicals known as prostaglandins which stimulate inflammation in the tissue and cause pain. These drugs are effective in relieving skeletal pain such as that due to arthritis. These drugs have many other effects such as reducing fever (antipyretic) and preventing platelet coagulation. Because of its anti-blood clotting action, aspirin finds use in the prevention of heart attacks.
Some other analgesics are Novalgin, Butazolidine or phenylbutazone, ibuprofen, naproxen and diclofenac sodium or potassium.

Narcotic (addictive) Analgesics:
Morphine and many of its homologues, when administered in medicinal doses, relieve pain and produce sleep. Adverse effects are vomiting, dysphoria, fatigue, mental confusion. In poisonous doses, these produce stupor, coma, convulsions and ultimately death. They are very potent drugs and their chronic use leads to addiction.
Morphine narcotics are sometimes referred to as opiates since they are obtained from the opium poppy. Another source of narcotics is a marijuana plant. These analgesics are chiefly used for the relief of postoperative pain, cardiac pain and pains of terminal cancer, bone fracture, and in childbirth. These analgesic relieve pain but they attack the central nervous system and produce sleep and unconsciousness.
Other narcotic analgesics are codeine, pethidine hydrochloride, methadone, heroin etc.

Tranquilizers or Hypnotics:
Tranquilizers are a class of chemical compounds used for the treatment of stress, mental tension, anxiety, mania ( a disorder of mood), insomnia (sleeping sickness), discomfort feeling and mild or even severe mental diseases. Tranquilizers are also known as psychotherapeutic drugs.
These relieve anxiety, stress, irritability or excitement by inducing a sense of well-being. They form an essential component of sleeping pills.
Reserpine and chlorpromazine, two powerful tranquilizers were introduced simultaneously.
Examples: Equanil (controlling depression and hyper tension), valium (diazepam), veronol, meprobamate (relieving stress), chlordiazepoxide, serotonin etc. are mild tranquilizers. Other examples are amytal, seconal, librium,


Barbiturates:
The derivatives of the barbituric acid obtained by condensation of urea and malonic acid are called barbiturates. They form another class of tranquilizers. Examples: Veronal, Amytal, Nembutal, luminal. Barbiturates act on the central nervous system and are hypnotic, i.e., sleep producing agents. Hence they are used to control hypertension and depression.
Treatment of Depression:
Noradrenaline is one of the neurotransmitters that play a role in mood changes. If the level of noradrenaline is low for some reason, then the signal-sending activity becomes low, and the person suffers from depression.
In such situations, antidepressant drugs are required. These drugs inhibit the enzymes which catalyze the degradation of noradrenaline. If the enzyme is inhibited, this important neurotransmitter is slowly metabolized and can activate its receptor for longer periods of time, thus the effect of depression is counteracted.
Drugs used are Iproniazid and phenelzine.
Side Effects of Tranquilizers:
They produce side effects like a headache, weight gain, discomfort, blurring of the vision.
Classifications of Drugs Used for Mental Treatment:
- Narcotics: used as analgesics and antidepressants. e.g. heroin, opium, pethidine.
- Hypnotics: used as tranquilizers and to reduce anxiety and mental tension. e.g. Equanil
- Sedatives (depressants): used to reduce the action of the central nervous system. They induce a feeling of relaxation, calmness, drowsiness, and reduces the wildness of the patient. e.g. valium, barbiturates
- Antidepressants: given to patients lacking confidence. They are called mood boosters. It induces a feeling of well being. e.g. Vitalin, Methadrine and cocaine.
Antifertility Drugs:
Antifertility drugs are the chemicals which are used to check pregnancy in women. These drugs control menstrual cycle and ovulation. These drugs are mainly used in the form of oral pills. The active ingredient in the pills acting antifertility agents are steroids.
The birth control pill is a mixture of synthetic estrogen and progesterone derivatives (synthesized steroids). They are more potent than natural hormones. Progesterone suppresses ovulation. Some of the contraceptive pills contain norethindrone (synthetic progesterone derivative) and ethynylestradiol (Novestrol) (synthetic estrogen derivative).
The active component of ‘morning after pill’ is a synthetic steroid mifepristone. It blocks the effect of progesterone and checks pregnancy.

Antacids:
Basic substances which neutralize the excess of hydrochloric acid in the stomach and raises the pH to appropriate level are called antacids
Examples: Magnesium hydroxide, aluminium hydroxide, Ranitidine (Zantac) is commonly used an antacid.
Overproduction of acid in the stomach causes irritation and pain. In severe cases, ulcers are developed in the stomach. The earlier treatment for acidity was the administration of antacids, such as sodium hydrogen carbonate or a mixture of aluminium and magnesium hydroxide.
However, excessive hydrogen carbonate can make the stomach alkaline and trigger the production of even more acid. Metal hydroxides are better alternatives because of being insoluble, these do not increase the pH neutrality.
These treatments control only symptoms, and not the cause. Therefore, with these metal salts, the patients cannot be treated easily. In advanced stages, ulcers become life-threatening and its only treatment is the removal of the affected part of the stomach.
A major breakthrough in the treatment of hyperacidity came through the discovery according to which a chemical, histamine, stimulates the secretion of pepsin and hydrochloric acid in the stomach. The drug cimetidine (Tegamet), was designed to prevent the interaction of histamine with the receptors present in the stomach wall. This resulted in the release of a lesser amount of acid. The importance of the drug was so much that it remained the largest selling drug in the world until another drug, ranitidine (Zintac), was discovered.

Pentaprazole and Omiprazole are the new drugs used to inhibit gastric secretion.
Antihistamines:
Antihistamines are the drugs that diminish or abolish the effects of histamine, a chemical released by most of the cells during an allergic reaction. Antihistamine by competing with histamine for binding sites of receptor where histamine exerts its effect. Basic Antihistamines are amines which are used as drugs to control allergy effects produced by histamine. Histamine is a potent vasodilator. It has various functions. It contracts the smooth muscles in the bronchi and gut and relaxes other muscles, such as those in the walls of fine blood vessels. Histamine is also responsible for the nasal congestion associated with the common cold and allergic response to pollen.
Synthetic drugs, brompheniramine (Dimetapp) and terfenadine (Seldane), act as antihistamines. They interfere with the natural action of histamine by competing with histamine for binding sites of receptor where histamine exerts its effect.
Antihistamines do not affect the secretion of acid in the stomach. The reason is that antiallergic and antacid drugs work on different receptors.

Examples: Synthetic drugs, brompheniramine (Dimetapp) and terfenadine (Seldane),
Other commonly used antihistamines are Diphenhydramine (Benadryl), pheniramine maleate (Avil), Chloropheniramine maleate (zeet), Chlorotheopyllinat (Avomine). They are used in hay fever, mild asthma, insect bites, cold etc.
The action of Microbes in the Body:
The living organisms which cannot be seen with the naked eyes (unaided eyes) and can only be observed through a microscope are called microorganisms or microbes. They include bacteria, fungi, algae, and viruses. They are present almost everywhere air, water, soil, inside and on our body. The disease-producing microbes are called pathogens.
Our body has an efficient defense structure against these pathogens. The skin prevents microbes to enter our body. Some secretions like lysosomes in tears, nasal secretions, saliva, fatty acids, lactic acid in sweat, hydrochloric acid in the stomach kill these microbes or inhibit their growth. The breach of this defense system allows the pathogens to reach tissues and cause infection in the body. Due to which normal metabolic activities are disturbed. This results in a disease. Pathogens produce toxins that may affect tissues and organs of the host.
Anti-malarials:
Medicines used to bring down the body temperature during malaria fever are called antimalarials. Malaria is a highly widespread infectious disease caused by Sporozoa called plasmodium. Malaria is characterized by periodic fever, anaemia, and enlargement of liver and spleen. The four species Plasmodium vivax (fever on alternate days), Plasmodium malariae (fever once in three days), Plasmodium ovale (fever once in three days), Plasmodium falciparum (fever once in four days) are responsible for malaria in the human being. The choice of drug depends on the point of action of the drug.
Drugs used are
- Primaquine: It destroys sporozoites in the liver. Its long use is not advisable because it is highly toxic.
- Chloroquine, Proquanil, Pyimethamine: These drugs kill the parasite in the blood.
Previous Topic: Mechanism of Action of Drugs
Next Topic: Antimicrobials, Antibiotics, Sulpha Drugs, Antiseptics, Disinfectants