Science > Chemistry > Physical Chemistry > Ionic Equilibria > Concept of Hydrolysis
In this article, we shall study the concept of hydrolysis. Before studying the concept we have to understand different types of salts.
Types of salts:
Salts are classified on the basis of the nature of the acids and bases from which they are derived. There are four types of salts.
Salts of strong acids and strong bases:
| Formula | Strong Acid | Strong Base |
| NaCl | HCl | NaOH |
| KCl | HCl | KOH |
| NaNO3 | HNO3 | NaOH |
| KNO3 | HNO3 | KOH |
| Na2SO4 | H2SO4 | NaOH |
| K2SO4 | H2SO4 | KOH |
Salts of strong acids and weak bases:
| Formula | Strong Acid | Weak Base |
| NH4Cl | HCl | NH4OH |
| FeCl3 | HCl | Fe(OH)3 |
| PbNO3 | HNO3 | PbOH |
| CuSO4 | H2SO4 | Cu(OH)2 |
Salts of weak acids and strong bases:
| Formula | Weak Acid | Strong Base |
| CH3COONa | CH3COOH | NaOH |
| CH3COOK | CH3COOH | KOH |
| HCOONa | HCOOH | NaOH |
| HCOOK | HCOOH | KOH |
| Na2CO3 | H2CO3 | NaOH |
| K2CO3 | H2CO3 | KOH |
Salts of weak acids and weak bases:
| Formula | Weak Acid | Weak Base |
| CH3COONH4 | CH3COOH | NH4OH |
| HCOONH4 | HCOOH | NH4OH |
| (NH4)2CO3 | H2CO3 | NH4OH |
Hydrolysis of a Salt:
The process in which cation or anion or both the ions of a salt react with water to produce acidity or basicity to the solution is called as hydrolysis.
Explanation :
Hydrolysis is reverse of neutralization. When salt is added to the water, then cation, anion or both the ions of salt react with water and if the solution becomes either acidic or basic then it is hydrolysis process.
When a cation of the salt reacts with water, weak base and acid solution is formed.
BA + H2O ⇌ BOH(aq) + H+(aq)
When anion of the salt reacts with water, weak acid and basic solution are formed.
BA + H2O ⇌ HA (aq) + OH–(aq)
When both ions of the salt react with water, weak base and weak base both are formed. The nature of solution depends on the relative strengths of acid and base.
BA(aq) + H2O ⇌ BOH(aq) + HA(aq)
Degree of Hydrolysis (h):
The fraction of the total number of moles of a salt that hydrolyzed at equilibrium is called as the degree of hydrolysis. It is denoted by ‘h’
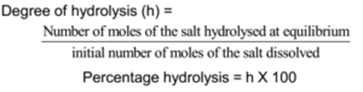
Hydrolysis Constant:
Consider following hydrolysis reaction.
Salt + Water ⇌ Acid + Base
Applying the law of mass action we have
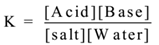
In hydrolysis water is a reactant as well as medium for the reaction, hence water is in large excess. Therefore [Water] = constant.
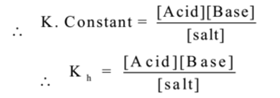
Where Kh is a constant called hydrolysis constant.
Hydrolysis constant is the modified equilibrium constant, obtained by applying the law of mass action to the hydrolysis reaction at equilibrium.
Characteristics of Hydrolysis:
- It is defined as a reaction in which cation or anion or both the ions of a salt react with water to produce acidity or alkalinity to the solution,
- Salt + Water Acid + Base
- It takes place to a very small extent.
- It is a reversible reaction.
- It is not possible for a salt of a strong acid and strong base.
- Dilution increases the degree of hydrolysis except in the case of salt of a weak acid and a weak base.
Example:
CH3COONa + HOH ⇌ CH3COONa + NaOH
Applying ionic theory and canceling common ion, we have
CH3COO– + HOH ⇌ CH3COONa + OH–
Thus the solution is basic in nature.
Characteristics of Neutralisation:
- It is a reaction between H+ ions of the acid and OH- ions of the base to form practically undissociated water.
- Acid + Base → Salt + Water
- It is almost complete.
- It is an irreversible reaction.
- It is possible with any type of acid and base.
- Dilution has no effect on neutralization reaction.
Example:
HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O
Applying ionic theory and cancelling common ion, we have
H+ + OH– → H2O
The resultant solution is neutral
Salt of a strong acid and strong base do not undergo hydrolysis.
salts of a strong acid and strong base produce strong acid and strong base when treated with water but the solution is neither acidic nor basic, hence these salts do not undergo hydrolysis.
Explanation:
Consider NaCl salt. It gives strong acid (HCl) and strong base (NaOH). In water solution, equilibrium exists as,
NaCl + H2O ⇌ NaOH + HCl
NaOH is a strong base and HCl is a strong acid
By ionic theory,
Na+ + Cl– + H2O ⇌ Na+ + OH– + H+ + Cl–
On cancelling common ions of both the sides
H2O ⇌ H+ + OH–
In this case [H+] = [ OH–] . The solution is neither acidic nor basic i.e. it is neutral to litmus. Neither cation nor anion reacts with water. Hence salts of strong acids and strong bases do not undergo hydrolysis.
Hydrolysis of salt of strong acid and weak base.
These salts on hydrolysis produce strong acids and weak bases. The resulting solution is acidic in nature.
Consider hydrolysis of ammonium chloride (NH4Cl). It gives strong acid HCl and weak base NH4OH, when treated with water and equilibrium exist as,
NH4Cl + H2O ⇌ NH4OH + HCl
(weak base ) (strong acid)
Applying ionic theory
NH4+ + Cl– + H2O ⇌ NH4OH + H+ + Cl–
Cancelling common ions of both the sides
NH4+ + H2O ⇌ NH4OH + H+
This solution contains free H+ ion. It is acidic to litmus and pH < 7.
These salts on hydrolysis produce weak acids and strong bases. The resulting solution is basic in nature.
Consider hydrolysis of sodium acetate (CH3COONa). It gives weak acid CH3COOH and strong base NaOH, when treated with water and equilibrium exist as,
CH3COONa + H 2O ⇌ CH3COOH + NaOH
(weak acid) (strong base)
Applying ionic theory
CH3COO– + Na+ + H2O ⇌ CH3COOH + Na+ + OH–
Cancelling common ions of both the sides
CH3COO– + H2O ⇌ CH3COOH + OH–
This solution contains free OH- ions. It is basic to litmus and pH > 7.
These salts on hydrolysis produce weak acids and weak bases. The nature of resulting solution depends on the relative strengths of the weak acid and the base formed..
Consider hydrolysis of ammonium acetate (CH3COONH4). It gives weak acid CH3COOH and weak base NH4OH, when treated with water and equilibrium exist as,
CH3COONH4 + H2O ⇌ CH3COOH + NH4OH
(weak acid) (weak base)
Applying ionic theory
CH3COO– + NH4+ + H2O ⇌ CH3COOH + NH4OH
As there are no free OH– or H+ ions. The relative strength of CH3COOH and NH4OH are the same. It is neutral to litmus and pH = 7.
One reply on “Concept of Hydrolysis”
It’s quite experience so far.
Literally, I loved the way the content is well explained. Thanks alot.
We expect more from u 🙌👍