Science > Chemistry > Physical Chemistry > Ionic Equilibria > Lewis Concept of Acids and Bases
In the previous article, we have studies the Arrhenius theory, Bronsted Lowry concept of acids and bases. In this article, we shall study the Lewis concept of acids and bases, its merits and demerits.
Lewis Concept of Acids and Bases:
In 1923, scientist Gilbert Lewis proposed a more general concept of acids and bases. This concept is based on the electronic theory of valency.
Acid:
Lewis acid is defined as any species (molecule, atom or ion) which can accept a lone pair of electrons to form a coordinate bond. Thus Lewis bases are electrophiles.
Examples: All cations like Al3+ , Mg2+ , Cu2+ , H+ , Zn2+, Fe2+, Ag+ etc. Neutral molecules like AlCl3, BF3, BeCl2, SO3, SiF4, SnCl2 etc. In these neutral molecules, the central atom has only six electrons around it and they have empty d orbitals. Atoms like S and O. In these atoms the atom has only six electrons in its valence orbit.
Base:
Lewis base is defined as any species (molecule, atom or ion) which can donate a lone pair of electrons to form a coordinate bond. Thus Lewis bases are nucleophiles.
Examples: Molecule like NH3, H2O, Amines, etc. All anions like SO4–, Cl –, Br–, O2- etc.
Neutralization:
By Lewis acid-base theory the process of neutralization is simply the formation of a coordinate bond between the electron donor and electron acceptor.
Consider the reaction between boron trifluoride BF3 and ammonia NH3. In BF3 boron atom contains six electrons in its final orbit thus boron has an incomplete octet. Thus boron is capable of accepting a lone pair of electrons, while nitrogen in NH3 has a lone pair of electrons.
During reaction between them ‘N’ atom in NH3 donate a lone pair of electrons to Boron and acts as Lewis base, while BF3 accepts the lone pair of electrons from ammonia and BF3 behaves like Lewis acid.
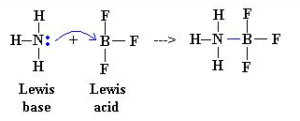
Note:
All Bronsted bases are also Lewis bases but all Bronsted acids are Lewis acids but the reverse is not true.
Lewis base is defined as any species (molecule, atom or ion) which can donate a lone pair of electrons to form a coordinate bond, while according to Bronsted Lowry theory a base is anything that donates a pair of electrons to acidic hydrogen. A Lewis base is anything that donates a pair of electrons, while a Bronsted base is anything that donates a pair of electrons to acidic hydrogen. Thus the Lewis and Bronsted Lowry definitions of bases are identical. Thus All Bronsted bases are also Lewis bases.
The Bronstead Lowry concept defines an acid as a substance (molecule or ion) which has a tendency to donate one or more protons ( H+) to other substances. Thus according to the Bronstead Lowry concept, an acid is hydrogen-containing compound. A Lewis acid is anything that accepts a pair of electrons, while a Bronsted acid accepts pairs of electrons at acidic hydrogen. Lewis acid may or may not contain hydrogen. Hence all Bronsted acids are Lewis acids but all Lewis acids are not Bronsted Lowry acids.
Acidic Nature of Boron Trifluoride:
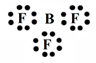
In BF3 boron atom contains six electrons in its final orbit thus boron has an incomplete octet. Thus boron is capable of accepting a lone pair of electrons, During the reaction, BF3 accepts the lone pair of electrons and behaves like Lewis acid.
Basic Nature of Ammonia:
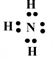
Nitrogen in NH3 has a lone pair of electrons. During reaction ‘N’ atom in NH3 donate a lone pair of electrons and act as Lewis base. Hence NH3 is Lewis base.
Notes:
- Compounds in which central atom has expanded octet act as Lewis acid using vacant d orbitals.
SnCl4 + 2 Cl– → [SnCl6]2-
Lewis acid Lewis Base
SiF4 + 2 F– → [SiF6]2-
Lewis acid Lewis base
- All simple cations which have vacant valency orbitals act as a Lewis acid.
Cu2+ + 4 : NH3 → [Cu(NH3)4]2+
Lewis acid Lewis base Complex
Zn2+ + 4: OH– → [Zn(H2O) 4 ]2+
Lewis acid Lewis base Complex
Ag + + 2 : NH3 → [Ag (NH3)2]+
Lewis acid Lewis base Complex
Fe3+ + 6 CN– → [Fe(CN)6}3-
Lewis acid Lewis base Complex
- Elements with electron sextet that is having six electrons in their valence shell, acts as Lewis acid.
O + SO32- → [O ¬ SO3]2-
Lewis acid Lewis base
Sulphite ion Sulphate ion
- Electron-deficient molecules act as Lewis acid. BF3, AlCl3, SO3 are electron-deficient molecules containing central B, Al and S atom respectively having only six electrons. They complete their octet by forming a coordinate bond.
O + SO32- → [O ¬ SO3]2-
Lewis acid Lewis base
Sulphite ion Sulphate ion
Limitations of Lewis Concept of Acids and Bases:
- All acid-base reactions do not involve co.ordinate bond formation.
- Lewis concept do not explain the behavior of well-known protonic acids like HCl, H2SO4, etc. which do not form coordination bonds with bases. Therefore, according to Lewis, these are not regarded as acids.
- This theory fails to explain the relative strength of acids and bases.
- Actually, the formation of a coordination compound is a slow process, but the acid-base reaction is a fast process. This behaviour cannot be explained on the basis of the Lewis concept.
- The catalytic activity of many acids is due to proton (H+). Lewis acids do not have proton hence Lewis acids do not possess catalytic property.