In this article, we shall study different types of nuclear reactions.
Nuclear Reactions:
A reaction in which there is a change in the composition of the nucleus is called a nuclear reaction.
Characteristics of Nuclear Reactions:
- There is a change in the composition of the nucleus.
- In nuclear reaction rearrangement of nucleons ( constituents of the nucleus) takes place and thus the composition of nucleus changes
- In nuclear reaction sum of atomic mass numbers and the sum of atomic numbers of reactant nuclei, should be equal to that of product nuclei.
- The rate of nuclear reaction is independent of temperature.
- In a nuclear reaction, the energy values are given in MeV per nucleus transformed.
Chemical Reactions:
Reaction in which there is change in chemical composition of reacting substances is called chemical reaction.
Characteristics of Chemical Reactions:
- There is a chemical change in reacting substances.
- In chemical reaction redistribution of electrons and rearrangement of atoms takes place
- The total number of atoms of each element must be the same on both sides of the chemical equation.
- The rate of a chemical reaction depends on temperature.
- In chemical reaction heat of reaction is given in kJ per mole.
Distinguishing Between Nuclear Reaction and Chemical Reaction:
| Nuclear reaction | Chemical reaction |
| Reaction in which there is change in the composition of nucleus is called nuclear reaction. | Reaction in which there is change in chemical composition of reacting substances is called chemical reaction. |
| In nuclear reaction rearrangement of nucleons ( constituents of nucleus) takes place and thus the composition of nucleus changes | In chemical reaction redistribution of electrons and rearrangement of atoms takes place |
| In nuclear reaction sum of atomic mass numbers and sum of atomic numbers of reactant nuclei should be equal to that of product nuclei | The total number of atoms of each element must be same on both the sides of chemical equation. |
| Rate of nuclear reaction is independent of temperature. | Rate of chemical reaction depends on temperature. |
| In nuclear reaction the energy values are given in MeV per nucleus transformed. | In chemical reaction heat of reactions are given in kJ per mole. |
Types of Nuclear Reactions:
Artificial Transmutation:
The process of conversion of a nucleus of atom one element into that of another element by using high-velocity projectiles is called as artificial transmutation.The new element form may or may not be radioactive.
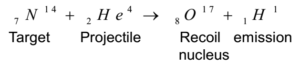
- Target: The nucleus of an atom which is bombarded by high-speed particles is known as the target.
- Projectile: A high-speed (accelerated) particle that strikes the nucleus of an atom (target) to carry out artificial transmutation is called a projectile. Projectiles used are 1H1 (proton), 2He4 (α -particles), -1 e0( β – particles), on1(neutron), 1D2 (deuterium) etc.
- Emissions: Particles ejected in artificial transmutation along with recoil nucleus is called emissions.
- Recoil Atom or Recoil Nucleus: Atom produced in an artificial transmutation having nearly the same atomic number and mass number as that of the target atom is called a recoil nucleus.
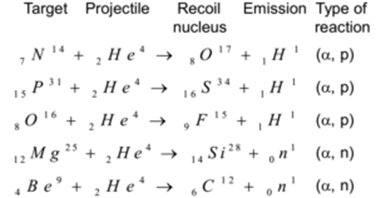
More examples with different projectiles are given below.
Using α – particles as projectile:
Using Protons as Projectile:
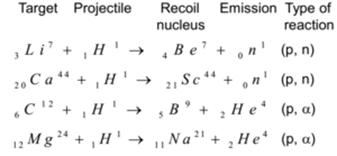
Using Deuterons as Projectile:

Using Neutrons as Projectile:

Neutrons are the Best Projectiles:
- The process of conversion of the nucleus of an atom one element into that of another element by using high-velocity projectiles is called as artificial transmutation. There is a positive charge on the nucleus while the negative charge is carried by extranuclear electrons.
- There is a positive charge on the particles like protons and deuterons. Due to the positive charge on them, they experience a greater force of repulsion while penetrating the positively charged nucleus of the target atom.
- Neutrons do not carry any charge. Due to chargeless nature, they are not deflected by extranuclear electrons similarly they are not repelled by the positive charge of the target nucleus. Hence neutrons are easily absorbed by the nucleus and the transmutation is carried out effectively. Hence neutrons are the best projectile in the transmutation of elements.
Artificial or Induced Radioactivity:
The process of conversion of a stable non-radioactive atom of one element into an unstable radioactive atom of another element by bombardment with high-speed projectile is called induced or artificial radioactivity.
The recoil atom decays at its own rate. The radioactivity exhibited by recoil nucleus itself is called artificial radioactivity.
In certain artificial transmutation reactions, product undergoes spontaneous disintegration even on stoppage of bombardment of projectile. During such nuclear reactions positrons ( +1 e0), neutrons (0n1), electrons (-1 e0) or γ rays are emitted.
Some of the induced radioactivity reactions using different projectiles are,
Using α – particle (2He4):

Using protons (1H1):

Using Deuterons (1D2):

Using Neutrons:

Natural Radioactivity:
The phenomenon of spontaneous and continuous and uncontrollable disintegration of an unstable nucleus accompanied by the emission of active radiations is called natural radioactivity. It is a spontaneous process shown by nuclei of heavy elements with an atomic number greater than 83.
- α, β, γ rays are emitted.
- No naturally occurring radioisotope emits positrons.
- I daughter element is radioactive hence it further undergoes disintegration and a series of radioelements is obtained.
- This reaction cannot be controlled as it is independent of external factors.
- A very large amount of energy is released.
Artificial Radioactivity:
The process of conversion of a stable non-radioactive atom of one element into an unstable radioactive atom of another element by bombardment with high-speed projectile is called induced or artificial radioactivity. It is a non-spontaneous process.
- Positrons ( +1 e0), neutrons (0n1), electrons (-1 e0) or γ rays are emitted.
- No artificially synthesized radioisotope emits α particles.
- The daughter element is non-radioactive hence a series of radioelements is not obtained.
- By controlling the flow of projectiles the number of nuclei undergoing artificial transmutation can be controlled.
- A small amount of energy is released.
- Artificial radioactivity can be introduced into lighter nuclei.
Difference Between Natural Radioactivity and Artificial Radioactivity:
| Natural radioactivity | Artificial radioactivity |
| The phenomenon of spontaneous and continuous and uncontrollable disintegration of an unstable nucleus accompanied by emission of active radiations is called natural radioactivity. | The process of conversion of stable non radioactive atom of one element into unstable radioactive atom of another element by bombardment with high speed projectile is called induced or artificial radioactivity. |
| It is spontaneous process shown by nuclei of heavy elements with atomic number greater than 83. | It is non spontaneous process. |
| α, β, γ rays are emitted. No naturally occurring radioisotope emits positrons. | Positrons ( +1 e 0 ), neutrons ( 0 n 1 ), electrons ( – 1 e 0 ) or g rays are emitted. No artificially synthesised radioisotope emits a particles. |
| Daughter element is invariably radioactive hence it further undergoes disintegration and a series of radio elements is obtained. | Daughter element is invariably non radioactive hence a series of radio elements is not obtained. |
| This reaction can not be controlled as it is independent of external factors. | By controlling the flow of projectiles the number of nuclei undergoing artificial transmutation can be controlled. |
| Very large amount of energy is released. | Small amount of energy is released. |
| Heavy nuclei exhibit natural radioactivity | Artificial radioactivity can be introduced in lighter nuclei. |
Nuclear Fission:
Nuclear fission is a process in which heavy nuclei break into lighter fragments of elements giving a very large amount of energy.

This reaction is used in atom bomb in an uncontrolled manner while it is used in a nuclear reactor in controlled manner.
Nuclear Fusion:
Nuclear fusion is a process in which nuclei of lighter elements combine to form a nucleus of the heavier element.

This process is used in the production of a hydrogen bomb