Science > Chemistry > Physical Chemistry > Ionic Equilibria > Bronsted- Lowry Concept of Acid and Base
In the previous article, we have studied the Arrhenius theory of acids and bases. In this article, we shall study the Bronsted Lowry Concept of acids and bases.
In 1923, scientists Bronsted and Lowry proposed more general definitions of acids and bases to overcome the limitations of the Arrhenius theory. This concept is independent of solvent and is also called a Protonic Concept.

According to the Bronsted Lowry concept
- Acid: An acid is defined as a substance (molecule or ion) which has a tendency to donate one or more protons (H+) to other substances. Thus acid is proton donor species. e.g. Molecules like HCl, HNO3, H2SO4, H2O ions like HSO4–, H3O+, HCO3–, NH4+, etc.
- Base: A base is defined as a substance (molecule or ion) which has a tendency to accept one or more protons (H+) from other substances. Thus base is proton acceptor species e.g. Molecules like NH3, RNH2, H2O ions like CH3COO-, OH-, HSO4-, Cl- etc.
- Acid-Base Reaction (Neutralization):
HCl(g) + NH3(g) → NH4+ + Cl–
(acid) (base) (acid ) (base)
In the above reaction, HCl and NH4+ are the acids as both donate a proton.
while NH3 and Cl– are the bases as they accept a proton.
Concept of Conjugate Acid-Base Pair:
When an acid donates a proton, the remaining part of it has a tendency to regain proton. Therefore it acts as a base which is called as linked or conjugate base.
Acid1 ⇌ Base1 + H+
Similarly, Base2 + H+ ⇌ Acid2
Acid1 and Base1 as well as Acid2 and Base2 differ by a proton and are called conjugate acid-base pairs. In an acid-base reaction, pairs of substances which differ by a proton and which can be formed from one another by the mutual gain or loss of a proton are called conjugate acid-base pairs. e.g.
HCl(g) + NH3(g) ⇌ NH4+ + Cl–
(acid1) (base2) (acid2) (base1)
Strength of Acid and Base on the Basis of Bronsted- Lowry Concept:
The strength of a base is measured in terms of its ability to capture proton while the strength of an acid is measured in terms of the ability to donate a proton. It is obvious that stronger the acid weaker its conjugate base and stronger the base weaker is its conjugate acid.
HCl ⇌ H+ + Cl–
(Strong acid) (Weak conjugate base)
Neutralization Reaction on the Basis of Lowry and Bronsted Concept:
According to this theory, a neutralization reaction is a reaction in which conjugate base and conjugate acid are formed from reacting base and acid respectively.
H2SO4 + H2O ⇌ H3O+ + HSO4–
(acid1) (base2) (acid2) (base1)
Amphoteric Nature of Water:
A substance which can act as an acid, as well as a base, is called an amphoteric substance. Thus by Bronsted -Lowry concept, a substance which has a capacity both to accept and donate protons is called amphoteric substance or amphiprotic substance.
Water is an amphoteric substance. Water can accept a proton and can act as a base, as well as it can donate a proton and can act as an acid. The dual nature of water depends upon the nature of other substances with which it is treated.
Water acts as a base when treated with a strong acid like HCl.
HCl + H2O ⇌ H3O+ + Cl–
(acid1) (base2) (acid2) (base1)
Water acts as an acid when treated with base stronger than itself like NH3.
H2O + NH3 ⇌ NH4+ + OH–
(acid1) (base2) (acid2) (base1)
Advantages of Bronsted – Lowry Concept:
- This theory made more general definitions of acids and bases.
- This concept is applicable to aqueous as well as non-aqueous solutions.
- This concept is independent of the solvent.
Limitations of Bronsted -Lowry Concept:
- Bronsted – Lowry concept can’t explain certain acid-base reactions which do not involve proton.
Some more examples of conjugate acid base pairs :
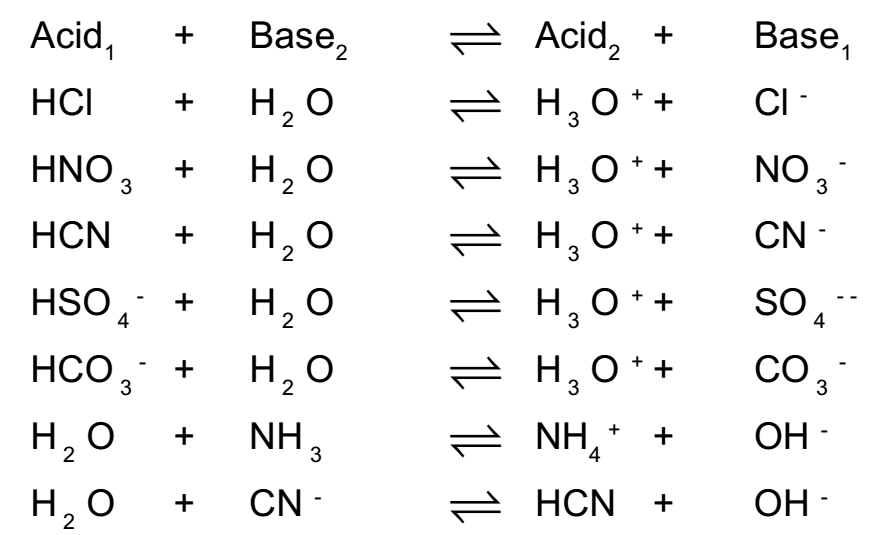
In above acid base reactions (acid1) and (base1 ) and (acid 2 ) and (base 2 ) are the conjugate acid base pairs