Science > Chemistry > Concept of Atomic Mass and Equivalent Mass > Double Displacement Method
In the last two articles, we have studied the hydrogen displacement method, oxide formation method, reduction method, and chloride formation method to determine the equivalent mass of metal. In this article, we shall study double displacement method and metal displacement method.
The equivalent mass of a substance is the number of parts by mass of the substance which combines with or displaces or contains 1.008 parts by mass of hydrogen, 8 part by mass of oxygen, or 35.5 part by mass of chlorine. If the equivalent mass is expressed in grams then it is called gram equivalent mass (GEM).
Illustration:
1.008 parts by weight of Hydrogen combines with 35.5 parts by weight of chlorine to give 36.5 parts by weight of HCI. Thus the equivalent mass of chlorine is 35.5.
Equivalent mass has no unit because it is a pure ratio. Some important equivalent masses are H = 1, O = 8, Cl = 35.5
Method – V (Double Displacement Method):
Procedure:
In this method, a known mass of a compound (say AB) is treated with a known mass of another compound say (CD). By the exchange of radicals, the new compound is formed. The mass of the new compound formed is found.
AB + CD → AD + CB
Then equivalent mass is calculated using following formula.
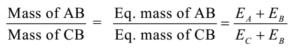
Numerical Problems on Double Displacement Method
Example – 01:
0.106 g of sodium carbonate was treated with an excess of calcium carbonate and the mass of calcium carbonate was found to be 0.1 g. Find the equivalent mass of calcium carbonate if that of sodium carbonate is 53.
Given: Mass of Na2CO3 = 0.106 g. Mass of CaCO3 = 0.1 g, Eq. Mass of Na2CO3 = 53,
To Find: Eq. Mass of CaCO3 = ?
Solution:
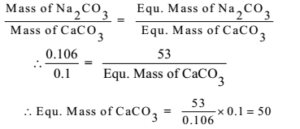
Ans: The equivalent mass of CaCO3 is 50.
Example – 02:
0.194 g of chloride of a certain metal, when dissolved in water and treated with an excess of silver nitrate yield 0.50 g of silver chloride. Calculate the equivalent mass of the metal. (Ag = 108, Cl = 35.5)
Given: Mass of metal chloride = 0.194 g, Mass of silver chloride = 0.50 g,
To Find: Eq. Mass of Metal = ?
Solution:
Let the equivalent mass of metal be E.

∴ 0.194 × (108 + 35.5) = 0.50 ( E + 35.5)
∴ 0.194 × 143.5 =0.50 E + 17.75
∴ 27.839 – 17.75 = 0.50 E
∴ 10.089 = 0.50 E
∴ E = 10.089 / 0.50 = 20.17
Ans: The equivalent mass of metal is 20.17.
Example – 03:
1.520 g of the hydroxide of metal gave 0.995 g of its oxide. Calculate the equivalent mass of the metal.
Given: Mass of hydroxide = 1.520 g, Mass of oxide = 0.995 g
Solution:
Let the equivalent mass of metal be E.

∴ 1.520 × (E + 8) = 0.995 ( E + 17)
∴ 1.520 E + 12.16 = 0.995 E + 16.915
∴ 1.520 E – 0.995 E = 16.915 – 12.16
∴ 0.525 E = 4.755
∴ E = 4.755 / 0.525 = 9.06
Ans: The equivalent mass of metal is 9.06.
Example – 04:
1.0 g of an acid when completely acted upon by magnesium gave 1.301 g of anhydrous magnesium salt. Find the equivalent mass of the acid. Mg = 24, H = 1.
Solution:
Atomic mass of Mg = 24
Equivalent mass of Mg = Atomic mass /valency = 24 / 2 = 12
Mass of acid = 1.0 g
Mass of magnesium salt = 1.301 g
Let equivalent mass of acid be E.

∴ 1 × (E + 12) = 1.301 ( E + 1)
∴ E + 12 = 1.301 E + 1.301
∴ 12 – 1.301 = 1.301 E – E
∴ 0.301 E = 10.699
∴ E = 10.699 / 0.301 = 35.54
Equivalent mass of acid = 1 + 35.54 = 36.54
Ans: Hence equivalent mass of acid is 36.54.
Example – 05:
Chloride of a metal ‘M’ contains 47.23% of the metal. 1.00 g of this metal displaced from a compound 0.88 g of another metal N. Find equivalent masses of M and N respectively.
Solution:
In chloride % of metal = 47.23, hence % of chlorine = 100 – 47.23 = 52.77
Let us consider 100 g of chloride
Mass of metal = 47.23 g, Mass of chlorine = 52.77 g

Hence equivalent mass of the metal M is 31.77.
Given that, 1.00 g of metal M displaced from a compound 0.88 g of another metal N.
Hence equivalent mass of N = 31.77 x 0.88 = 27.96
Ans: The equivalent mass of M is 31.77 and that of N is 27.96..
Example – 06:
4.215 g of metallic carbonate was heated in a hard glass tube and CO2 evolved was found to measure 1336 ml at 27 °C and 700 mm of pressure. What is the equivalent mass of the metal? (IITJEE 1976).
Given: V = 1336 ml, P = 700 mm of Hg, T = 27 °C = 27 + 273 = 300 K, PO = 760 mm of Hg, TO = 273 K
Solution:

Molecular mass of CO2 = 12 + 16 x 2 = 44 g
1 mole of CO2 at STP occupies 22.4 dm3 by volume.
44 g of CO2 at STP occupies 22.4 dm3 by volume.

Mass of metal carbonate = 4.215 g
Mass of CO2 evolved = 2.2 g
Mass of metal oxide = 4.215 – 2.2 = 2.015 g
Let the equivalent mass of metal be E.

∴ 4.215 × (E + 8) = 2.015 ( E + 30)
∴ 4.215 E + 33.72 = 2.015 E + 60.45
∴ 4.215 E – 2.015 E = 60.45 – 33.72
∴ 2.2 E = 26.73
∴ E = 26.73 / 2.2 = 12.15
Ans: The equivalent mass of metal is 12.15.
Example – 07:
For dissolution of 1.08 g of metal 0.49 g of sulphuric acid was required. If the specific heat of metal is 0.06. Find the atomic mass of the metal.
Solution:
Mass of metal = 1.08 g
Mass of sulphuric acid = 0.49 g
Let the equivalent mass of metal be E.

Hence equivalent mass of metal is 108.
Specific heat = 0.06

Actual atomic mass = Equivalent mass x valency = 108 x 1 = 108
Ans: The atomic mass of the metal is 108.
Method – VI (Metal Displacement Method):
Procedure:
In this method known mass of metal is added to the solution of a salt of the other (Placed lower in electrochemical series).
Metal A + Salt of metal B → Salt of metal A + Metal B
The precipitate formed is washed dried and carefully weighed.
Equivalent mass is calculated using following formula.

Numerical Problems on Metal Displacement Method
Example – 01:
1.296 g of silver metal was displaced when 0.382 g of copper was added to the solution of silver sulphate. If the equivalent mass of silver metal is 108. Find that of copper.
Given: Mass of silver = 1.296 g, Mass of copper = 0.382 g, Eq. mass of silver = 108
To Find: Eq. mass of copper =?
Solutions:

Ans: The equivalent mass of copper is 31.83
Example – 02:
1.8 g of iron displaces 2.04 g copper from copper sulphate solution. If copper has an equivalent mass of 31.7. Find that of iron.
Given: Mass of iron = 1.8 g, Mass of copper = 2.04 g. Eq. mass of copper = 31.7
To Find: Eq. mass of iron =?
Solution:

Ans: The equivalent mass of iron is 27.97.
Example – 03:
2.47 g of CuO obtained by oxidising 1.986 g of copper by nitric acid. 0.335 g of copper was precipitated by 0.346 g of zinc from CuSO4. Find the equivalent mass of copper and zinc.
Given: Mass of CuO = 2.47 g. Mass of copper = 1.986 g.
To Find: the equivalent mass of copper and zinc =?
Solution:
Mass of oxygen = 2.47 – 1.986 = 0.484 g

Eq. mass of copper = 32.83

Ans: The equivalent mass of copper is 32.83 and that of zinc zinc is 33.91
Previous Topic: Equivalent Mass by Oxide Formation, Chloride Formation, and Reduction Method
Next Topic: Equivalent Mass Using Faraday’s Laws of Electrolysis